2D CAD is a method of computer-aided design (CAD) that consists of drawing the projected views of a 3D object without requiring a 3D model of it. This is different from 3D CAD, where you create a 3D model.
One example of where 2D CAD is useful is in generating models for CNC machining, as you only need the top view of the model you want to machine. Likewise, in architectural applications, modeling a whole room including doors, windows, furniture, and all necessary elements would be counterproductive when you can simply create a top-view drawing that uses symbols to indicate locations and dimensions.
In fields like mechanical engineering, design, and architecture, having knowledge of 2D CAD is expected. 2D CAD software usually offers drawing tools, default symbols for annotations, certain objects, different line types, and dimensions to simplify the process of creating a technical drawing.
In this article, we’ll go over some of the best 2D CAD tools around. But first, let’s look at how we put together the list and what makes good 2D CAD software.
Considerations
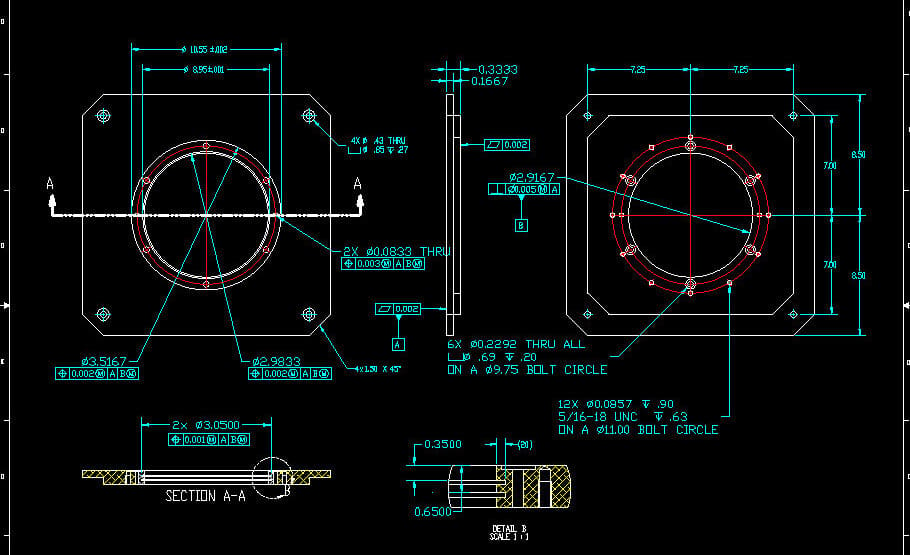
To select the best options, we took into account reviews, forums, and user experience to know which software the community recommends. We also gave weight to the following considerations:
- Pricing: We’ve selected options that range from free all the way up to professionally focused programs, so there should be something here for everyone’s budget and intended use.
- Range of features: All the programs on this list include the full basic 2D CAD suite of tools in their standard version, although some also offer upgraded versions with expanded functions.
- Compatibility: Many 2D CAD programs work under the same principle, and have similar UI, shortcuts, and so on. This makes it more convenient for a user to switch from one tool to another. As such, an intuitive UX and compatibility with a good range of file formats are some big advantages we took into account.
So, now that we know what we’re in for, let’s see the software!
AutoCAD

AutoCAD was developed by Autodesk and is the most well-known 2D CAD program. Wherever you ask for a CAD recommendation, this will be the first option suggested. It’s considered an industry standard in mechanical design and architecture.
Its features are centered on 2D drawing and isometric drawing. Working with AutoCAD is notorious because it’s based on commands. This means you can use the program by just typing instructions without ever using a mouse, or you can use a combined workflow where you rely on the mouse to supplement commands. Fortunately, AutoCAD has autofill suggestions for the commands, so you don’t have to completely memorize them.
Even though there are many pricing options, the main disadvantage that keeps people from AutoCAD is its elevated price. This makes it inaccessible for many to do independent work with it unless they’re affiliated with a company. For some, AutoCAD LT might be the more suitable program.
One of the advantages of having a paid subscription to either AutoCAD or AutoCAD LT is access to AutoCAD Web. It’s a lightweight browser-based version of AutoCAD that can be accessed from anywhere. Besides the collaborative feedback and sharing features, it’s possible to create and edit basic designs. For those without a subscription to the fuller versions of the software, it’s possible to get the web version for as low as $10 a month.
- Main features: Work by layers, isometric drawing, command-based operations
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS
- Focus: Mechanical and electrical engineering, architecture
- Pricing options: Free 7-day trial, subscription plans start at~$245/month, academic licenses available
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is free, open-source 3D CAD software. It’s popular among freelancers because of its accessible price and wide range of features. Although FreeCAD is a 3D modeling tool in essence, 2D modeling is also possible. The software’s tools and functions are organized into many different workbenches, which are default layouts to suit the kind of work you’re going to do. One of these workbenches is the Draft workbench, where you can do traditional 2D CAD drawings (without first requiring a 3D model).
FreeCAD runs on Windows, Linux, and MacOS. Its files are compatible with all platforms, which is an advantage when working collaboratively, as having the same OS can be hard to guarantee. FreeCAD can become unstable with big projects, though, and it doesn’t have an architecture library of symbols as it’s not its area of focus.
- Main features: Essential 2D editing and drafting tools in a free program; personalization of the grid
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS, Linux
- Focus: Mechanical design
- Pricing options: Free
- Where to get it: FreeCAD
NanoCAD
NanoCAD is highly recommended in many different 2D CAD communities. The main disadvantage seems to be that it only runs on Windows, so it’s not accessible for you if you have a Mac. It’s also harder to work in teams if everyone doesn’t have the same OS.
That said, NanoCAD is a powerful and stable 2D CAD program, which makes it a great option for highly complex mechanical modeling – from small-scale personal projects to industry-scale applications like power plants. It allows for layout customization to display multiple viewports, which can be useful when working on large projects.
It’s usually compared to AutoCAD due to their similar interfaces, and both programs have stable and durable builds. Similar to AutoCAD, it works by layers, with fully constrained lines, patterns, hatching, and more. In customer stories available on the NanoCAD site, users mention that they made the switch from AutoCAD because NanoCAD was a much more affordable option.
According to reviews, NanoCAD isn’t hard to learn. It’s pretty much the same as other 2D CAD software, so the switch is seamless. The only issues are some occasional bugs that need to be fixed.
There are many versions of NanoCAD you can download, including a free legacy version. On the paid side, there’s the base NanoCAD platform, plus additional modules including 3D Solid Modeling, Mechanica, which focuses on 2D and 3D mechanical modeling, and Construction, which is geared for construction engineers and AEC processes, among a few others.
- Main features: Command-based UI, file format compatibility across software, parametric modeling based on Excel-like tables to organize data and formulas
- Operating systems: Windows
- Focus: Mechanical design, architecture, electronics
- Pricing options: Free trial available, ~$250/year for the basic software, plus ~$200/year for each additional module
- Where to get it: NanoCAD
LibreCAD
LibreCAD is another great option that’s free and open source. It’s highly recommended by the CAD community for many reasons. For starters, LibreCAD is compatible with AutoCAD. Not only can it read DWG files generated with AutoCAD, but it will also keep and correctly translate the lines and blocks, dimensions, hatches, and so on. For this reason, people recommend it if you have access to AutoCAD on university computers or workplace computers but not at home.
Additionally, LibreCAD has CAM capabilities included for free in the full program. So, you can not only design projects but also set them up for manufacturing, too.
However, it’s important to note that, according to reviews, LibreCAD can have a bit of a steeper learning curve due to the symbology used, which is different from the standard CAD symbols, so it may take a bit of practice. Reviews also mention that with heavy drawings, the program can become slow. However, ratings remain relatively high, around 4/5.
- Main features: CAM tools, DWG import and export, working in layers, contour vectorization
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS, Linux
- Focus: Mechanical design, CNC
- Pricing options: Free
- Where to get it: LibreCAD
Solid Edge
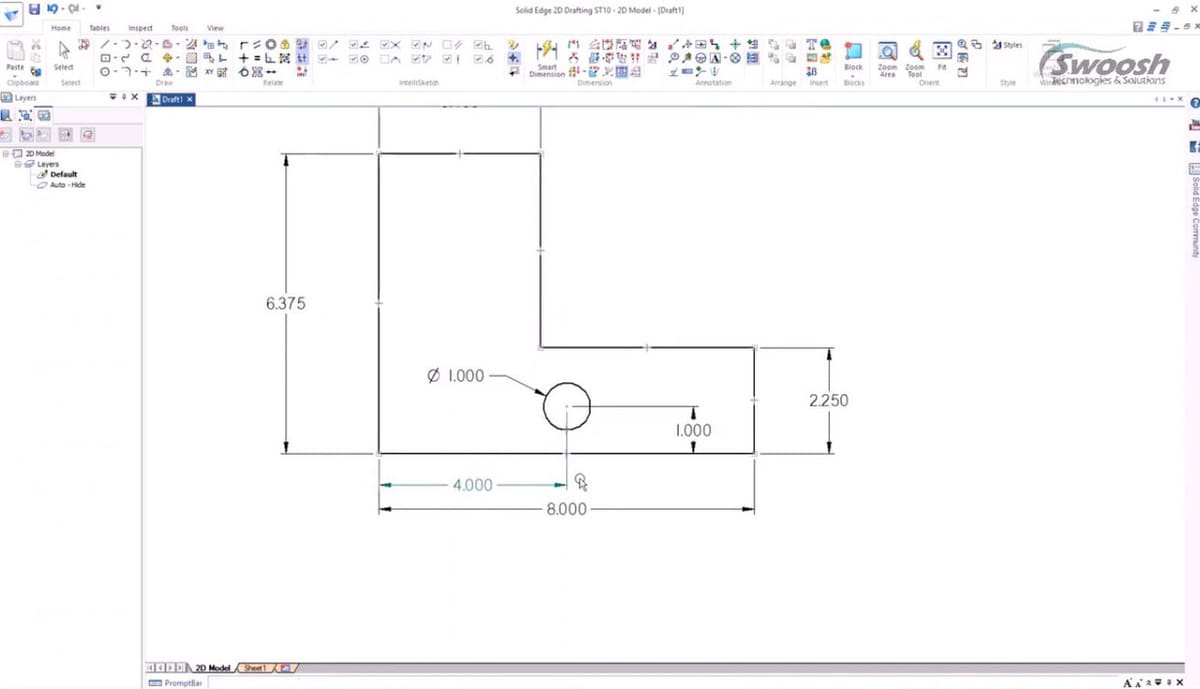
Solid Edge is CAD software developed by Siemens, a German company that’s just about everywhere in the engineering world. The company develops energy solutions, control hardware, and a variety of software tools, including modeling software. Even though Solid Edge is fundamentally a 3D modeling tool, it has many functions suitable for 2D CAD, including mechanical and electrical 2D drawing tools as well as FEA simulation.
Solid Edge is considered a good option for small businesses and freelancers, as it has a 30-day free trial, or if you have a startup company or project, you can also apply for a free license.
As for pricing, it’s largely dependent on the tools you’ll need to use. The 2D drafting package is free, but this can only offer basic CAD drawing, annotation, and editing tools. For additional functionality like CAM or 2D nesting, you’ll have to contact the sales group for pricing.
- Main features: Sketch to model, parametric modeling, assemblies, fully constrained drawing
- Operating system: Windows
- Focus: Mechanical and electrical design
- Pricing options: Free for 2D drafting, starting at ~$85/month for basic 3D CAD packages, special free license for startups
- Where to get it: Solid Edge
QCAD
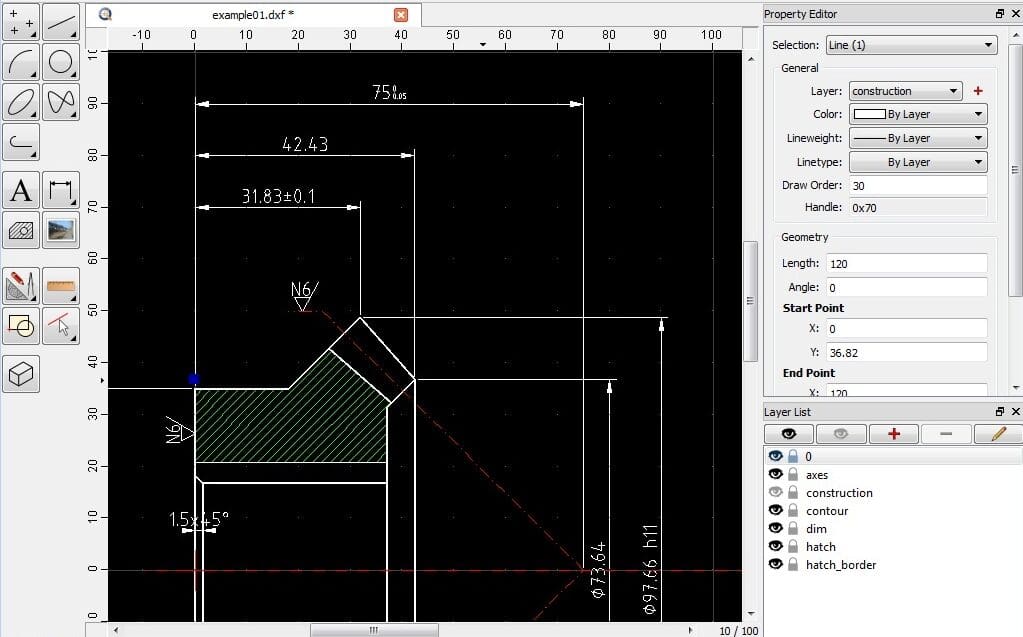
QCAD is great 2D CAD software that’s highly recommended by the community. It’s also based on commands, similar to AutoCAD. However, it’s worth mentioning that if you’re coming from AutoCAD, the learning curve can be a bit steep as the commands used are all different. So, you won’t be able to use your prior knowledge.
QCAD is mainly focused on mechanical design, and it has DWG and DXF input and output. An attractive advantage is that, contrary to AutoCAD, it has modification tools. In AutoCAD, a line is fully constrained from creation, and if you need to modify it, you either use tools to rotate and scale or remove the line and create it again. QCAD, on the other hand, can rely on dimensions and other modification tools to alter an existing drawing.
QCAD can also export G-code for CAM, but the CAM toolset is rather simple, focusing on the path – not so much tool used – and other properties. Reviews are solid with a 4.3/5 on G2. The main disadvantage people mention is the steep learning curve. You might want to look into some training before starting out with QCAD, as it’s not easy to just understand on your own.
- Main features: Working in command blocks, saving formats and templates, exporting G-code, many different printing tools
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS, Linux
- Focus: Mechanical design
- Pricing options: Free limited version, ~$40 perpetual license
- Where to get it: QCAD
DraftSight

DraftSight is software developed by Dassault Systèmes, a French company known for SolidWorks. SolidWorks is 3D modeling software, and though it has some drafting features that let you generate a 2D blueprint from a 3D model, it’s not intended for directly doing 2D drafting.
Instead, DraftSight is a 2D CAD software solution that offers many applications like architectural or mechanical 2D drawing. In regards to architecture, it has design tools for both designing the interior and façade of buildings.
Reviews are generally good with a rating of 4/5 on G2. The feedback tends to focus on making some tools more efficient, especially in regards to exporting PDF blueprints and setting up formats.
If you’re coming across from other CAD software, this is a good transitional program because it uses common and compatible commands and symbols, specifically those from AutoCAD. DraftSight even offers a transitioning guide.
You can download a 30-day free trial, after which the full product has an annual price of ~$250. Alternatively, you can buy the premium edition, which also has 3D modeling tools for ~$550 annually. However, if you’re upgrading to access 3D modeling, SolidWorks would be a much more complete option.
- Main features: Seemless compatibility with other professional design software, version comparison tools, batch printing blueprint pages, G-code generation, macros and scripting capabilities
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS
- Focus: Mechanical design
- Pricing options: Free 30-day trial, subscriptions starting at ~$250/year for DraftSight Professional
- Where to get it: DraftSight
Ares Commander
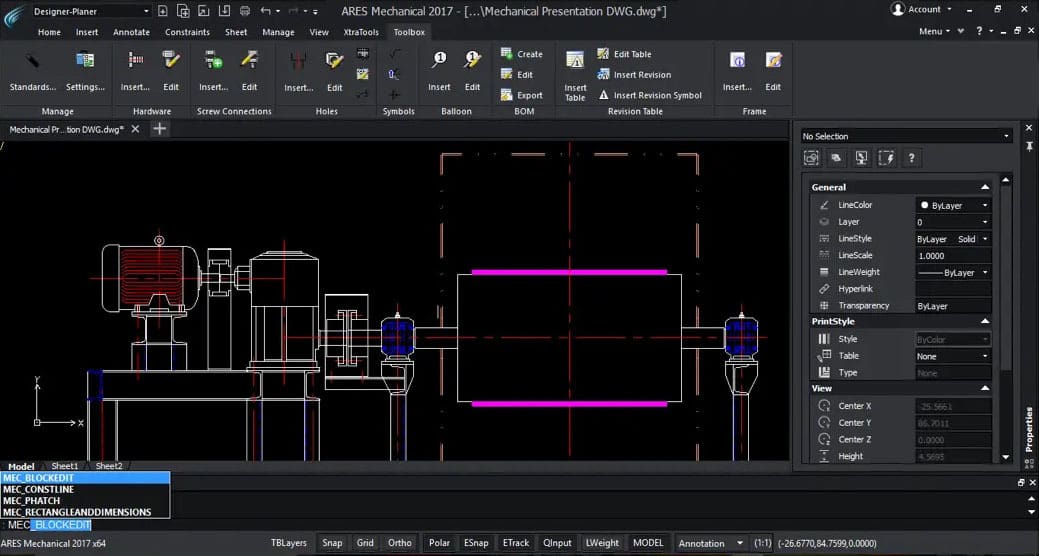
Ares Commander is a 2D and 3D CAD program developed by Gräbert (often written as Graebert), a German company that develops design software solutions in many fields. Even though it’s not as well known, it’s recommended by the community because it provides drawings in high quality and has a functionality reach similar to AutoCAD at a more affordable price point.
Users give Ares Commander a perfect score, with every review we’ve seen rating it 5/5. It runs on Windows, MacOS, and Linux, which is an advantage over other software presented on this list, and Gräbert works with a cloud system, so you can do collaborative design with Ares Commander.
The main pricing options are to buy a yearly license or a perpetual license for ~$1,300, although it’s possible to buy the program bundled with other Gräbert software for different pricing deals based on subscription plans.
- Main features: Version comparison tools, custom blocks and parametric settings, DWG as native working file type
- Operating systems: Windows, MacOS, Linux
- Focus: Mechanical and civil engineering
- Pricing options: Packages starting at ~$450/year with Trinity, ~$1,300 for perpetual license
- Where to get it: Ares Commander
BricsCAD

BricsCAD is software that can be used for 2D and 3D modeling. Even though it has tools for both mechanical and architectural applications capable of showing amazing results, the main focus is 2D architecture drafting. Aside from traditional architecture, it plays a role in the engineering world in the design of production plants, thermic systems, and similar – often combining 2D and 3D features.
A notable use case is when BricsCAD was used in the renovation design of a Mazda manufacturing facility, an impressive example that showcases perfectly its capabilities for professional applications. Reviews remark that although it has many support channels, they’re not always the most effective, and it’s not the most compatible software to use alongside other third-party programs. The software has different pricing options, including the choice between a perpetual license or an annual subscription.
- Main features: Working with layers and organizing blocks of design in hierarchies, hover menus called “Quad Cursor” similar to Blender’s Pie menus
- Operating systems: Windows, Linux
- Focus: Architecture, design of industrial plants
- Pricing options: Free 30-day trial, ~$315/year or ~$700 perpetual license for BricsCAD Lite, full version starts from ~$710/year or ~$1,600 perpetual license
- Where to get it: BricsCAD
SketchUp
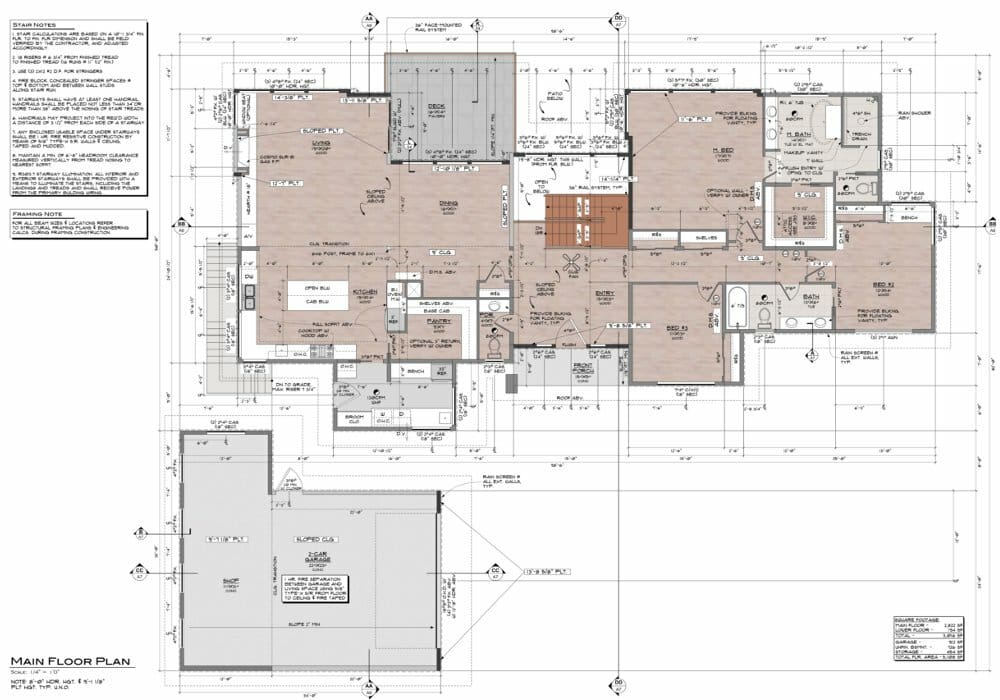
SketchUp is an intuitive 3D modeling program for architecture. Its main focus is allowing users the artistic freedom to create architectural designs, without worrying too much at first about measurements and dimensions. However, SketchUp also has a 2D drafting suite that’s recommended by the community specifically for architectural work.
You can draw directly in 2D and go back and forth between 2D and 3D views very smoothly. It runs on Windows, MacOS, and iPad OS. As for the pricing, many previous versions are free, and it’s possible to get them online. If you’re looking for the most recent versions, there are three options: a free limited browser-based version, a full “Pro” desktop version for around $350/year, or a full web “Go” version for less than half the price. If you’re a student, you can also apply for a discounted version of the full desktop option and pay only ~$55/year.
- Main features: 2D layout view, object and material library, 2D to 3D mode
- Operating systems: Windows, Mac, iPad
- Focus: Architecture
- Pricing options: Free limited web version, ~$120/year web app, starting at ~$350/year for desktop app, discounts for students
- Where to get it: SketchUp
License: The text of "The Best 2D CAD Software (Some Are Free)" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
CERTAIN CONTENT THAT APPEARS ON THIS SITE COMES FROM AMAZON. THIS CONTENT IS PROVIDED ‘AS IS’ AND IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE OR REMOVAL AT ANY TIME.



