Triple Bogey
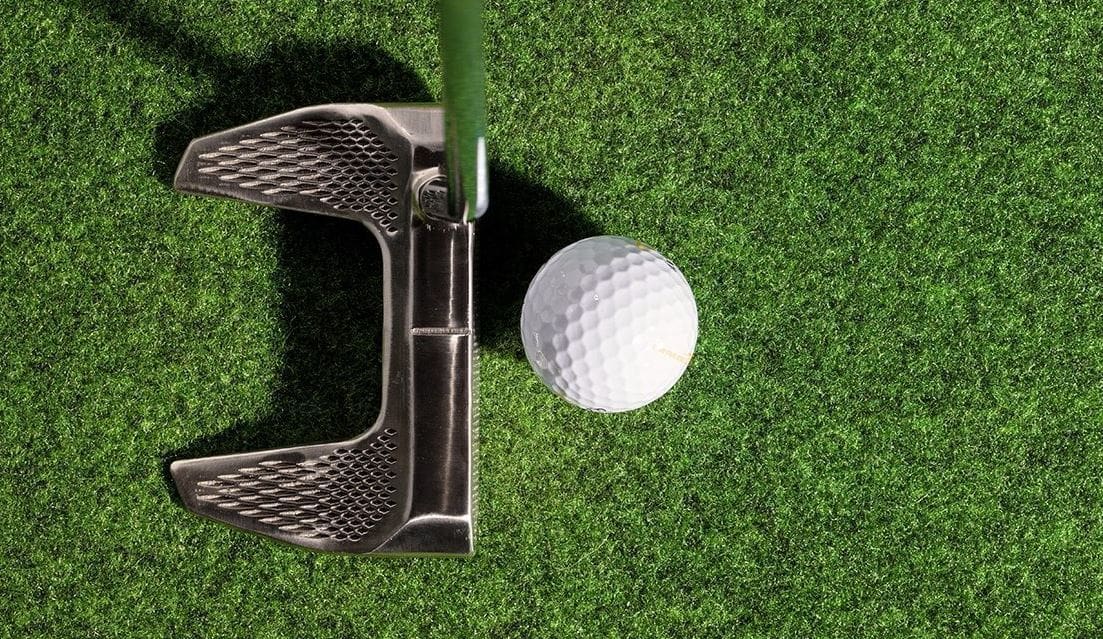

Given the growth of its capabilities and applications, 3D printing continues to expand into different domains, including the world of sports. Equipment such as running shoes, bikes, wheels, and mouth guards, among many others, have all benefited from the innovations of 3D printing. Golf clubs have recently joined the pack.
Novel infills and designs in special materials have entered the world of golf thanks to 3D printing. Besides the end products, the speed of prototyping has impacted the entire design process. Additionally, 3D printing allows for the customization of golf clubs for individual players and their styles.
In this article, we’ll present a few inspiring golf club projects that involve 3D printing. Although there aren’t any available 3D printable models for most of these projects, they still show off the capabilities of 3D printing. For each project, we’ll discuss what printing techniques were used, the materials, and more.
Cobra Golf: King Supersport-35 Putter
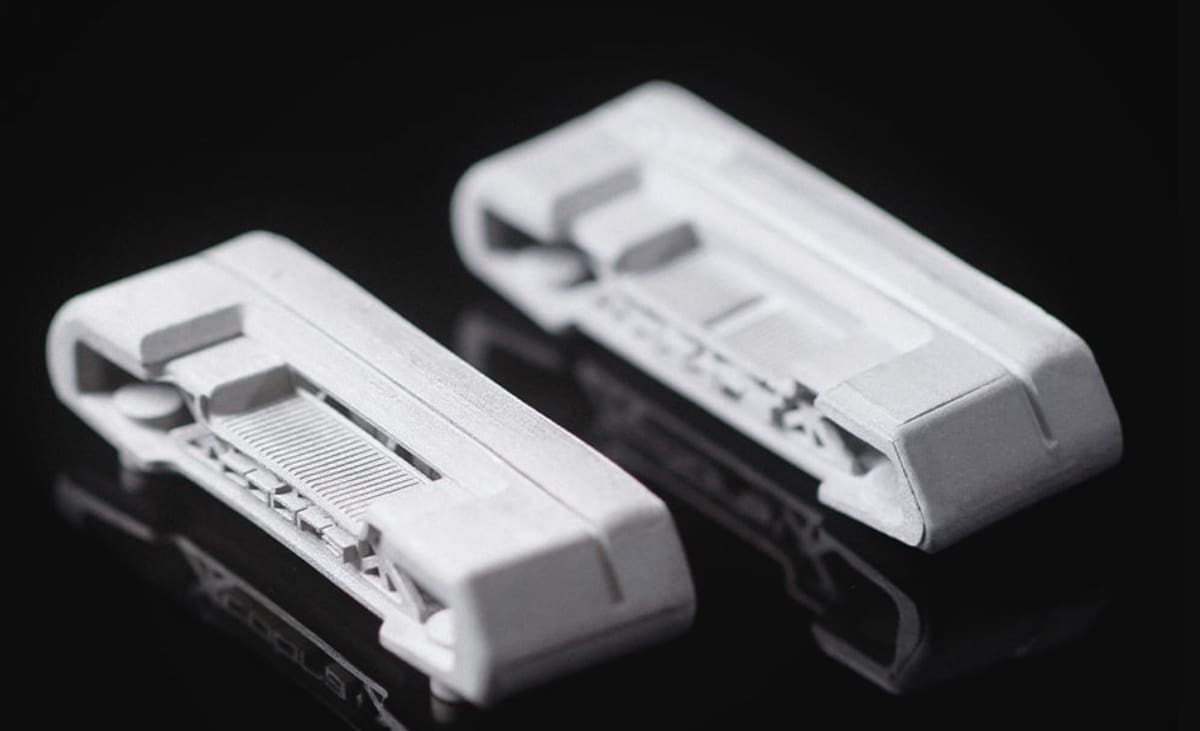

The first project on our list was conceived by Cobra Golf, a company that specializes in advanced golf clubs and accessories. Cobra Golf partnered with the printer company HP, SIK Golf, and Parmatech to make a unique limited edition putter club – the King Supersport-35 – which cost about $400 per club.
The collaborating companies used HP Metal Jet printers to print the club’s components. This printing technology allows for the high-volume manufacturing of high-grade metal parts, which proved useful for mass-producing golf clubs.
The golf club’s design includes a 3D printed steel body. A 3D printed lattice structure was incorporated into the design in order to optimize the distribution of the putter’s weight. Further, CNC milling was used on the head for cosmetic finishes. One other special feature of the King club is an aluminum descending-loft design for the face of the putter, a style developed and patented by SIK Golf for a consistently accurate roll.
Cobra’s use of 3D printing in this design allowed the company to explore the potential of 3D printing in the golf industry, especially the fabrication of specially-made and lightweight clubs. According to Cobra, 3D printing made the manufacturing process faster and also enhanced quality and precision. They were able to rapidly prototype and test designs, allowing them to achieve a final product faster than traditional manufacturing and prototyping methods.
Krone Golf: KD-1
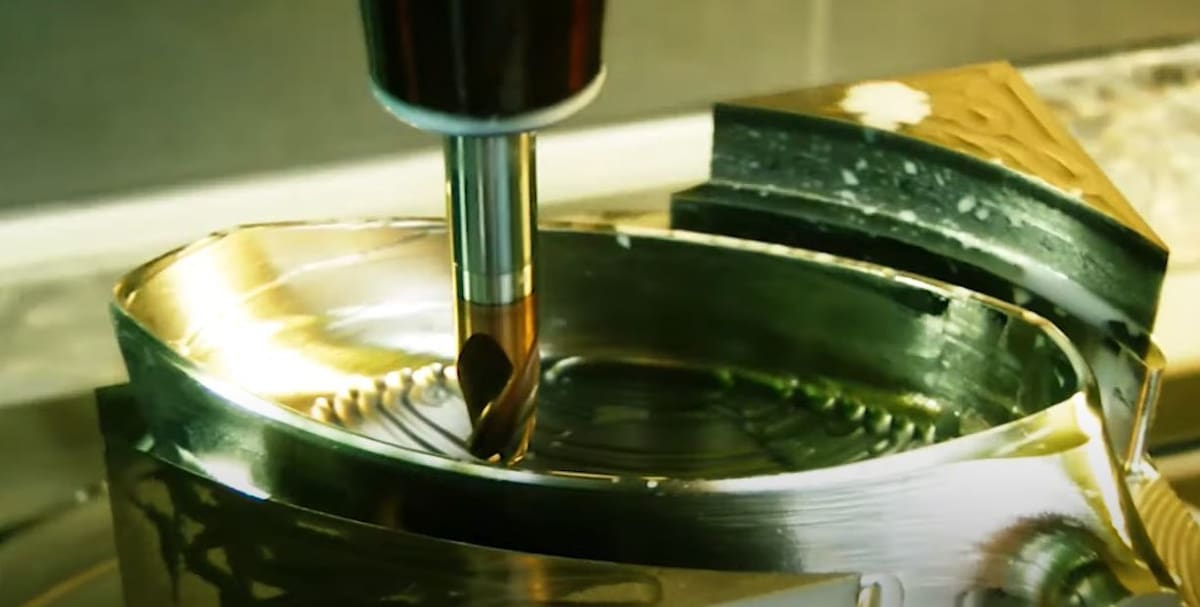

Krone Golf was a golf technology company that developed the KD-1, a specially-manufactured and partially 3D printed golf driver club. To create the KD-1, Krone partnered with the CRP Group, an Italian company that uses 3D printing, among other technologies, to help companies and organizations execute projects.
Since the launch of their golf club project in 2016, Krone Golf has gone radio-silent, and their website no longer exists. For this reason, we presume that they went out of business, but their golf club is still an excellent example of the power of 3D printing.
Krone wanted to demostrate how additive (3D printing) and subtractive (CNC milling) manufacturing could make a great golf club. The company’s previous manufacturing methods were labor-intensive and did not yield dimensionally accurate products. Also, the methods did not allow for the easy customization of parts.
The use of 3D printing and CNC milling in designing the KD-1 made the manufacturing process easier and improved the quality of the product. For the body of the head, Krone Golf used SLS 3D printing and a special material known as Windform SP, which is a strong carbon composite material that yields dimensionally-accurate parts.
The driver’s front face is CNC machined from a titanium alloy, which makes the face strong and lightweight. It also possesses a lattice structure, which reduces weight while mostly maintaining strength.
On top of all that, there’s also a brass CNC-milled clip component that holds the other pieces together. The brass part actually has specific holes for screws to clasp or bind the other components.
After production, Krone found that combining 3D printed and CNC-machined parts yielded an impressive golf club with many benefits over traditionally-manufactured drivers. Swinging speeds increased due to the lightweight design, and the parts were more precise than those made with injection molding or other traditional manufacturing methods. Lastly, the company experienced enhanced flexibility in the design process: Engineers were able to tweak the driver’s design to improve the club without making a new mold like with traditional manufacturing methods.
TaylorMade Golf: SIM Fairway
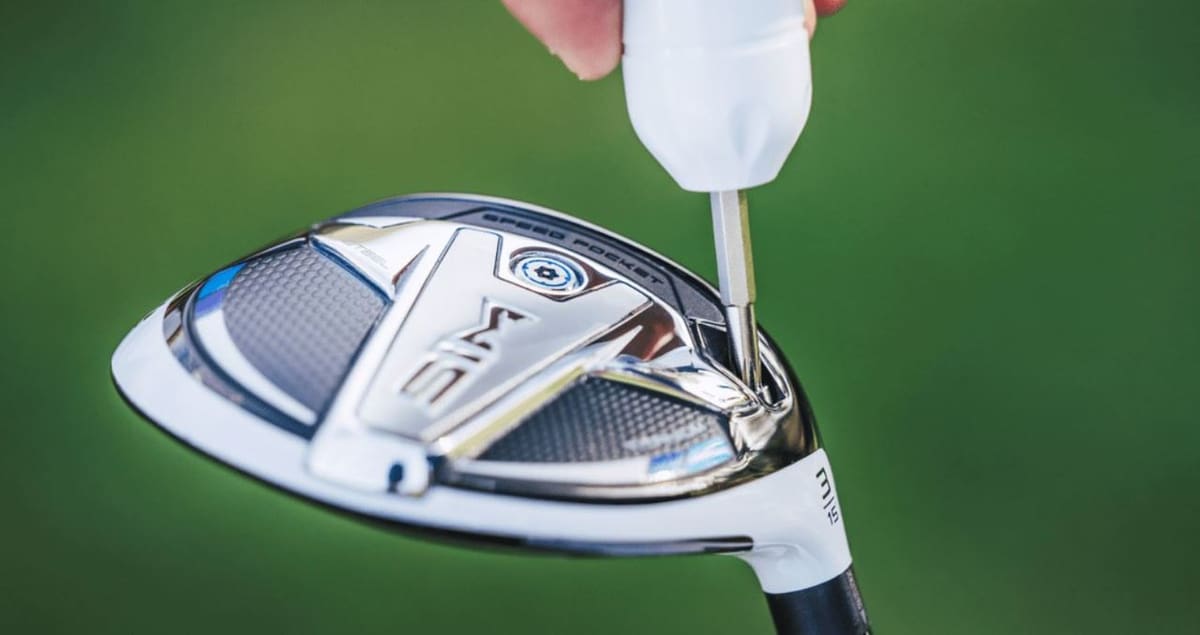

TaylorMade Golf is another professional golf company that makes clubs of all types and other golf equipment, and they used 3D printing to prototype their new products faster. As the company developed one of the first metal head drivers, it’s no surprise that they’re continuing to innovate, in this case by applying 3D printing to the design of their golf clubs.
While the company didn’t actually 3D print the final club, they used the technology to perfect the design and improve certain qualities. To do this, TaylorMade partnered with FormLabs, a manufacturer of professional-grade SLA 3D printers, to create precise prototypes during the design of their reliable SIM Fairway golf club.
TaylorMade Golf wanted their SIM Fairway club to have improved features, including a lower center of gravity, better turf traction, and a more “forgiving” face, among other improvements. Additionally, TaylorMade hoped to build on their current method for users to add weights to the club, in order to make the weight adjustment process for every player easier.
The company’s designers and engineers began designing their SIM Fairway club in 2D and then used 3D printing to develop prototypes of the CAD designs to ensure that their expectations were met. TaylorMade used FormLabs’ SLA printers, which use a laser to bond resin particles together in selective areas to form the desired part. By utilizing 3D printing for rapid prototyping, TaylorMade was able to quickly test new shapes for the weighted inserts to finalize a better design.
Callaway Golf: Odyssey Putter
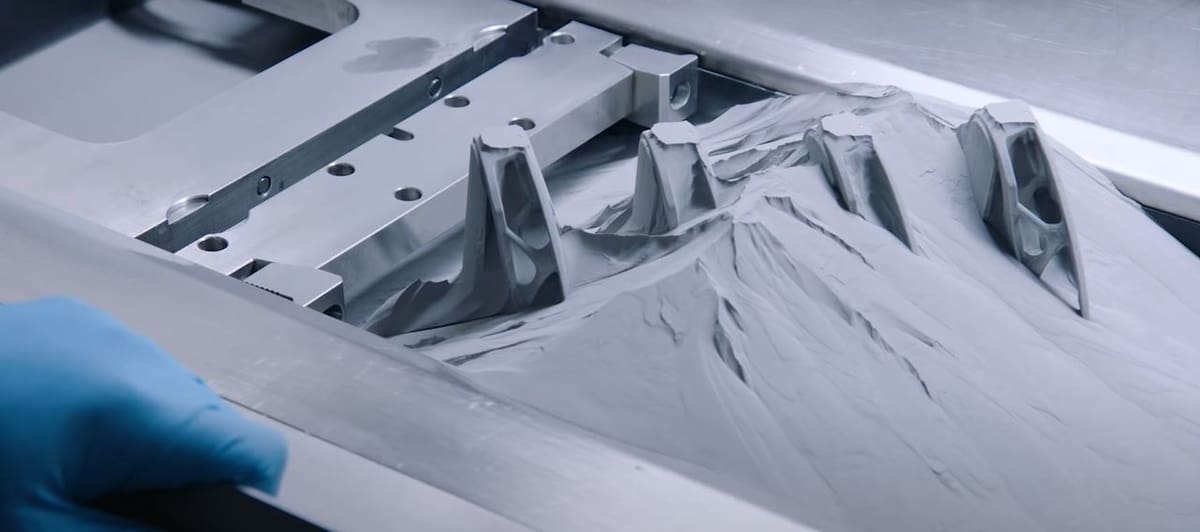

Joining the list of companies that used 3D printing to redesign their golf club is Callaway Golf, a well-known company whose line of Odyssey Putters is one of the top-selling clubs on the market. Callaway Golf partnered with GE Additive to redesign one of Callaway Golf’s putter heads, the Odyssey R-Ball Prototype.
Their original design of the Odyssey R-Ball worked great. Still, Callaway Golf wanted to change the acoustic signature – the sound that it makes when hit – without adjusting the already-effective materials and design. Their solution was to add internal geometries, essentially infill, which is only possible with 3D printing. GE Additive’s team also designed supports for overhangs in the putter head’s design as well as for thermal stresses, which likely helped to prevent distortion by dissipating excess heat.
Callaway seems pretty committed to exploring the design and manufacturing benefits of additive manufacturing. In addition to their work with GE Additive, they partnered with Titomic, an Australian company specializing in metal additive manufacturing. Their patented Titomic Kinetic Fusion technology is marketed as “the world’s largest & fastest metal 3D additive manufacturing technology.”
3D Printable Attachments

If you don’t want to buy a specially-manufactured 3D printed golf club that costs a few hundred dollars, you can always try to print your own. As you probably know, consumer 3D printers are pretty limited in build volume, so you can really only print the head of a club.
Many 3D models of golf club heads can be found on the popular 3D design repositories, and below are some great examples:
- 60-degree wedge: This club, as the name suggests, is a golf club wedge head at a 60-degree angle.
- Titleist 7-iron: This golf club head is a replica of a Titleist 7-iron club and fits any 0.37-inch shafts.
- Putter: This golf club head is a putter with a 16-mm sleeve diameter. According to the maker, it takes around three hours to print.
- Rake: This rake model can be attached to a shaft. While this attachment isn’t used for hitting the golf ball, rakes are used to create as smooth a surface as possible in a bunker.
Unless the end use is mini-golf or another situation where you don’t swing hard or fast, 3D printed heads aren’t very useful if they aren’t printed in metal. That’s because almost all retail 3D printers exclusively print in photosensitive resin that, as impact-resistant as it can be, will shatter instantaneously when hit against a golf ball at typical swing speeds. Resin drivers are decimated on impact at high speeds, as demonstrated in 3D Printing Nerd’s video.
If you really want to go all in for printing metal golf clubs and you aren’t concerned about cost, metal 3D printers are always an option. Two popular desktop metal 3D printer companies include Desktop Metal and Markforged. Both companies offer expensive but quality machines capable of printing in a variety of metal materials including 17-4 PH stainless steel, H13 steel, or even copper.
Customization Services
Maybe you have your own custom golf club design and want it 3D printed, but where would you go? Luckily, there are 3D printing services that can help you print a customized golf club. Using a service, you don’t have to purchase extremely expensive machinery to 3D print difficult materials. Below, we’ve pulled together a few great options.
Craftcloud
With Craftcloud, printing your golf club design is easy. With partners all around the world, Craftcloud offers some of the best prices and lead times. Using the platform is intuitive and easy to use. Quotes and estimated delivery times are generated instantly based on your uploaded 3D model and location.
Various metal options are available, including titanium, aluminum, and a few different grades of steel. And, if you were inspired by Cobra Golf’s King Supersport-35 Putter, CNC milling services are also available.
JawsTec
Offering both on-demand CNC machining and 3D printing services, JawsTec is a company that specifically indicated that its services can be used for 3D printing golf clubs. They offer a few high-grade materials, mostly for multi-jet fusion 3D printing, like nylon 11, nylon 12, polypropylene, and more. These materials, however, are all thermoplastics, so they might not work for golf clubs, which have to be super impact-resistant.
Fortunately, JawsTec also offers metal 3D printing services. To order 3D printed parts in metal from JawsTec, you have to fill out their order form, which asks which metal material you want and the type of services you’re looking for. Some of their options include 316L stainless steel, MS1 steel, Monel K500 MK5, and more. These metal options will definitely cost more than the plastic alternatives but will make for a more sturdy golf club.
Proto3000
Another option for a metal 3D printing service is Proto3000, a company that offers services and sells high-quality equipment for 3D printing. Proto3000 offers two services capable of 3D printing metal parts: direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and bound metal deposition (BMD). A few of the metal materials they offer include 316L stainless steel, titanium Ti64, cobalt chrome MP1, copper, H13 metal, and more.
In their article about printing golf clubs, the company mentions how BMD is a great way to inexpensively prototype new golf club models. Compared with CNC machining and DMLS technology, BMD is significantly cheaper.
Lead image source: FormLabs
License: The text of "Incredible 3D Prints: Can You 3D Print Golf Clubs?" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


