More than 2.2 million additive manufacturing professionals read All3DP Pro in 2022. Our list of most-read articles of the year provides a snapshot of what engineers, industrial designers, and business owners like you want to know — and what sparks your curiosity.
From deep dives into metal 3D printers to a cost-saving case study at PepsiCo to selecting the best in CAD software, our articles, guides, and news reports aim to deliver the most accurate information you need now to make smart business decisions.
To ensure you don’t miss any All3DP Pro features in 2023, sign up for our free monthly Pro Newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
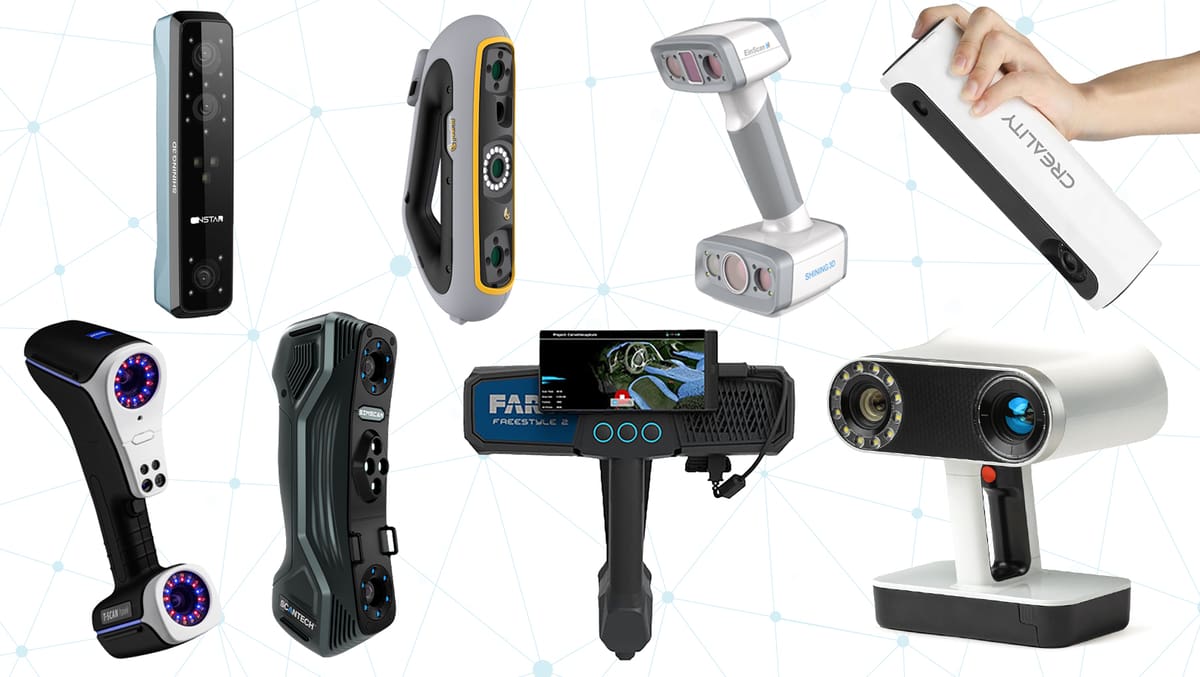
Best Professional 3D Scanners
Whether it’s to reverse engineer a component, get accurate measurements of an object, create virtual reality, or catalog antiquities for posterity, there’s so much today’s 3D scanners can do.
Used by manufacturers for quality control, museums to digitize their collections, medical professionals to create customized orthotics, and law enforcement to analyze the scene of a crime, professional-level 3D scanners offer more power and precision than ever before.
New professional scanners introduced in 2022 include these:
read more …
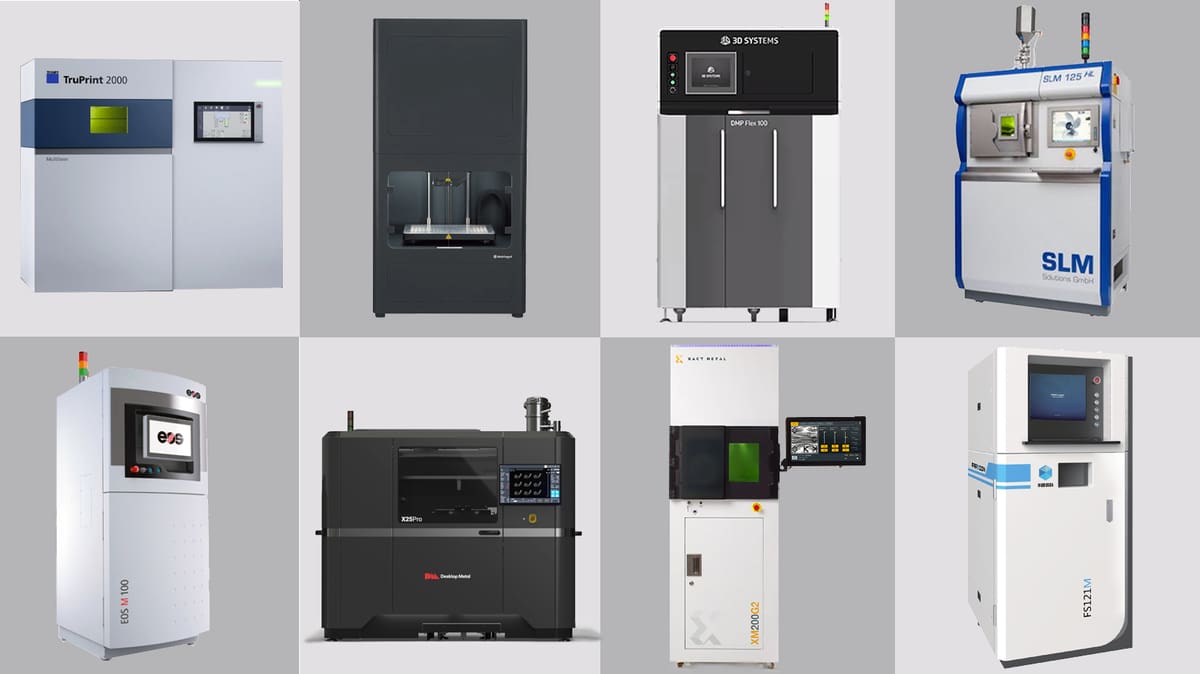
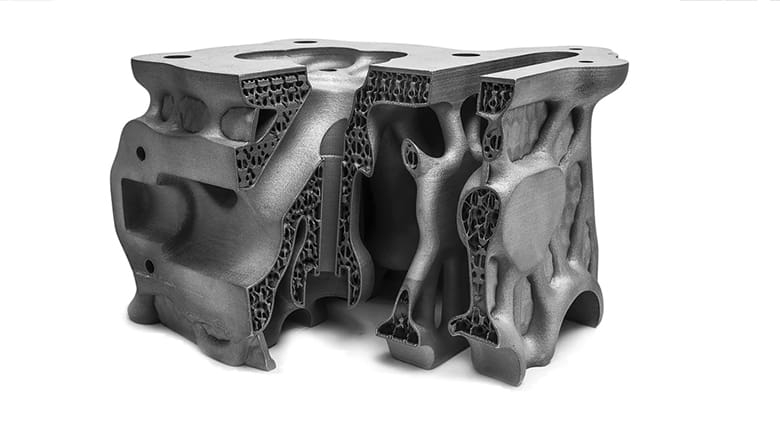
Best Metal 3D Printers – Buyer’s Guide
Metal 3D printing provides a proven menu of benefits to a growing number of industries. Not only can you create parts with shapes and internal structures that could not be cast or otherwise machined, but metal 3D printing can create parts within parts so engineers can design a complex assembly in one piece. This saves the time and labor of assembling parts or performing processes, such as welding, and increases the efficiency of the final part.
But which metal 3D printing technology is right for your application, and which 3D printer fits your budget and needs? Find out in our popular guide to the best metal 3D printers on the market.
New and notable metal 3D printers in 2022 include these:
- E-Plus3D EP-M1250 & EP-M450H
- HP Metal Jet S100 System
- Xact Metal XM300G
- Digital Metal DMP2500
- Farsoon FS200M×2
- Mitsubishi AZ600
read more …
Best CAD Software & Free CAD Software
All3DP readers not only want to learn about the best CAD software, but they’re also sensitive to cost. That’s why our Best Free CAD Software guide was so popular in 2022. Our other CAD software guides also ranked high with readers, including the Best CAD Software for Commercial Use and our expert comparison articles, including Fusion 360 vs SketchUp: The Differences and SolidWorks vs Fusion 360: The Differences.
There’s no doubt that CAD knowledge is key to additive manufacturing success. All 3D printed parts start out as digital files and there are more options than ever for designing for additive manufacturing. See which CAD tool matches your skills, application, and budget.
read more …
Biggest Companies Building 3D Printed Houses
House building, generally speaking, has changed little since humans began stacking rocks to make shelters. Most homes today still require teams of workers to add layers of bricks, cinder block, or other building materials atop each other manually. The 3D printing construction approach, however, promises to build houses faster, cheaper, and more accurately with fewer people. 3D construction companies also say their material will last longer and are stronger than most traditional building materials.
read more …
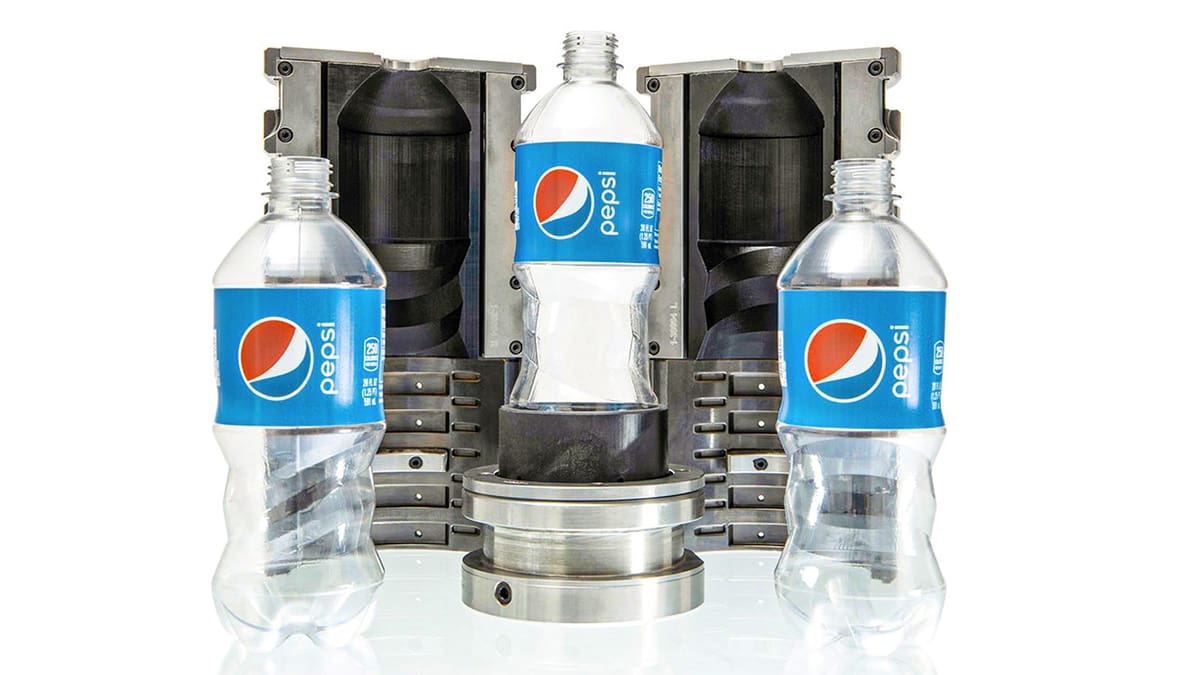
PepsiCo Saves 96% by 3D Printing Bottle Molds
Our most popular case study of the year revealed how PepsiCo gained speed, lowed cost, and expanded flexibility by turning to 3D printers to make bottle molds.
Creating conventional metal tooling for the blow molding of bottle prototypes at PepsiCo’s R&D campus in Valhalla, N.Y., used to mean weeks of waiting and thousands in costs. PepsiCo could spend up to $10,000 to produce a single metal mold tool set depending on its complexity, according to Max Rodriguez, senior manager of global packaging R&D, advanced engineering and design, at PepsiCo’s research center.
Working with Chicago-based additive manufacturing technology distributor Dynamism, the PepsiCo team explored industrial 3D printing solutions that could meet their requirements for both size and materials.
read more …
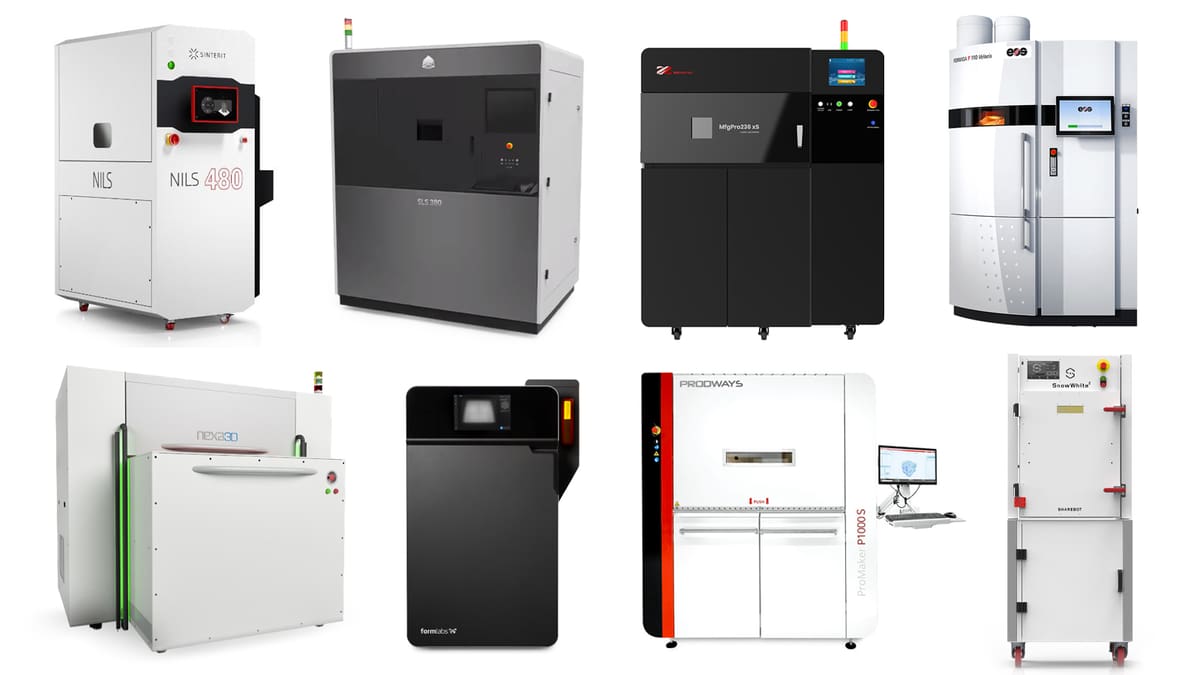
Best SLS 3D Printers – Buyer's Guide
Prized for its ability to create engineering-grade parts with excellent mechanical properties, fine resolution, and incredibly fast, SLS (selective laser sintering) 3D printing is what engineers and industrial designers turn to for functional rapid prototypes and end-use parts.
If you’re looking to buy your first SLS 3D printer or upgrade to a more powerful version, this updated buyer’s guide takes a deep dive into the technology and the latest desktop- and industrial-scale SLS printers on the market.
Top SLS 3D printers launched in 2022 include these:
read more …
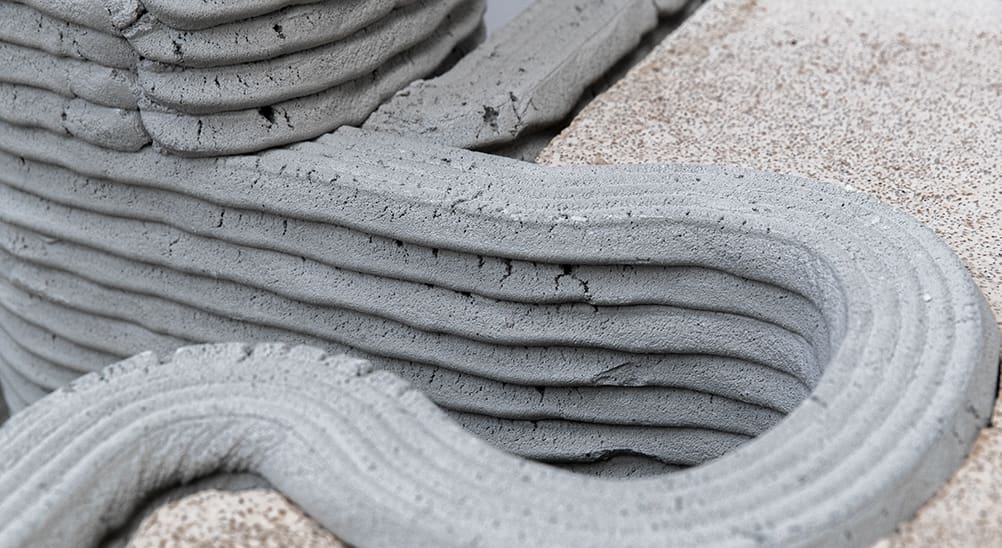
3D Concrete Printing - The Ultimate Guide
In 2022, more than ever with plummeting housing inventories, the industry sorely needs innovations to cut costs and catch up on lost time. Enter 3D concrete printing.
3D concrete printing technology is used today for homes, architectural features, and construction projects from wells to walls. Proponents say it has the potential to significantly disrupt the entire construction industry if it can get over a few hurdles first.
In this feature, we looked at how companies are 3D printing with concrete (mortar, soil, and recycled products) today, what 3D printers they’re using, and what materials make it possible. You’ll learn about the basics and benefits of 3D concrete printing and what advantages it can offer over traditional construction techniques.
read more …
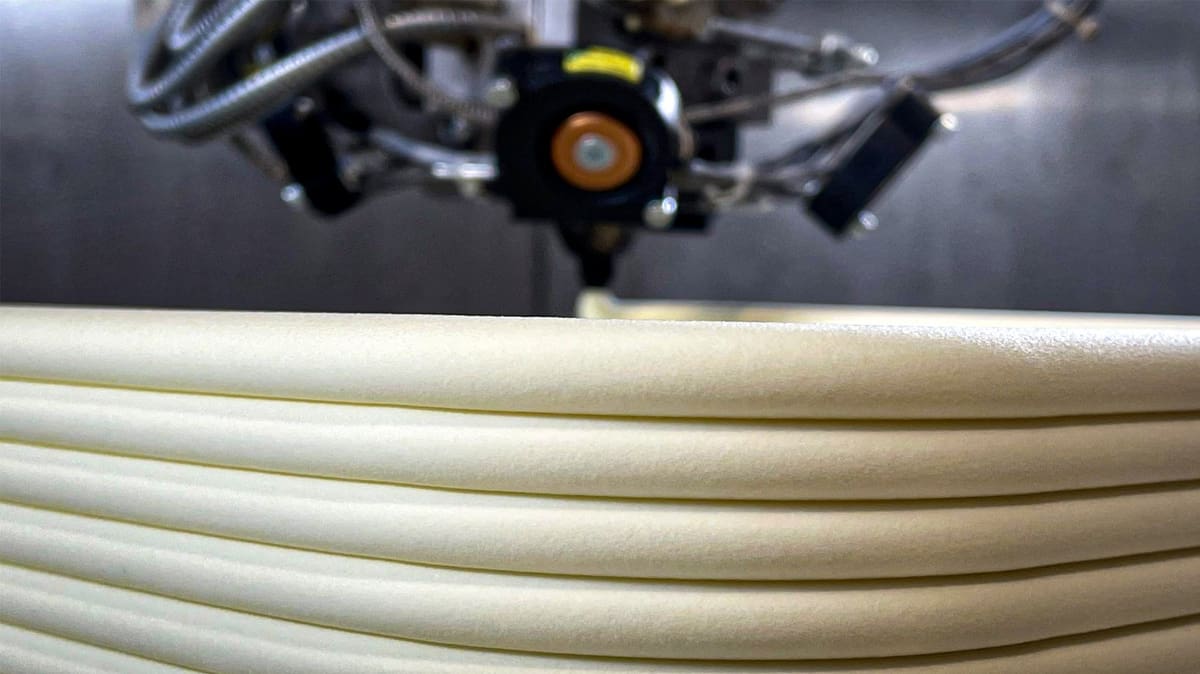
Foam & Lightweight Filament - How and Why to 3D Print with It
For lighter-weight drones, faster printing molds, and a host of new applications, 3D printing with foaming materials opens new doors for professional and hobby applications.
In this feature, we explored how new foaming and ultra-lightweight materials are key to optimizing the weight in your designs, improving your products’ mechanical properties, and maybe breathing new life into old projects that just wouldn’t fly or float.
On the professional side, foaming materials have huge potential. Foamed structures in general encounter less shrinkage and better dimensional stability due to the lower material input. They also offer significant thermal and acoustic insulation properties.
read more …
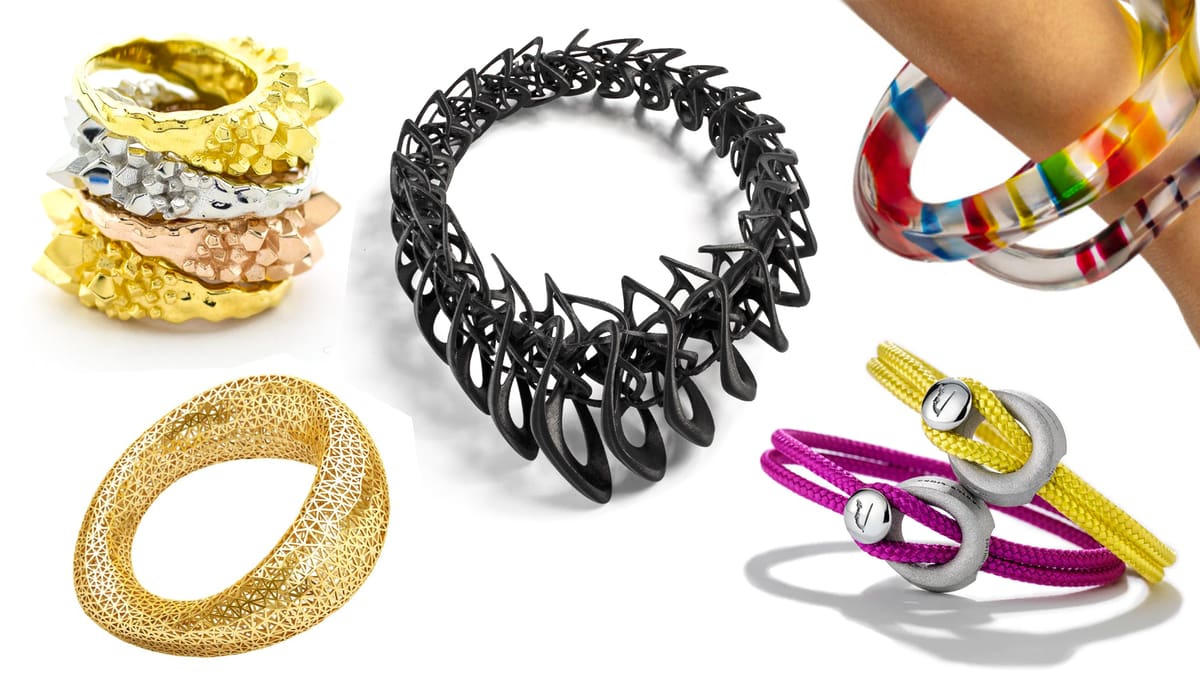
Best 3D Printers for Jewelry 0f 2022
Our ultimate guide to the best 3D printers for jewelry not only covers the machines but all you need to know to select the right one for your business, including the technologies and the materials.
Traditional jewelry-making is a detailed and time-consuming process. Nobody can deny the skill and craftsmanship that goes into a handmade ring or pendant, and there will always be something unique about manually sculpted personal adornments. Still, the fact stands that it takes a lot of time and patience to make jewelry completely by hand.
Many jewelers and goldsmiths have woken up to this reality and started looking for solutions to make jewelry production easier, and faster, and cut costs. Additive manufacturing and 3D printing have stepped in to help.
read more …
Best Carbon Fiber 3D Printers of 2022

Reliable, affordable, and easy-to-operate carbon fiber 3D printers, alongside innovative carbon fiber materials, are bringing the strength and durability of carbon fiber parts to the desktops of businesses and mid-size manufacturers worldwide.
Chances are, if you’re looking to buy a carbon fiber fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printer, you already use carbon fiber materials in your business but need a faster and cheaper way to make your carbon fiber tools and parts. But another reason so many companies are turning to 3D printing carbon fiber is to replace expensive metal parts and machined aluminum components with something just as strong but far lighter and available in hours, not days. You may also choose carbon fiber 3D printing to create stronger functional prototypes that can withstand the rigors of mechanical testing or even carbon fiber final products, such as jigs and fixtures for manufacturing.
read more …
3D Printing Lattice Structures - The Ultimate Guide
Move beyond infills to lattices for lighter weight, better functioning 3D printed parts and products.
Lattice structures in 3D printing are a powerful design tool. Well-designed lattices can make parts lighter and stronger, absorb impact more efficiently, and be better customized to their end-use. Understanding how to use and create these structures is an essential part of product engineering and industrial design in 3D printing for prototypes and production parts.
Although you may be familiar with infills, which are a specific application of lattice structures, most non-specialist designers underutilize latticing. But in this feature, you’ll learn that it’s not that difficult to apply if you follow the five essentials.
read more …
WAAM! What is Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing?
Is it welding, or is it metal 3D printing? Here we looked at the surging interest in wire arc additive manufacturing technology (WAAM), who’s using it, and for what.
This method of 3D printing has actually been employed in heavy industry and aerospace for years. In the 1970s, it was called shape welding, but it’s come a long way since then. Today, it’s being eyed as a way manufacturing, heavy industry, defense, and aerospace can produce large metal parts at a fraction of the time and cost of traditional forging, castings, or machining. It also may be a solution for clogged industry supply chains, market pressures to innovate, and faster repair and spare part delivery.
read more …
What Do You Want To Read About?
You made these articles our most popular in 2022, but we’d also love to hear from you about the articles and guides you’d like to read in 2023. Is there a new technology that you’re interested in? Is there a hurdle in your adoption we can have experts address?
Send your article ideas and requests to us at Pro@All3DP.com or leave them in the comments below.
License: The text of "The Best of All3DP Pro 2022" by All3DP Pro is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.