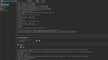
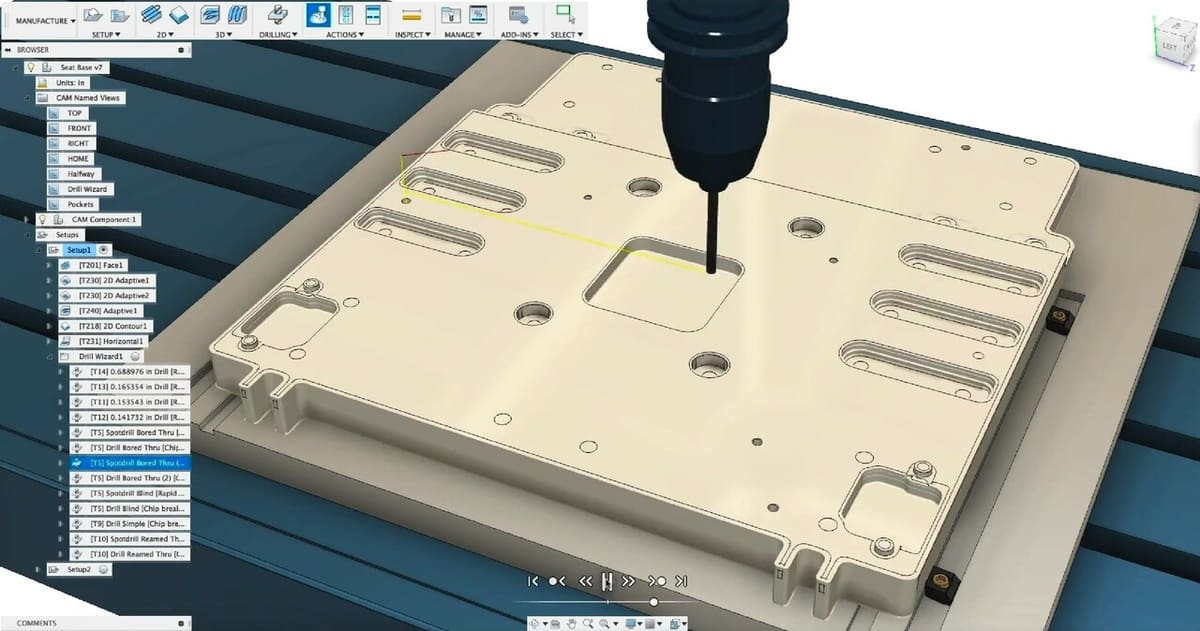
Computer numerical control (CNC) machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computer programs to control the movement of machine tools, enabling the creation of precise and intricate parts from various materials, such as metals, plastics, and composites.
The computer program contains instructions for the tool’s movement along multiple axes, allowing for extremely accurate cuts with minimal human intervention. This technology has become a crucial part of modern manufacturing and is used in a range of industries such as the aerospace and automotive fields, and for medical devices.
CNC machining is a subtractive process well-suited for creating complex parts from a wide range of materials. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive process better suited for producing customized parts with intricate internal structures. CNC machining is generally faster for producing large quantities of parts, while 3D printing is more cost-effective for producing small quantities or customized parts. Material selection and finishing options also differ between the two methods.
In the end, the decision between opting for CNC machining or 3D printing depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the project.
In this article, we’ll go over the basics of CNC machining, the types of CNC machines, the advantages and disadvantages of the manufacturing process, its applications, DIY CNC machining, and what to expect for the future of CNC. But let’s start from the beginning.
A Little Bit of History
The development of CNC machining was driven by the need for precision parts in the aerospace industry in the 1940s. Initially, the machines were manually controlled by skilled operators using punch cards. However, in the 1960s, the advent of minicomputers enabled the development of more sophisticated CNC machines that could be programmed with numerical data.
As CNC machines became more widely adopted in manufacturing, the need for more efficient and accurate programming became apparent. This led to the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software in the 1980s. CAD allowed designers to create 3D models of parts, and CAM software translated the design data into machine instructions. We’ll look at these in more detail next.
The goal of CAD and CAM software was to make the design and production of complex parts more efficient and accurate, reducing the need for manual programming and increasing productivity. The integration of CAD and CAM software with CNC machines revolutionized the manufacturing industry, allowing for the production of parts with higher precision and greater complexity than ever before.
Today, CNC machining is an essential part of modern manufacturing. The technology continues to evolve, with advancements such integrating robotics and automation into CNC machines to further enhance their capabilities.
The Basics
In modern manufacturing, CAD, CAM, and CNC are three essential components that work together to streamline the manufacturing process, from design to production.
- CAD (computer-aided design) software is used to create 2D or 3D digital models of parts or products, and it allows designers to create, modify, and optimize designs quickly and accurately.
- CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) software is used to generate toolpaths and instructions, taking the CAD design and generating a set of commands that the CNC machine can use to produce the part. This set of instructions is called G-code, which is a kind of script that contains information like the coordinates where the machine has to move and at which speed.
- CNC (computer numerical control) is, as mentioned, the manufacturing process that uses computerized controls to operate machinery, such as mills, lathes, and routers. CNC machines use the instructions generated by CAM software to precisely control the movement of cutting tools and produce parts with high accuracy and consistency.
Overall, CAD, CAM, and CNC work together to streamline the manufacturing process, from design to production, resulting in faster, more efficient, and more accurate production of complex parts and products. While CNC machining has the same principle, there are different manufacturing options.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines come in a variety of types, each designed for specific manufacturing applications. Among the most common are:
- Milling machines, which use rotary cutting tools to remove material and create complex parts.
- Lathes, which rotate a workpiece and use cutting tools to create cylindrical or conical shapes.
- Plasma cutters, which use a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through metal plates.
- Waterjet cutters, which use a high-pressure stream of water and abrasive material to cut through various materials.
- Laser cutters and engravers, which use a high-powered laser beam to cut through or engrave various materials.
- Router machines, which use a rotating cutting tool to carve out shapes and designs on wood, plastic, and other materials.
CNC manufacturing clearly has a lot to offer, but it also has some downsides.
Advantages & Disadvantages
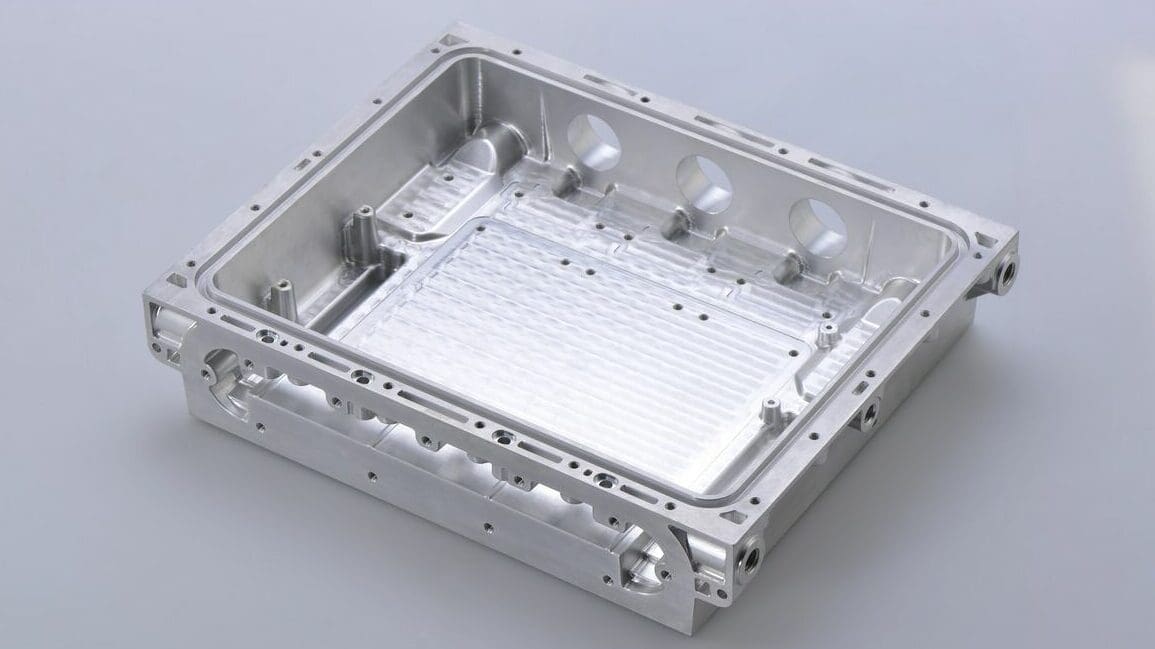

CNC machining has a significant number of advantages to offer over non-computerized or manual manufacturing methods.
It provides high precision, accuracy, consistency, and flexibility. CNC machines can make precise cuts and movements that are difficult or impossible to achieve manually, resulting in parts with a high degree of accuracy. They can also produce identical parts with consistent quality, reducing production time and labor costs. Additionally, CNC machines can produce complex parts with intricate geometries that may be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods, giving manufacturers flexibility in the parts they produce.
Although CNC machining provides many benefits, it also has some significant drawbacks. The machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain. As a rough estimate, small machines can cost up to $2,000, while large production machines can reach up to $300,000 or more. This complexity and cost can make it difficult for small businesses to adopt the technology.
Furthermore, CNC machines require skilled operators, and programming can be time-consuming. Additionally, they can’t always be left operating alone and need regular monitoring, which can also be costly in terms of repair and lost production time. As a result, CNC machining may not be a viable option for some manufacturers, especially those with lower production volumes or limited budgets or staff.
Applications

CNC machining has revolutionized industrial manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex parts with exceptional precision and accuracy. As mentioned, the technology has become integral to many industries.
In aerospace, CNC machining is used to create critical components such as engine parts, landing gear, and wing structures. In the automotive industry, the process is being used to produce engine parts, transmission components, and other crucial elements. The medical field also relies on CNC machining for the production of orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and other devices that require high precision and accuracy.
Beyond industrial applications, CNC machining has also gained popularity among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts. With the availability of more affordable desktop CNC machines, hobbyists can now produce custom parts and prototypes from their own homes. This technology has opened up new possibilities for creativity and craftsmanship, allowing hobbyists to create everything from custom car parts to furniture and musical instruments. The accessibility of CNC technology has also enabled individuals to develop new skills in manufacturing and engineering, providing a stepping stone for those interested in pursuing careers in these fields.
While hobbyist CNC machines may not have the same level of precision and speed as industrial machines, they still offer a cost-effective and accessible way for individuals to engage in CNC machining and bring their ideas to life. Hobbyist CNC machines are also becoming more sophisticated, with features such as automatic tool changers and multi-axis capabilities, bringing them closer in line with their industrial counterparts.
Overall, the increasing popularity of CNC machining among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts demonstrates the broad appeal and versatility of this technology. But how easy (or difficult) is it to build a DIY CNC router?
DIY
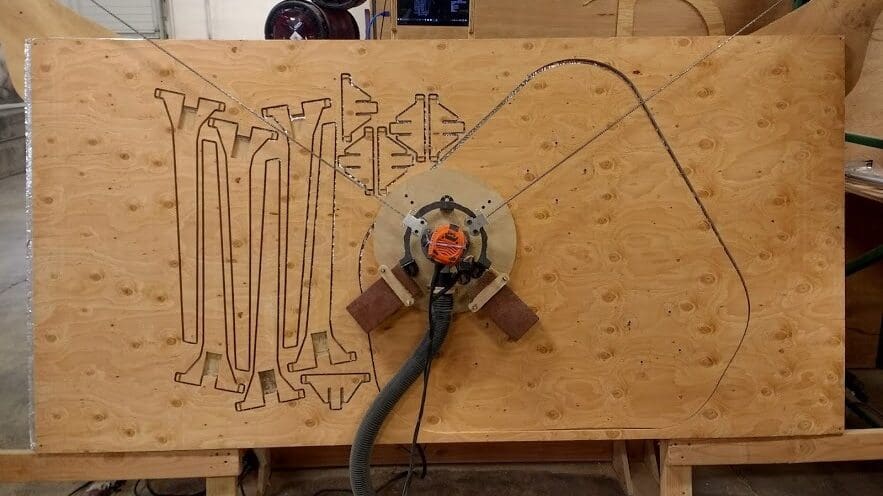
Building a DIY CNC router requires a significant amount of technical knowledge, but there are many resources available online to help guide beginners through the process. A basic DIY CNC router typically consists of a frame, linear bearings, stepper motors, a controller board, a spindle, and a cutting tool. Although building a CNC machine from scratch is a fun endeavor, it can be quite challenging.
Hardware
If you’ve never built a machine, there are several options for DIY CNC router kits and projects available on the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The price range for these kits will vary depending on the machine size and capacity, starting from about $300, and reaching over $5,000. Here are some of the best options:
- Shapeoko: The Shapeoko is a popular DIY CNC router kit that’s known for its ease of use and versatility. It’s available in several sizes and can be upgraded with additional features, such as a laser cutter or a 3D printer.
- Inventables X-Carve: The X-Carve is another popular DIY CNC router kit that comes in a range of sizes with plenty of customization options. It has a strong community of users and offers a variety of upgrades and add-ons, such as a dust collection system.
- Maslow CNC: The Maslow CNC is a unique DIY CNC router kit that uses a hanging router design, allowing it to cut large sheets of material with a relatively small footprint. It’s a more affordable option compared to other kits on the market.
- OpenBuilds: OpenBuilds offers a range of DIY CNC router kits and parts, allowing users to build custom machines to fit their specific needs. The company offers a variety of sizes and designs, including gantry-style routers and desktop machines.
- MillRight CNC: The MillRight CNC is a budget-friendly DIY CNC router kit that’s known for its ease of assembly and use. It’s available in several sizes and can be upgraded with additional features, such as a laser cutter or a rotary axis.
These are just a few of the best DIY CNC router options available on the market. When choosing a DIY CNC router, it’s important to consider factors such as budget, size, complexity, and available features and upgrades.
Software
As you dive into CNC milling, you’ll notice that you’ll need more than one single program to go from a project idea to a finished part. Next, we’ll get to the core of the CAD, CAM, and CNC triad mentioned earlier, although it should be noted that the toolchain will be different from person to person, from project to project, and from machine to machine.
There are several software options available for CNC router programming and operation. Here are some of the best CNC router software options:
- Autodesk’s Fusion 360 is a popular choice for CAD design and CNC router programming, offering 2D and 3D modeling tools, CAM programming, and simulation capabilities. Fusion 360 is very complete software, relatively easy to use, and has a big community providing help for newcomers. It’s paid, but you can have a hobbyist license with some tool restrictions.
- SolidWorks is a powerful software suite that includes tools for 3D modeling, CAM programming, and simulation, making it a versatile choice for CNC router programming. This is paid software often used for professional use.
- Vectric’s Aspire is a comprehensive software package that includes basic tools for 2D and 3D modeling, CAM programming, and toolpath simulation. It’s paid software with a free trial available, and is popular for G-code generation.
- Mach3 is popular software for CNC router operations, as it provides control over CNC routers using G-code and offers features such as toolpath simulation and optimization. If you’re building a router, this could be a serious contender for machine control, and it’s also widely used in makerspaces.
- LinuxCNC is free, open-source software used for CNC machine control. It offers real-time motion control and supports a variety of different machines and configurations.
- Easel Pro, from Inventables, who make the X-Carve machine, offers intuitive 2D and 3D design tools, CAM programming, and machine control capabilities. Easel Pro also offers features such as material probing and machine analytics to optimize CNC carving workflows. It’s paid software with a free trial available.
These are just a few of the best CNC router software options available on the market. When choosing CNC router software, it’s important to consider factors such as compatibility with your router, your level of experience, and the specific features and tools you need for your projects.
Final Thoughts & the Future

CNC machining has revolutionized many industries and has become an essential technology for manufacturing complex and precise parts. One of its biggest advantages is the ability to create functional prototypes and test them before moving into full-scale production, which has drastically improved the design process and reduced time-to-market.
Looking toward the future of CNC machining, we can expect to see several exciting developments. One of the main trends is automation, where machines are becoming more autonomous and can perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention. This trend is being fueled by advancements in automation technologies, including robotics and artificial intelligence.
Another trend is the integration of CNC machining with other technologies such as AI, IoT, and big data analytics. This integration allows for more efficient and optimized manufacturing processes, reducing costs, and improving quality.
While 3D printing and CNC machining are often seen as competing technologies, we can expect to see increased use of 3D printing in conjunction with CNC machining. This combination allows for 3D printing to create complex prototypes or molds that are then finished with CNC machining.
In the future, we can also expect to see CNC machines becoming smaller and more portable, allowing for CNC machining to be done in a wider range of environments. This trend toward miniaturization will also allow for greater customization and personalization of products, meeting the growing demand for tailored and unique items.
Overall, the future of CNC machining is bright, with continued advancements in technology and increased demand for precision manufacturing driving innovation and growth in different industries.
License: The text of "The Basics of CNC Machining – Simply Explained" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.