Despite being around since the 80s, 3D printing’s only recently being more widely adopted across various industries. Yet, having now proven its commercial potential, it’s safe to say this technology is here to stay.
Whenever a new technology enters the market, it’s invariably accompanied by an increase in demand for specialized professionals. Take the internet, for example, or the smartphone app industry. Dozens of new job titles, like “User Experience Designer” and “Product Owner”, were created to fill gaps in these new markets.
Now, imagine the impact such a disruptive technology like 3D printing will make, or rather, is already making. It thrives in both digital and hardware environments and can be applied in multiple areas, from tiny nano-printing applications to constructing entire buildings.
In this article, we’ll be exploring the jobs that are emerging as 3D printing technologies are adopted by more and more industries. While some of the jobs and industries discussed here already existed in one form or another, some will call for a different approach altogether, either by completely changing the way they work or by requiring deep knowledge of 3D printing processes. Let’s take a look!
Printer Manufacturers
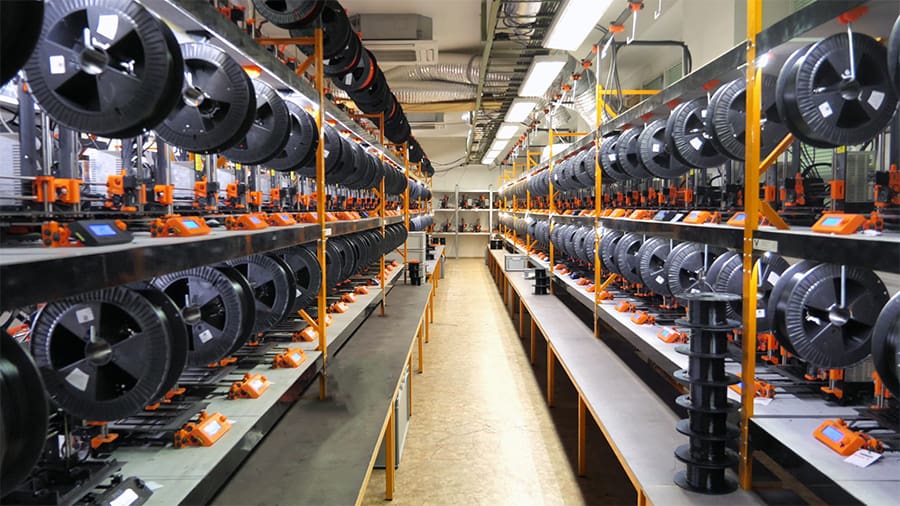

While 3D printing isn’t an entirely new technology, the recent interest in different additive manufacturing techniques – FDM, SLA, SLM, Binder Jetting, and more – has contributed to a boom of 3D printer manufacturers all around the world.
Jobs & Positions
This is a case where a completely new product has entered the market, and as such, new jobs. While designing and producing machines isn’t novel, the aforementioned 3D printing methods require new specialists to support not only development and creation but also the adoption and sales of machinery. This also includes material specialists and R&D departments that continuously improve these systems.
Both prosumer 3D printer manufacturers (like Prusa Research and Formlabs) and industrial-focused ones (like Stratasys and 3DSystems) require various professionals, such as sales representatives, field service engineers, product developers (for hardware and software), and even tech support.
Materials
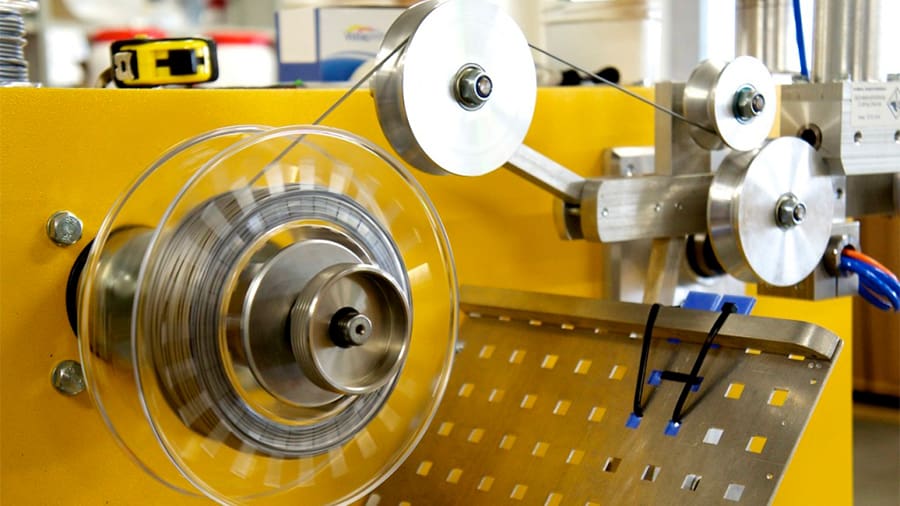

3D printers need their feedstock, and while many hardware manufacturers also produce and commercialize their own line of materials, there are a huge number of independent filament and resin producers for different levels of printers.
Jobs & Positions
As with 3D printer manufacturers, these new products have created a demand for companies that weren’t there before. In particular, the filament market is currently booming with the somewhat recent popularization of DIY and desktop 3D printing, leading to many job openings. Companies like Hatchbox, ColorFabb, and Proto-pasta were all established as independent manufacturers, while big players in the market, such as BASF and Igus, have also joined this trend, though focusing on high performance and engineering materials.
Services
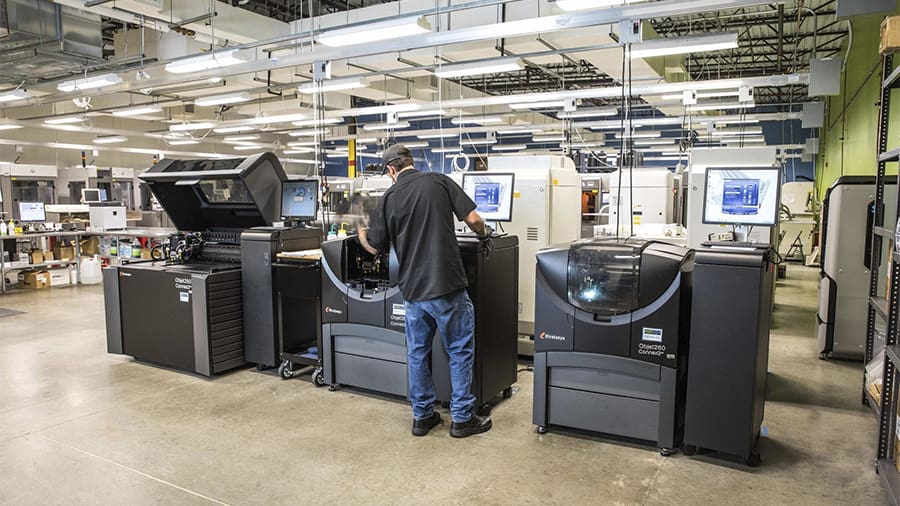

Undoubtedly, 3D printing has gained the most visibility through prototyping and, until recently, was even referred to by many as “rapid prototyping”. This reflects what was, until now, the biggest commercial application of 3D printing: outsourcing to external 3D printing shops and service companies.
The rapid development of 3D printing technologies has also enabled these companies to offer more than prototypes, as small-batch functional parts are now commercially viable. This is the case of multi-technology service providers like Protolabs, Sculpteo, Shapeways, and more recently, 3D Hubs and Craftcloud.
Additionally, small metalworking shops have also added 3D printers to their machine floor. Even some home users are offering their printing expertise to customers in shops like those on Etsy.
Jobs & Positions
The jobs in this area mainly center around setting up, monitoring, and post-processing single as well as batches of prints. Such work requires experts in additive manufacturing and finishing techniques (like sanding, painting, and so on). In some cases, there are also professional designers who help develop or optimize customers’ visions.
Another huge side of 3D printing is customer support, which includes everything from simply helping customers place orders to accommodating special projects.
Content Creation

The popularization of DIY and desktop 3D printers has also created a demand for more information and content on the subject. Reviews, tutorials, and tips – you name it.
A lot of 3D printing-related content is also available online. In fact, you are consuming such content in this very article! Plenty of magazines and journals are dedicated to 3D printing and additive manufacturing, exploring various segments from the home DIY user to the industrial manufacturing market.
Jobs & Positions
While content creation isn’t new, creating content around 3D printing does require a level of familiarity and new technical knowledge.
Those working for magazines, tech platforms, and similar forms of media must have at least a minimal technical understanding of 3D printing and related fields, hire tech-savvy freelancers, or both. In some cases, writers and editors even come to their positions as a direct result of their technical familiarity. (Sound like something you might be interested in? Then head on over to our Content Academy!)
If you type in “3D printing” on YouTube today, you’ll be showered with hundreds of videos and channels, like those of Thomas Sanladerer or Joel Telling, a.k.a. 3D Printing Nerd. Many of these creators use their channels as sources of income.
Architecture
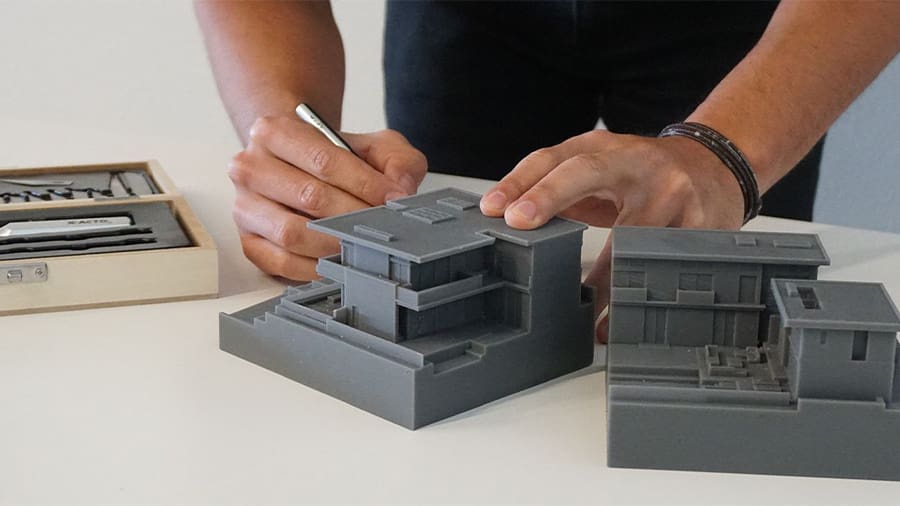
While many new career possibilities have been made possible by 3D printing, quite a few existing field have been heavily impacted, as well. This is the case for architects, who can now produce highly precise scale models at a lower cost and with shorter lead times.
Architectural models are very important communication tools between architects and clients. Before 3D printing, model making was rather time-consuming and artistic work, used sparingly only for the most important projects.
With 3D printing, model making has become much simpler and faster since most architectural development today is already done through digital 3D modeling. All that’s left is to send a model to a 3D printer and show it off to clients or coworkers.
Jobs & Positions
By nature of the fact that 3D printing has essentially simplified an already existing process, its primary impact on architecture has mostly been to slightly expand an architect’s skillset, namely in preparing and executing a 3D print. Interestingly, it’s also resulted in clients being able to demand and receive customized patterns for everything from tiles to lamps.
Construction
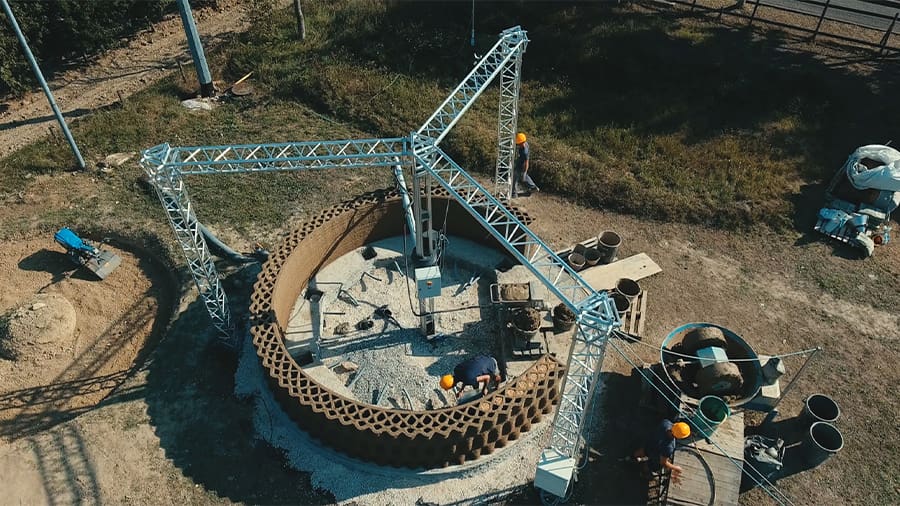

Construction represents a particularly fascinating application of 3D printing. Today, there are many companies perfecting huge 3D printers required, while others are already erecting buildings ready for use. The benefits are many: quick to build, eco-friendly, and inexpensive when compared to traditional construction.
Jobs & Positions
While 3D printed construction is still construction in some form, these jobs will ask that workers learn how to operate and monitor a massive 3D printer on a different kind of build site. Part of this is special material mixing. Architects and civil engineers will also need to adapt to these construction techniques in order to design structures that are safe, livable, and functional, especially with respect to integrating windows, plumbing, electrical works, and so on.
Manufacturing
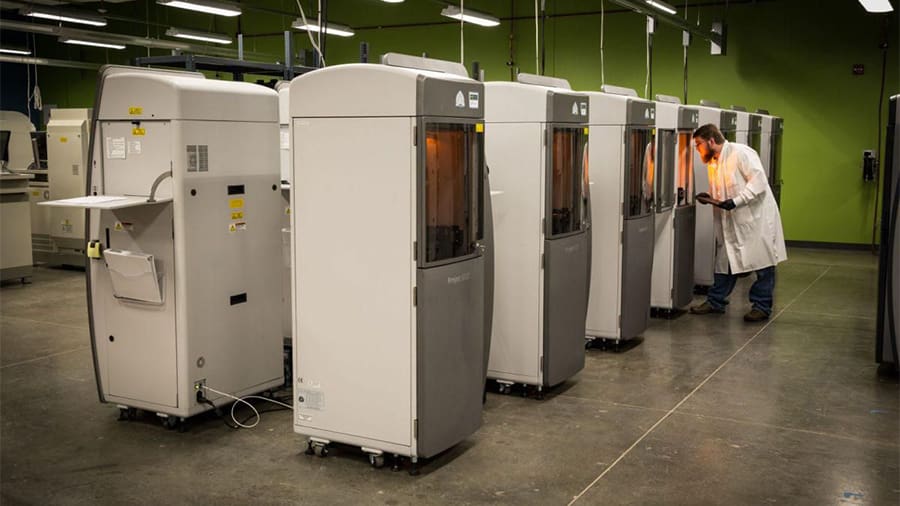

3D printing has come a long way, and it’s now known to produce end-use parts for some pretty complex products. Still, you won’t yet find 3D printers on every shop floor.
Besides the ever-popular prototyping capabilities of 3D printing, many manufacturing plants across the world have been leveraging the flexibility of FDM for tool creation and, in some cases, on-demand spare parts production.
3D printed jigs and fixtures expedite part assembly and come with the perks of being cheaper, as they take minimal inventory space and don’t have to be outsourced. That’s the case for well-known automotive companies like BMW and Volkswagen, which have been internally producing jigs for quite some time now.
Jobs & Positions
The manufacturing industry has certainly been affected by 3D printing, as it has opened up a whole new way to manufacture. In addition to needing professionals who know how to use 3D printing to manufacturing parts, maintenance departments are investing more in this technology and the labor force capable of handling these machines.
Outside of general manufacturing, the automotive and entertainment industries are two areas where the use of 3D printing is increasing for customized parts and props, respectively.
Dentistry
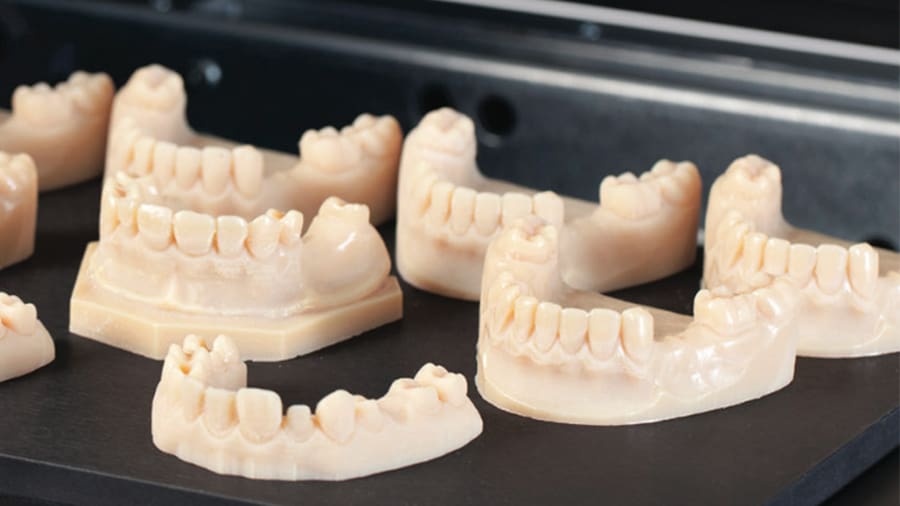
Another area that’s been heavily affected by 3D printing is the dental industry. 3D scanning and printing processes drastically changed the way many prosthetic and orthotic devices can be produced. Rather than manually molding and sculpting dental arches, today’s professionals can digitize that work, leaving much, but not all, of the heavy work to the 3D printers.
The printed objects are often used as tools for creating the final prosthetics and orthotics like aligners, and the high-precision prototypes provide a much higher quality final part, not to mention the reduced fabrication times. Additionally, special materials developed exclusively for dental applications can be used to create surgical guides and final placement parts.
Jobs & Positions
Dentists from all areas are either jumping right into 3D printing processes or, in some cases, outsourcing the fabrication to external shops and service providers. This has lead to new demand for skills and know-how around using professional-grade printers, like the J700 Dental from Stratasys. Skilled CAD technicians are also needed to convert scans and measurements into printable 3D models.
Education
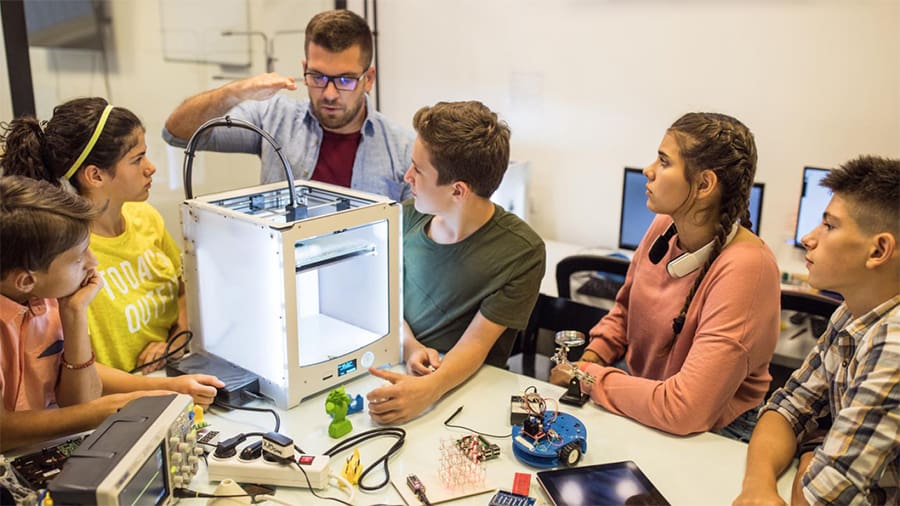

Manufacturing, in all its various forms, has been taught and studied for centuries, allowing it to undergo constant development as new processes and materials are invented. Universities and research centers are usually at the forefront of new technologies, but as early as elementary school, students are learning about and getting their hands on 3D printers.
In terms of changing the field, it’s more that 3D printing has added a new subject area for both teachers and students to engage in. Indeed, 3D printing and design is something that students of all ages can learn.
Jobs & Positions
In elementary schools, instructors are learning the basics of 3D modeling and slicing so that they can demonstrate how to use the 3D printers entering some libraries. In middle and elementary schools, entire units of curriculum are being woven into workshop- and electronics-oriented courses. Towards this end, many manufacturers, like Makerbot, Ultimaker, and ZMorph, have been investing in early education, including bringing 3D printers into the classroom.
It’s likely that, in the near future, all new professionals in the sciences will require specialized education of 3D printing processes and applications. In fact, some top universities like MIT and Nottingham University already offer special courses in additive manufacturing.
Hospitals
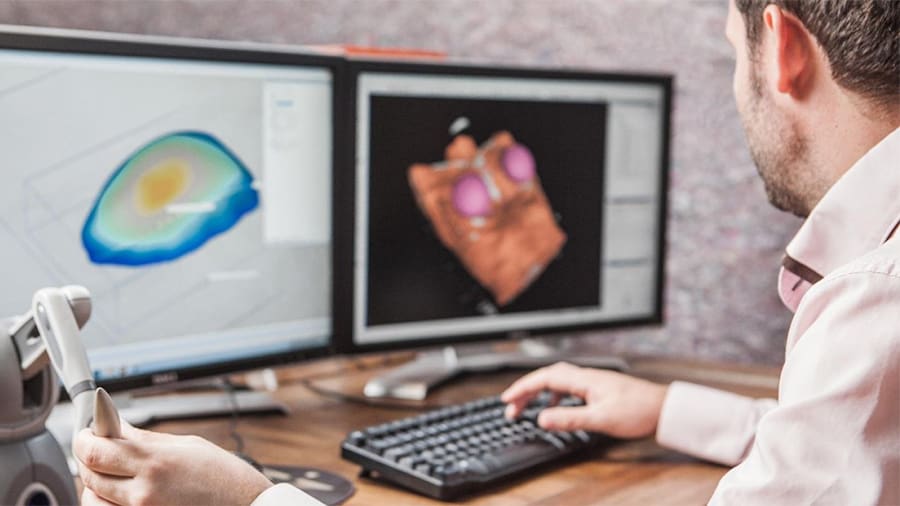
Metal 3D printing goes a long way with medical implants. For one, patient-specific development provides custom-fit parts that not only improve performance but also make surgery much simpler. As of today, cranioplasty procedures require the implant to be shaped during surgery with the patient opened, decreasing both surgery and recovery times.
Jobs & Positions
Customizing medical implants, like hip replacements, requires specialized 3D modeling techniques in dedicated software (like InVesalius), not to mention a deep knowledge of biomechanics. Moreover, the designer or engineer must be able to comprehend the patient’s conditions and interpret CT scans.
Laboratories
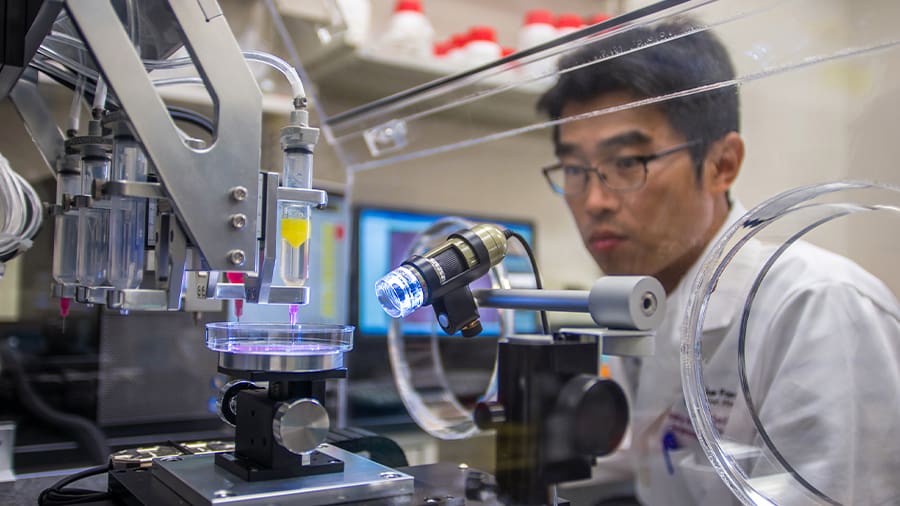

3D bioprinting is a very promising application of 3D printing. It’s similar to regular extrusion-based techniques like FDM, but rather than filament, it uses organic materials (bioinks) to create tissues, organoid structures, and even more complex 3D printed organs.
Although many important milestones have already been reached, 3D printing fully functional organs is still a promise. Yet, many private and educational institutes have been continuously working with 3D bioprinting and have had several breakthroughs in skin and heart tissues, for example.
Jobs & Positions
Using 3D printing to create potential organ replacements, the holy grail of bioprinting, is something that was unimaginable before 3D printing. This is a case where 3D printing has created a completely new field.
It goes without saying that this exciting area requires a special kind of professional. We imagine that these innovators will need a set of skills that are a combination of chemist, biologist, engineer, and doctor, who can also develop printable organic materials or even work on bioprinting equipment development.
Courtrooms
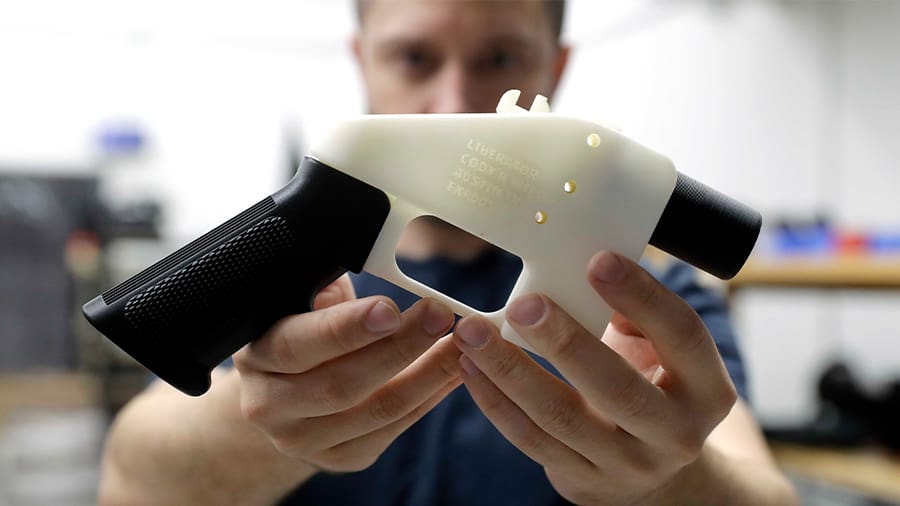

The flexibility provided by digital fabrication allows easy reproducibility of parts and products. With 3D printing, anyone can produce things by simply having access to digital 3D models. In addition, with the increasing popularization and accessibility of 3D modeling software, you can even replicate a product design and share it with whomever you want. Normally, this is a great thing.
However, sometimes designing and sharing can go against intellectual property (IP) ownership, like patents, copyright, and trademarks. A real-world example took place back in 2017, when all Star Wars models were removed from Thingiverse by Disney. Lego also made a similar move in 2019. While there’s a big debate on the rights and wrongs of each side, it’s quite clear that there’s an issue at hand.
If things were problematic with Star Wars figurines, imagine when entire catalogs of products become available online for download. Now imagine that with restricted products like weapons and guns. All of this raises very serious and complicated legal issues.
Jobs & Positions
This new area of IP will need experts to defend, protect, and interpret the law. A lawyer would need to have a nuanced and in-depth understanding of both 3D printing technologies and intellectual property and licensing laws. Since 3D printing’s accessibility makes its reach so broad, this area of expertise will certainly be a new niche for lawyers.
Fashion
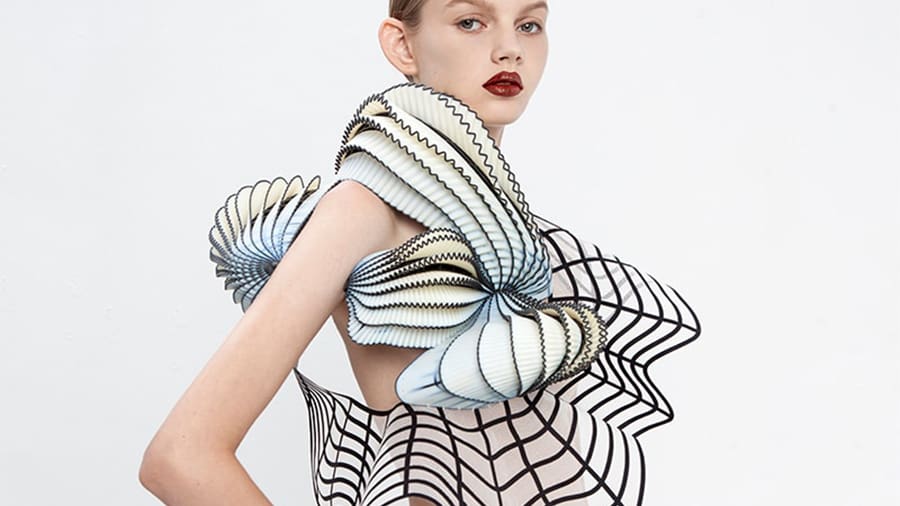

The wearable industry has also turned its head toward 3D printing technologies. And by wearables, we mean anything from clothing, accessories, garments, and even shoes. In fact, big brand names such as Adidas, Nike, and New Balance have all invested in SLA printing methods to create stunning and high-performance products such as the AlphaEdge 4D and the FuelCell Echo Triple.
When it comes to dresses, Iris van Herpen is a prominent name in 3D fashion, designing and producing the first 3D printed dress – the Skeleton – back in 2011. Today, fashion designers must be able not only to model designs digitally but also to understand the various 3D printing technologies and choose the best suited for each application.
Jobs & Positions
3D printing has opened up possibilities in construction, design, and prototyping. While fashion has been around for thousands of years, these technologies and capabilities provide a whole new world of possibilities.
For fashion designers, having knowledge of 3D design and modeling will be essential moving forward. We anticipate that, as has already happened in the shoe industry, performance wear will continue to exploit this technology for further innovation.
Jewelry
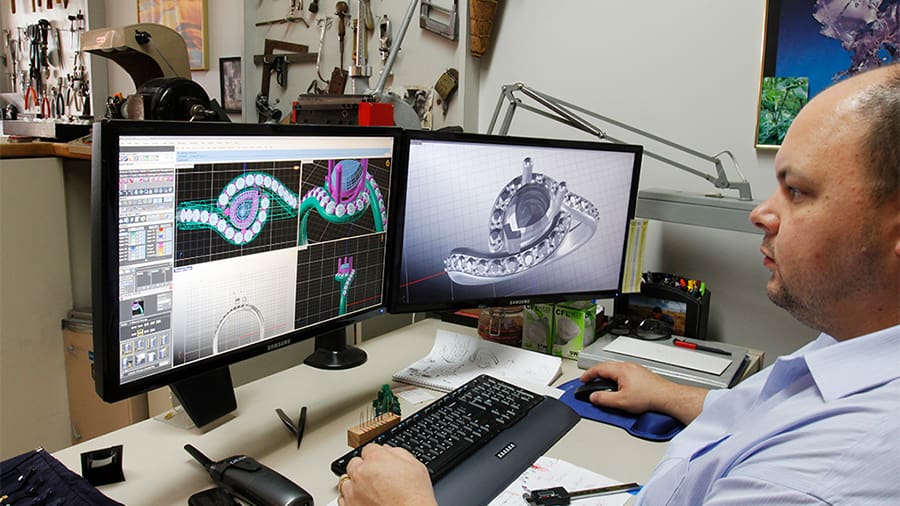

Jewelry has been truly revolutionized by 3D printing processes, especially SLA. Designers have gained unprecedented design freedom with digital 3D modeling techniques and casting these pieces with 3D printed resin molds. This automated fabrication can replace many of the hand-craft techniques that are so laborious and time-consuming.
While a few big companies have already implemented the 3D printing process to fabricate their products, many independent jewelry makers or even amateurs are taking advantage of this process to sell their own product line. Service providers of metal 3D printed parts are also a great way to go as the necessary machines aren’t particularly accessible.
Jobs & Positions
3D design and modeling of jewelry, as well as how to 3D print it, are new skills and positions that those in the jewelry industry have to either learn or hire for.
Regardless, it’s incredible how accessible 3D printing jewelry is, as evidenced from hobbyists casting custom rings and small-scale professionals creating designer pieces.
Kitchens
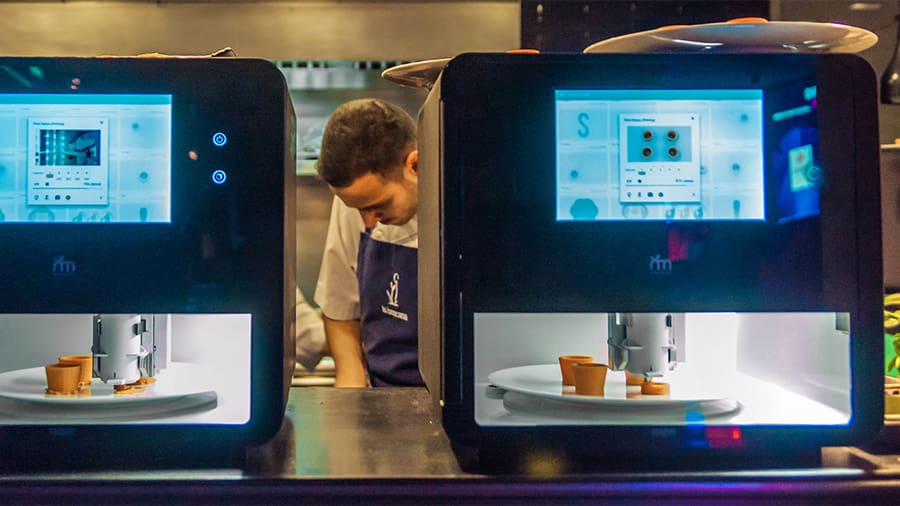

Gastronomy might not be the first thing that comes to mind when thinking about 3D printing. Yet, 3D printed consumables are already a thing. While still not a Star Trek replicator machine, there are a handful of food 3D printers already in the market and a few restaurants, like Food Ink, that only serve 3D printed food.
Jobs & Positions
In the world of culinary arts, 3D printing hasn’t yet fundamentally changed the way we get our food, but it certainly has the potential to do so.
Chefs creating intricate and beautiful dishes with a 3D printer is something that will likely become more of the norm. In the near future, 3D printers could become a regular fixture in restaurants’ kitchens, meaning chefs will need to know how to operate and best make use of 3D printers.
Lead image source: GE
License: The text of "3D Printing Jobs: New & Shifting Job Markets" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.












