Our most-read articles of 2021 provides a snapshot of what additive manufacturing professionals like you wanted to know, and what sparked your curiosity.
From deep-dives into metal 3D printers to an in-depth guide on selecting the best filament for your application, our articles and news reports aimed to deliver the most accurate information you need now to make smart business decisions.
To make sure you don’t miss any All3DP Pro features in 2022, sign up for our monthly Pro newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
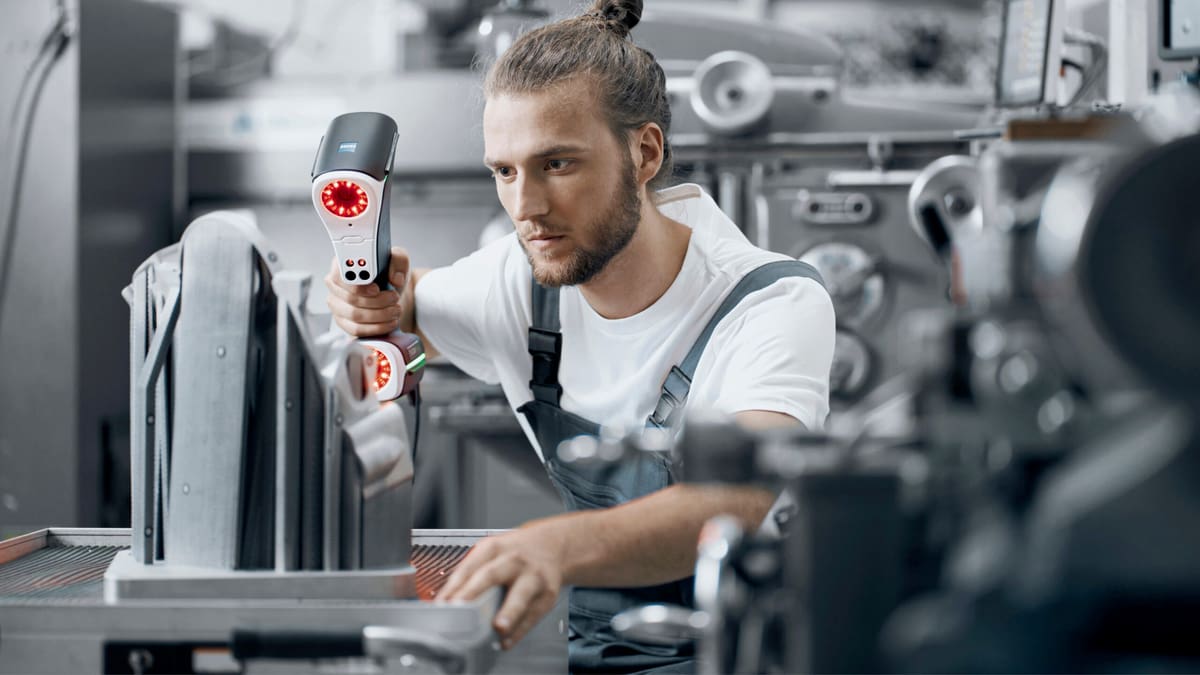
Best Professional 3D Scanners
Whether it’s to reverse engineer a component, get accurate measurements of an object, create virtual reality, or catalog antiquities for posterity, there’s so much today’s 3D scanners can do.
Used by manufacturers for quality control, museums to digitize their collections, medical professionals to create customized orthotics, and law enforcement to analyze the scene of a crime, professional-level 3D scanners offer more power and precision than ever before.
read more …
Biggest Companies Building 3D Printed Houses
House building, generally speaking, has changed little since humans began stacking rocks to make shelters. Most homes today still require teams of workers to add layers of bricks, cinder block, or other building materials atop each other manually. The 3D printing construction approach, however, promises to build houses faster, cheaper, and more accurately with fewer people. 3D construction companies also say their material will last longer and are stronger than most traditional building materials.
read more …
Best Metal 3D Printers – Buyer’s Guide
Metal 3D printing provides a proven menu of benefits to a growing number of industries. Not only can you create parts with shapes and internal structures that could not be cast or otherwise machined, but metal 3D printing can create parts within parts so engineers can design a complex assembly in one piece. This saves the time and labor of assembling parts or performing processes, such as welding, and increases efficiency of the final part.
read more …
Best 3D Architecture Software (Many are Free)
Professional architects today don’t even have pencils within reach. Everything, from initial sketches to final building instructions, is digital. So it’s no surprise that there are quite a range of software options available for the different stages of architectural development and the various levels of architect.
read more …
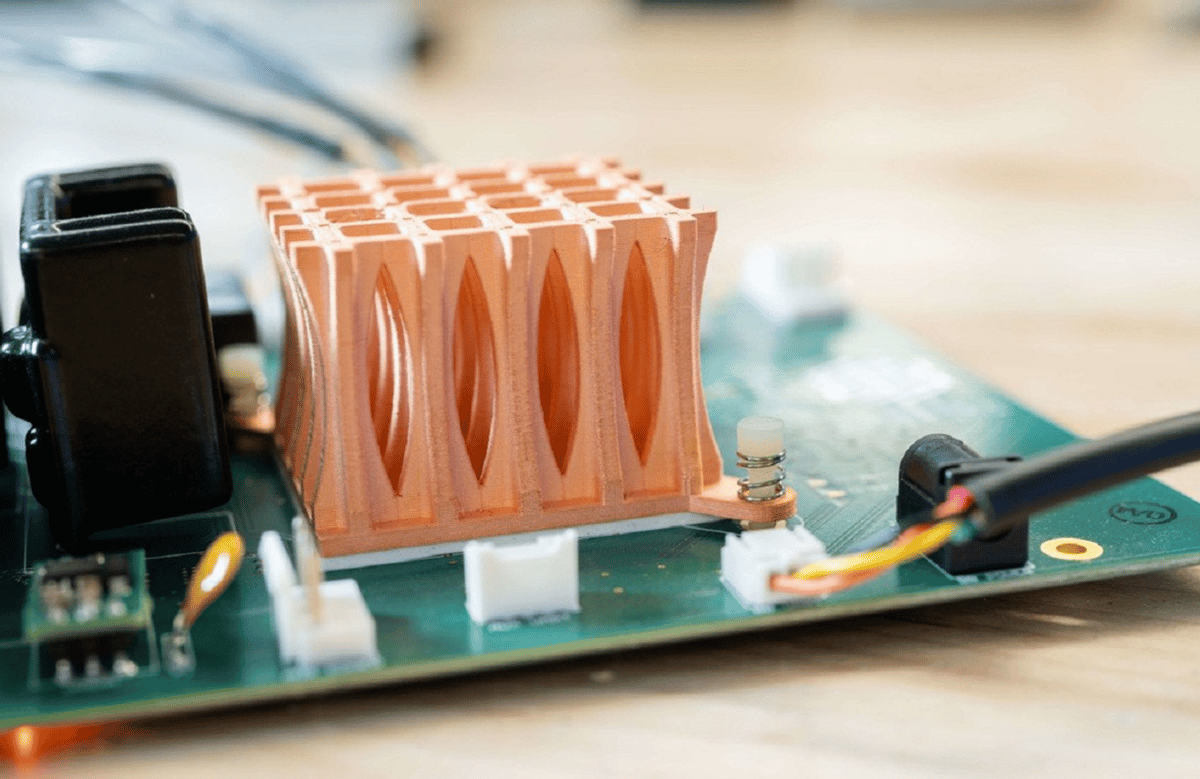
Copper 3D Printing – The Ultimate Guide
Copper is one of the newest and most promising areas of metal 3D printing for everything from electric motors to heat sinks.
Previously, it was a challenge to 3D print with copper because of the metal’s reflectivity and high heat conductivity, but advances in printers and materials have largely met those early challenges. Today, 3D printed copper propulsion systems send rockets into space, 3D printed copper heat sinks keep CPUs cool, and 3D printed copper coils boost electric motor performance.
read more …
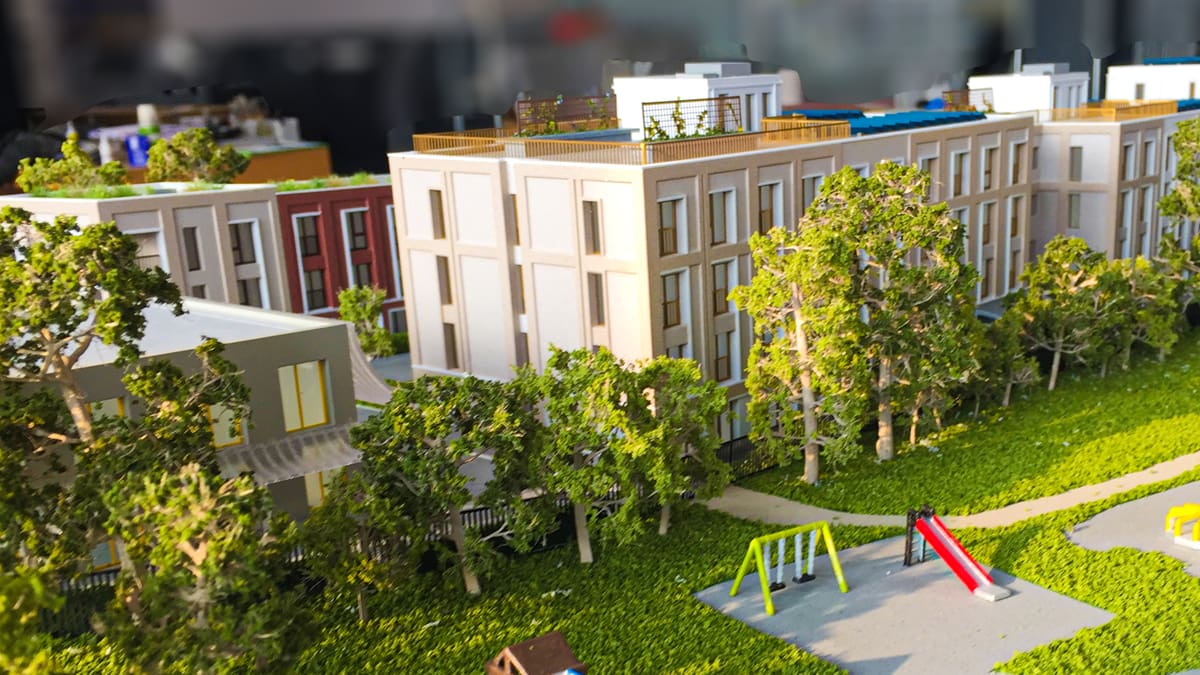
How to Make a 3D Printed Architecture Model
Advances in 3D printing technology over the past 20 years have changed the way many industries operate and the architectural sector is no exception. 3D printing has found a home at many stages in the property development lifecycle, and one can easily argue that architecture firms benefit the most from the advantages 3D printing brings in terms of speed, detail, cost, and efficiency. Traditional model-making service providers are also rapidly embracing the technology that helps them produce more precise models, faster and cheaper.
read more …
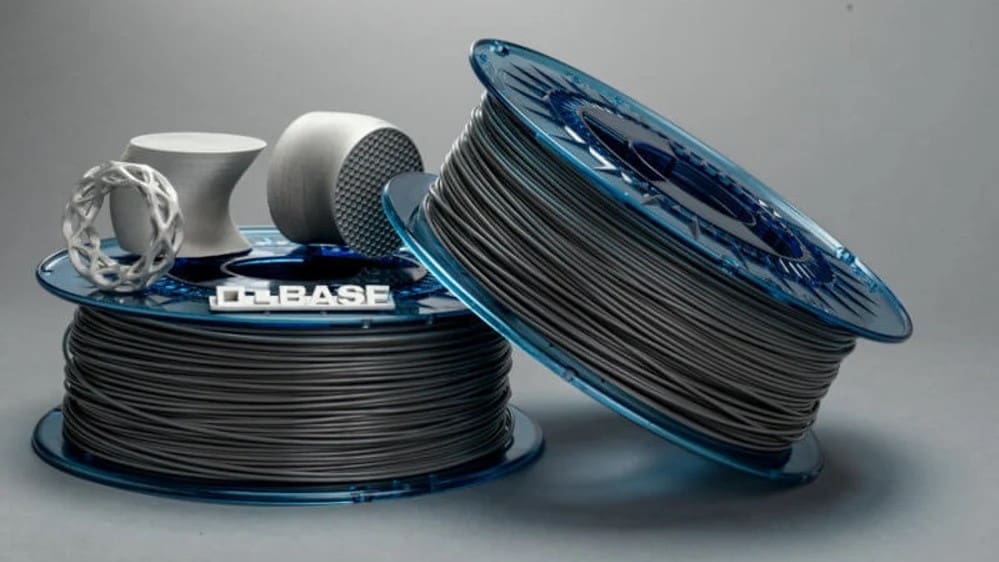
3D Printing Filament: A Guide for Professionals
When you 3D print with FDM filament in (or as) your business, you can’t have poor layer adhesion or material inconsistency. Your parts can’t unexpectedly break, warp, melt, or delaminate. Plus, wasting time and raw materials fine-tuning printer settings over and over again is out of the question.
In this guide, we walk you through how to choose and use a professional FDM filament that will meet the mechanical and aesthetic specifications of the parts you need to print. You’ll learn how to read a filament specification sheet and why all of those measurements matter.
read more …
Best SLS 3D Printers – Buyer's Guide
Prized for its ability to create engineering-grade parts with excellent mechanical properties, fine resolution, and incredibly fast, SLS (selective laser sintering) 3D printing is what engineers and industrial designers turn to for functional rapid prototypes and end-use parts.
If you’re looking to buy your first SLS 3D printer or upgrade to a more powerful version, this updated buyer’s guide takes a deep dive into the technology and the latest desktop- and industrial-scale SLS printers on the market.
read more …
Switching from Injection Molding to 3D Printing Cut Costs 95%
Often, the smallest innovations can make the biggest impact on productivity. Take the manufacturing of printed circuit board (PCB) assemblies at tech giant Mercury Systems for example. Turnaround of the company’s mission-critical PCB technologies was hampered by a slow, expensive step in the middle of an otherwise high-tech process until a 3D printed solution changed everything.
read more …
TPU Filament: The Basics & Best Brands
There are countless reasons why your 3D printed part may need to be flexible, bendy, elastic, or soft to the touch. Fortunately, there’s a growing range of filaments on the market that can deliver just the characteristics you’re looking for while being easy to print.
read more …
Metal Filament for Real Metal Parts: All You Need to Know
Filament for 3D printers has come a long way from the brittle plastics of a decade ago as professionals and hobbyists alike explore new applications for 3D printed parts. Today’s plastic filaments are stronger, sturdier, and more flexible than ever, but one goal has eluded users of fused deposition modeling (FDM) printer technology: solid metal parts.
That is, until metal filament came along.
read more …
Why Your Business Should 3D Print With Eco-Friendly & Recycled Filament
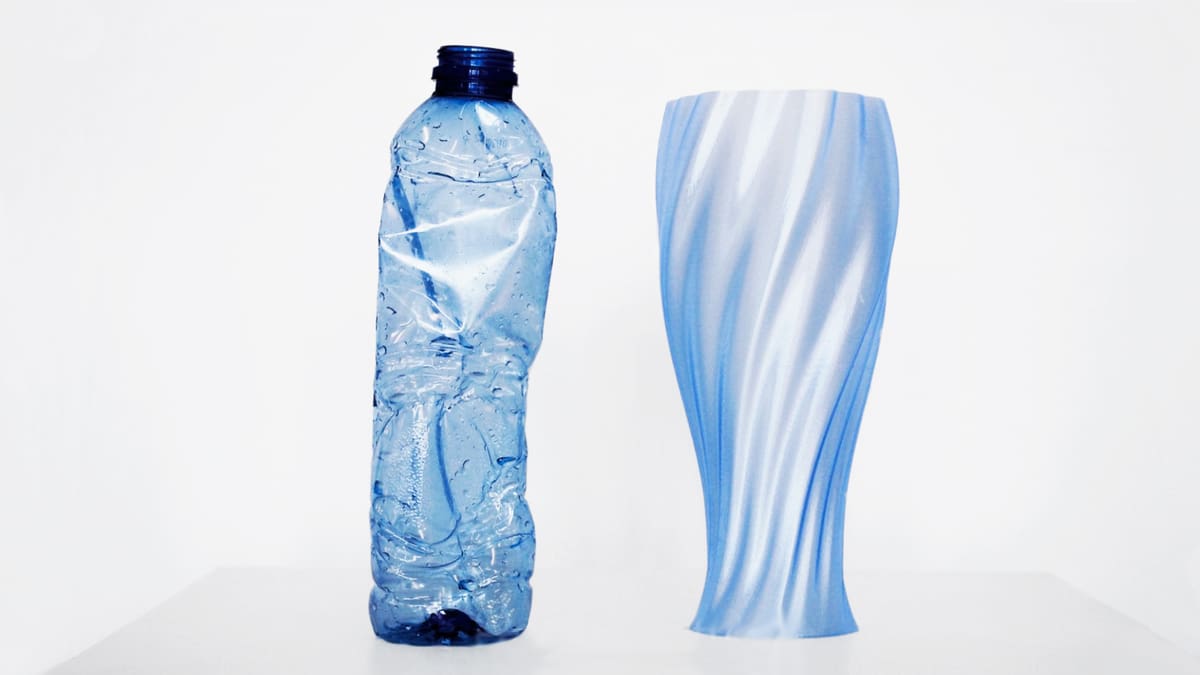

Using plastics responsibly – in other words working toward eliminating plastic overuse and waste, using recycled and plant-based plastics where ever feasible, and having a company-wide plan for recycling – is a mantra smart companies are adopting to not only be more sustainable, but telegraph a sustainable public image.
read more …
License: The text of "The Best of All3DP Pro 2021" by All3DP Pro is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.