What's Scanning, Again?
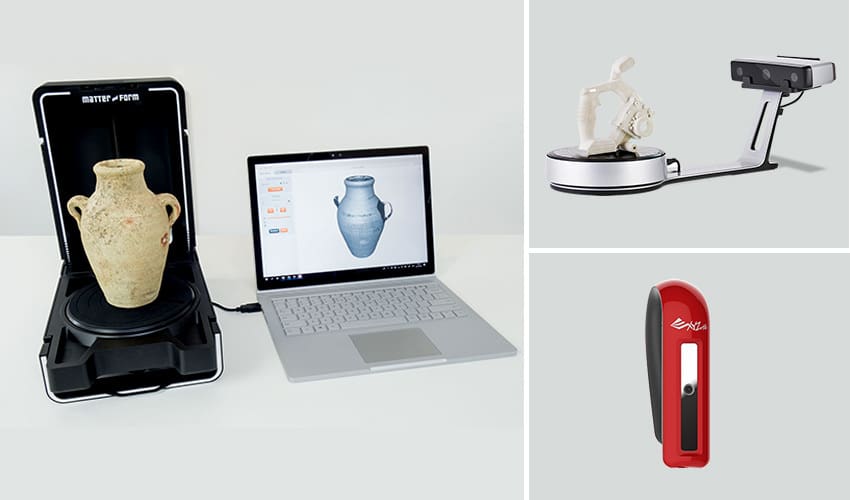

3D scanning is the process of using light and angle measurements to create a computer image of any 3D object. It’s a common way to create digital forms of small physical objects and reverse-engineer parts.
Each 3D scan collects a mountain of digital data called a point cloud, and each point represents a measurement in space. There are a couple ways 3D scanners do this, but laser measurements and other light sources are the most popular and accurate. Those points are then connected to create a digital picture of the object, which can then be used to recreate, modify, or store the object’s qualities for future copies.
Advancements in 3D scanning over the last half-decade have greatly expanded the potential and quality of the process, and now it’s just as easy to scan an entire room as it is to scan an apple!
But Why?
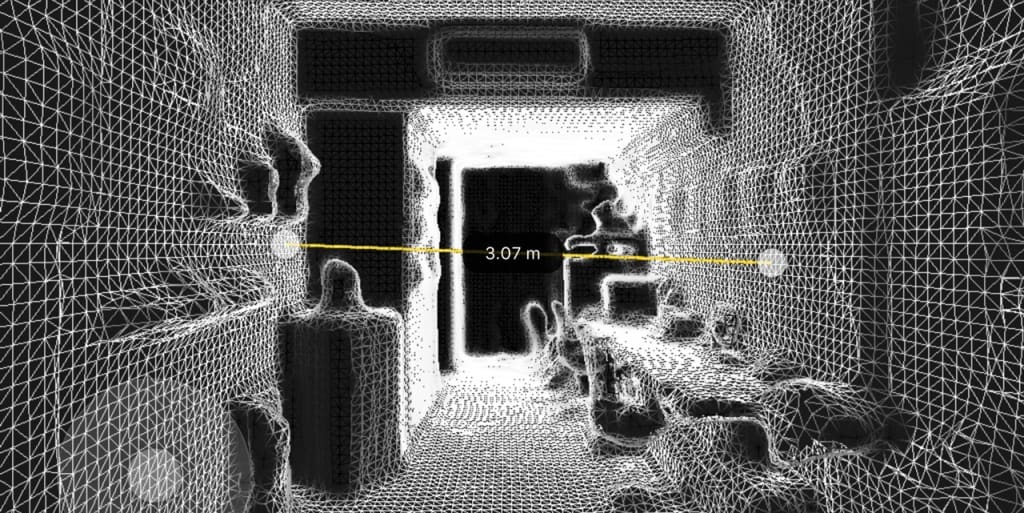
3D scanning has many real-world applications:
- Measuring your space: A good 3D scan is all about getting the proportions of your scanned object right, and 3D scanning a room is no different. You can use the measurements captured for everything from total square footage for a real estate listing to figuring out how big your new couch should be.
- Creating a 3D model: While this is the main objective of 3D scanning any object, 3D scanning a room often acts as a starting point for other creative processes. Interior designers use 3D scans of rooms as their blank canvas, as do architects and building engineers. And the increasingly low cost and high usability of the technology over the past few years gives this power to anyone with a smartphone or tablet.
- Preservation: 3D scanning a room is a wonderfully unobtrusive way to recreate and study spaces that should not be physically disturbed. Many historians and archeologists use 3D scans to get details from rooms in houses and ancient structures that would fall apart if studied by normal inspection methods. Plus, when you have a 3D scan of a room, you can recreate that space digitally and share it online, all while keeping the room safe from the usual disturbances regular visitors bring.
What You Need

You need several things to ensure a successful scan:
- 3D scanner: There are several different types of 3D scanners, but if you want to 3D scan a room, make sure you get one that utilizes time-of-flight for its scanning method. This is actually much easier to find than its name makes it sound. In fact, there are many apps that let you use your existing smartphone or tablet as a 3D scanner, and they’ll be ready to use as soon as they download them.
- Correct lighting: The right lighting is crucial for a useable 3D scan, especially in the case of a large space like a room. Fortunately, this is also something that’s easy to get right even if you don’t have any professional equipment. Diffused white light with minimal shadows is best, which means if you have the evenly-spaced overhead light found in most enclosed rooms, you’re all set. Don’t be tempted to use natural light, even if you have large windows. After all, you can’t control the coverage of sunlight so the scan will more than likely be uneven and missing details.
- CAD program: The software that comes with your 3D scanner will compile the millions of data points you’ll get from your 3D scan of the room. Your CAD program will complete the picture, show you the measurements, and let you manipulate anything you want to change. Our only tip here is to make sure you have a program that you’re comfortable using. Check out our comprehensive list of all the best CAD tools available if you’re still looking for one.
How It Works
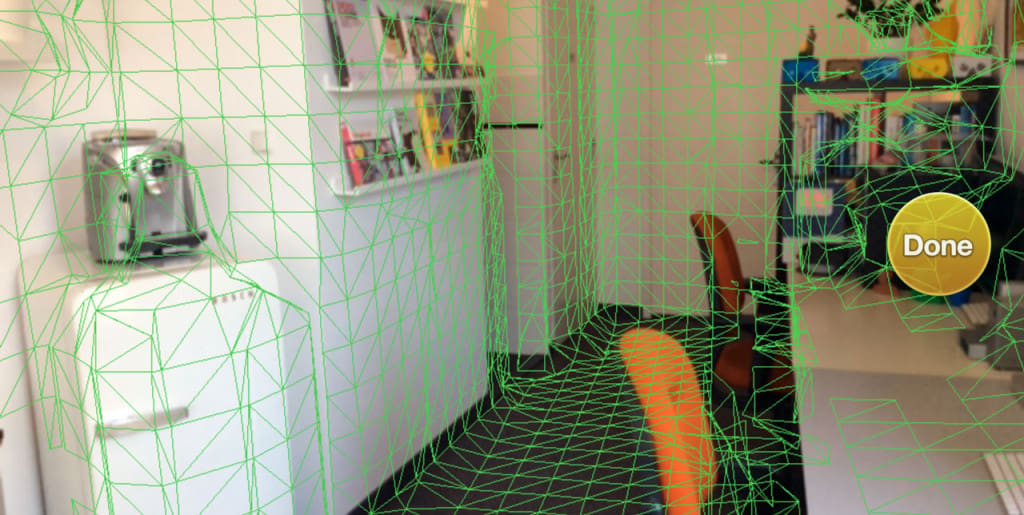

Once you’ve got the right equipment for the job, the process of 3D scanning a room only requires a few steps:
- Learn your scanning program: Before you’re ready to use it, make sure you have a good idea of where the necessary controls are within your scanning program. If you’re using your smartphone or a tablet, it will be very similar to how you take photos. Knowing how this works before you start your scan will make the scanning process go more smoothly.
- Focus your scanner: Once you’re ready to start scanning, focus your 3D scanner on one area of the room. Make sure it has different textures for the scanner to pick up, such as a full bookshelf. This will calibrate the scanner to the conditions in your room.
- Pan and scan: When your scanner has been calibrated, pan it around your room into every area you want to show up in your 3D scan. Do this extremely slowly. The scanner will map objects in the space according to how it recognizes objects in the scan, so you must focus on the different areas long enough. Otherwise, you’ll get errors, blank spots, and incorrect textures.
- Fix the scan: Depending on your scanner and your scanning process, you may need to fix errors that show up in the initial 3D scan of your room. Areas that show holes or errors may need to be scanned again and incorporated back into the rest of the scan. You can do this within your 3D scanner software.
Quick Tips
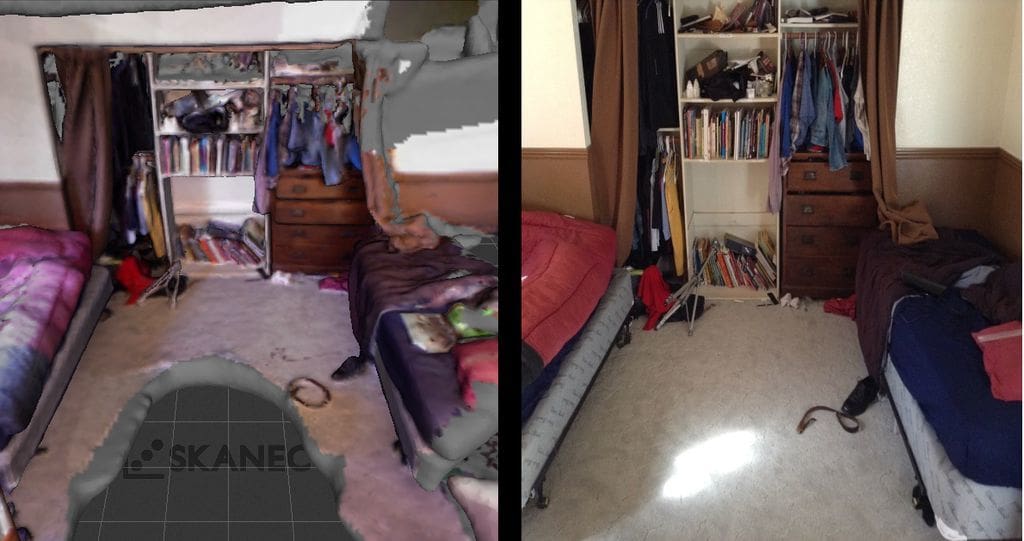

In theory, 3D scanning a room is straightforward. In practice, it takes practice and attention to a few unique details to get just right. Here are some general pointers:
- Don’t start on a blank surface: When you start your 3D scan of your room, you need to give the scanner texture to focus and calibrate on. If you don’t, the details of your room will be lost in the full 3D scan, and you won’t get the precision you need.
- Cover reflective surfaces: Anything reflective or shiny will interfere with the lighting of your 3D scan. It will confuse your scanner and give the visual equivalent of static to your scanning images, so if you have any mirrors or polished surfaces in the room, cover them up. If you’re worried about obscuring shapes too much, you can use special non-reflective paint that comes off easily when you’re done.
- Start three feet away: The best distance to capture detail in an object is roughly three feet, dead-on to the object.
3D scanning a room is a great way to make a realistic copy of your room for design, construction, or personal purposes. Happy scanning!
(Lead image source: wired.com)