If you’re a student or young adult looking to gain experience in tools that will come in handy later in your educational path or career, you’ve come to the right place. There are so many CAD programs out there, and getting the hang of any one of them will take time and dedication, so it’s important to pick one that’ll be aligned with your goals.
The concept of CAD (computer-aided design) can be applied to a wide range of tools and software that are fundamental to many industries. But before you feel lost with so many available options and technical terms, take a deep breath! This article will help you sort through the maze of software and navigate your way to success.
Let’s explore this special list of the best CAD options for students, chosen not only for their design capabilities but also for access to student discounts and dominant presence in educational institutions and the job market. So, get ready for a journey that goes beyond classrooms and laboratories, directly into the beating heart of creativity and innovation!
About CAD
By using CAD, designers and engineers can create accurate, detailed models of products, buildings, machines, and more. They may start, for example, by drawing basic geometries, such as lines, circles, and rectangles, and then apply operations such as extrusion, revolution, and interpolation to transform these basic shapes into complex, three-dimensional objects that can be viewed from any angle.
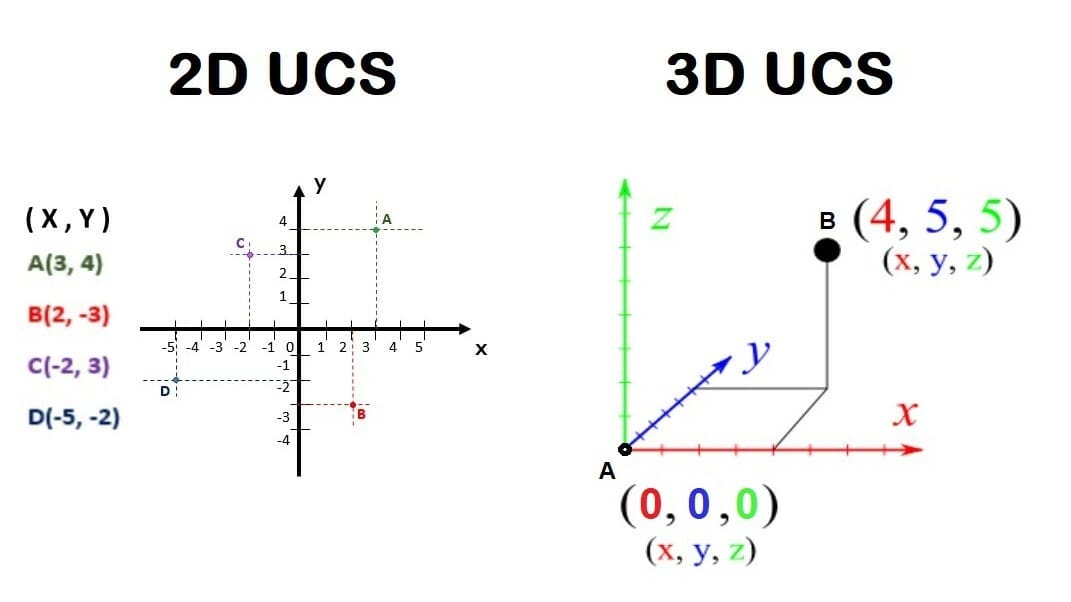
The UCS (user coordinate system) is a universal and fundamental concept in CAD software. It’s a three-dimensional grid that allows users to orient themselves and the position and size of objects in virtual space defined by numerical coordinate values on orthogonal axes called X, Y, and Z. It’s essential to get familiar with working in this space, as it’s universal and applies to any option you’ll encounter out there.
As you delve deeper into the world of CAD, you’ll encounter various approaches to modeling and drawing, each with its unique advantages and applications. Let’s explore some of the most common types utilized in CAD software
Main Types of Modeling and Drawing
- Parametric modeling is based on constraints and relationships between elements. Changes to one parameter automatically affect other model elements. It’s useful for projects that require flexibility and frequent updates.
- Direct modeling allows users to directly manipulate elements, as if sculpting. It’s intuitive and useful for projects that require creative freedom and quick iterations.
- Surface modeling focuses on creating and manipulating surfaces, rather than solids. It’s used for designing products with complex shapes, such as cars and consumer products.
- Solid 3D modeling is used to create solid models with volume. It’s useful for engineering and designing parts that need to be physically manufactured with many traditional methods.
- Point cloud-based modeling uses point cloud data, generally obtained by 3D scanning, to create models. It’s used in reverse engineering, architecture, and the creation of custom parts.
Common Acronyms
In the world of CAD, many technical acronyms will come up. Here’s a list of important and common acronyms that you may come across:
- CAM: Computer-Aided Manufacturing
- CAE: Computer-Aided Engineering
- PDM: Product Data Management
- PLM: Product Lifecycle Management
- BIM: Building Information Modeling
- FEA: Finite Element Analysis
- DFM: Design for Manufacturing
- EDA: Electronic Design Automation
- PCB: Printed Circuit Board
- MBD: Model-Based Definition
- BOM: Bill of Materials
- CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics
- CNC: Computer Numerical Control
- PMI: Product and Manufacturing Information
Considerations
CAD has revolutionized the way projects are conceived and executed in a wide variety of industries and disciplines. Before CAD, designers relied on time-consuming and error-prone manual methods to create their designs. CAD of today not only saves time and money but is often integrated with other simulation and analysis tools, allowing designers to predict and optimize the performance of their designs under simulated real-world conditions.
While those features sound neat, their complexity can hike up the cost of CAD programs, be more demanding on your computer, and require much more time to get familiar with. With that in mind, there are three more important things to consider before we get into the list of the best CAD programs.
Limitations of Educational Versions
Keep in mind that the free and student versions may have major limitations in features and characteristics when compared to the commercial versions. Most of the time, student versions will cover the main design features that you will need to go quite far in CAD, but not all the way to an expert user.
In this article, we cover the features found in the commercial versions so that you can get a sense of the capabilities of each software while also highlighting the restrictions of the educational version, when available. You should also be aware that educational software is restricted to specific users and may require proof of age or academic registration, among others.
Computer Requirements
Just as important as understanding where you want to go is understanding what you will need for your journey. It’s common to underestimate the importance of your computer’s GPU and only consider the CPU and RAM, but for complex 3D geometries and simulations, a dedicated graphics card is essential.
Therefore, it’s best to choose a computer that meets the professional demands of CAD. Keep in mind that computers good for games will not necessarily be good for CAD programs as well.
Patience is Needed
Mastering CAD is like stepping into a realm where creativity meets precision, where every pixel and measurement holds significance. As a student delving into CAD, embrace the learning process with curiosity and resilience. Allow yourself to make mistakes, as they’re essential to the learning curve.
While it may seem daunting at first, every line drawn, and every shape created contributes to a deeper understanding and mastery of this indispensable tool. Through trial and error, you’ll discover new techniques, shortcuts, and approaches that will enhance your skills. Remember that CAD isn’t just about mastering software; it’s about refining your problem-solving abilities, fostering creativity, and ultimately shaping the future through innovation and ingenuity.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a program from the French giant Dassault Systèmes and has been a leading CAD software since it came to market in 1995. It’s used in several major industries and universities in more than 140 countries. According to reviews, many users of SolidWorks are in small and medium-sized businesses in the fields of mechanical engineering, industrial design, and product simulation. Skills learned in SolidWorks translate well to Catia, also from Dassault Systèmes, which is the next step up, covering large industries such as naval, aerospace, and automotive.
One of the reasons SolidWorks (and Catia) is such a popular option in industry is the PDM (product data management) functionality that allows multiple users to collaborate on the same document simultaneously. This is very useful for geographically distributed teams and for versioning, change tracking, and setting access permissions to ensure data integrity.
Besides being one of the most widely used options on the market, SolidWorks stands out as a flexible choice that caters to a wide range of professionals across different technical fields through specific versions and modules.
Purchase options for students include a discounted desktop application and a more limited web-based version. When a part of an educational institution, students can gain access to various other resources such as dedicated support and learning materials. It’s also possible to get certified in various aspects of the software, which is great for applications and resumes. Dassault includes software tutorials, eCourses, and certification preparation courses in academic licenses to help set you up for success.
- Platform: Windows
- Main Features: CAM, CAE, PDM, FEA, BOM, CFD, motion simulation, rendering, virtual reality visualization, stress analysis, frequency analysis, and more
- Price: $60 per year for browser-based apps (limited), $99 per year for Student Edition desktop software
Creo
Creo, produced by PTC, entered the market in 2010 to serve industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, mechanical engineering, product design, and more. Renowned for its robustness and advanced modeling capabilities, Creo stands out for its extensive user base, comprising companies of various sizes and sectors worldwide. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for simulation and analysis, including PLM and FEA, that are essential for optimizing design performance, especially in safety-critical sectors like automotive and aerospace.
Creo also offers hybrid modeling to complement its model-based definition (MBD) approach, combining direct and parametric features for cutting-edge 3D design capabilities. Alongside the core design program, extensions for additive manufacturing, generative design, and IoT integration expand its scope significantly.
There are a few different options for students to get a free or discounted version of Creo. For the younger students, PTC provides “Creo K12” for primary and secondary education for free with yearly renewable possible. University students can access the Student version of the software for free (with proof of enrollment) or purchase the heavily discounted “Creo 10 University Student Edition” to gain access to advanced features. Moreover, PTC also offers a free version of their browser-based CAD program “Onshape” to students (we’ll see more about that later).
More comprehensive licenses may be provided directly from academic institutions, but the Student version is sufficient for many purposes, lacking only more advanced manufacturing features, for example, and using a “lite” version of simulation tools. Creo is available in many languages, including German, English, French, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, and Chinese (simplified).
- Platform: Windows
- Main Features: CAM, CAE, PDM, FEA, BOM, CFD, IoT, AR, motion simulation, parametric modeling, generative design, heat flow analysis, and more
- Price: Free University Student Edition (limited), ~$220 per year for University Student Edition Premium license
SketchUp
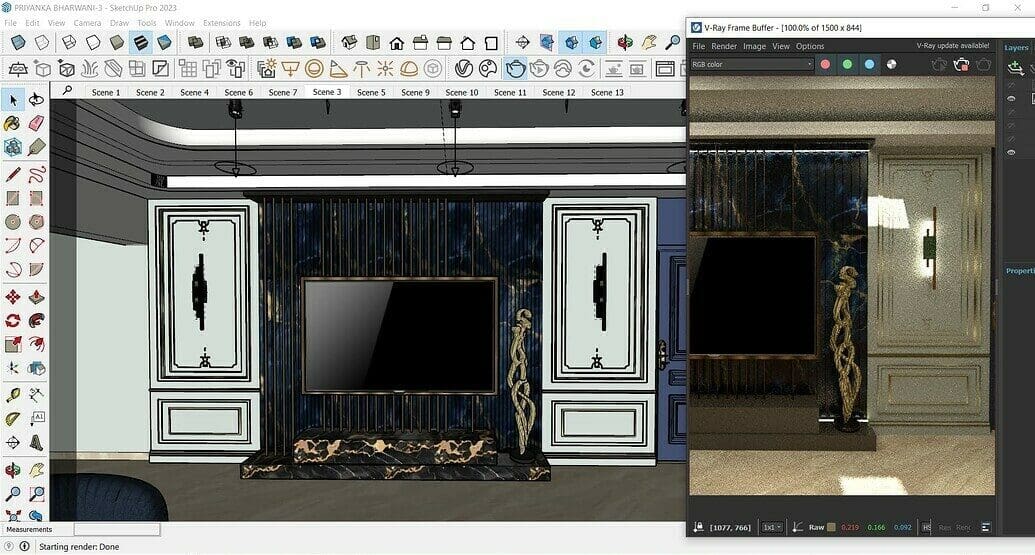
The darling of architects, SketchUp was created in 1999 by Brad Schell and Joe Esch as a tool to lessen the 3D modeling learning curve for architects and designers. After changing hands a couple of times, a free version, called Google SketchUp 6, was made available to the public, which led to a massive boost in popularity. With its user-friendly interface and robust CAD capabilities, SketchUp has become a popular choice not only for architects but also for interior designers, landscapers, engineers, and many other professionals looking for a versatile and easy-to-use tool to create renderings of structures and scenes.
A primary factor in its success, aside from making a free version of the software publically available, is the large, collaborative community that formed around SketchUp. Users could share free templates, textures, and custom plug-ins, as well as participate in discussion forums and online tutorials. This created a very active learning and support environment where users could directly exchange practical knowledge and improve their SketchUp skills at their own pace.
Today, resources and repositories for models in SketchUp are as active as ever, with popular ones including SketchUcation and SketchupCgtips, where ready-made, high-quality templates make designers’ lives easier. There’s also the 3D Warehouse, hosted by SketchUp and included with a paid subscription, that houses over five million 3D models that can be directly imported into your scene. SketchUp is always expanding its capabilities, with advanced features like animations, virtual reality, and even resources aimed at 3D printing becoming available in recent years.
As a prospective student looking at paths in civil engineering, architecture, or landscape planning, SkechUp is the perfect entry point to the kinds of software used in industry, and with all of the available online resources, self-paced learning is at your fingertips. Users still have the option to use the free, browser-based application to get started, but the complete desktop application is much more capable and heavily discounted for students. It’s also worth checking out the 14 free courses from SketchUp Campus on how to get the most out of the software.
- Platform: Windows, Mac, browser
- Main Features: BIM, VR, rendering, animation, face-based modeling, direct modeling, and more
- Price: $55 per year for higher education students, browser-based version always free (limited)
Fusion
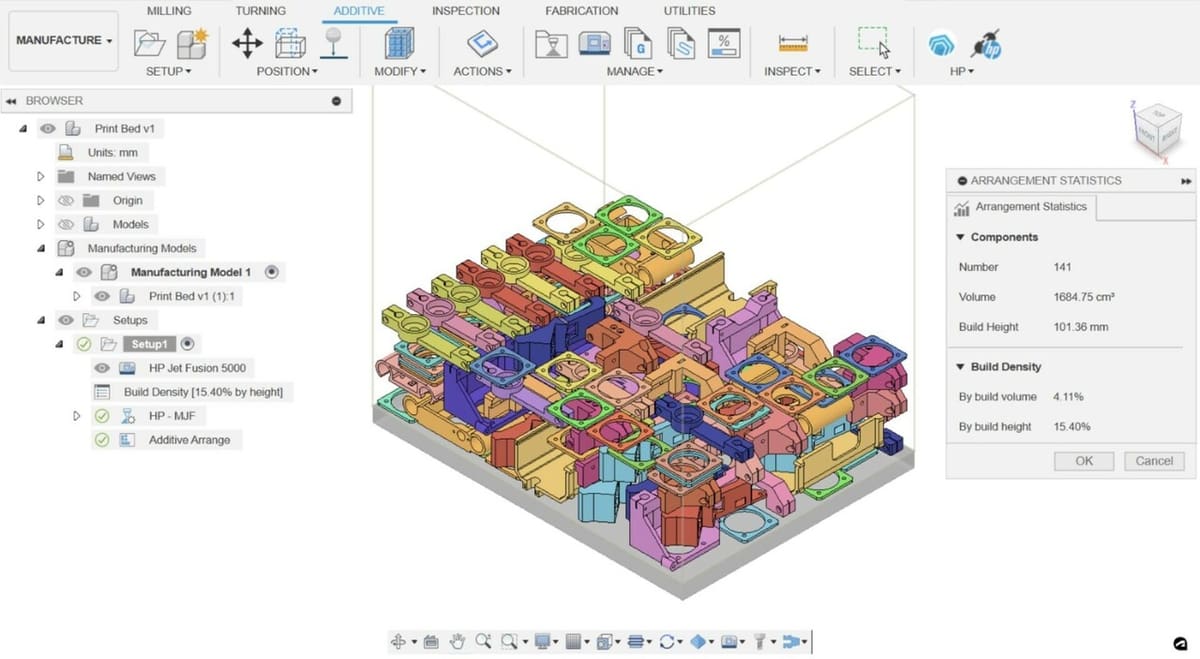
Fusion (previously Fusion 360) is a CAD/CAM/CAE platform from Autodesk that encompasses product design, mechanical engineering, and digital manufacturing and features powerful tools, including simulations and cloud collaboration. Autodesk can be considered a pioneer of CAD software, launching AutoCAD in the 1980s and revolutionizing the industry by providing accessible solutions for designers and engineers. Over the years, Autodesk expanded its offerings, with the launch of Fusion in 2013 making a big splash in the product design and manufacturing industries, especially for small- and medium-sized businesses.
Fusion integrates parametric 3D modeling, simulation, manufacturing, data management, and collaboration within a single cloud-based platform. It’s often a favorite for CNC machining, but its capabilities extend even to PCB manufacturing and generative design. Fusion continues to evolve, incorporating features from other Autodesk software, like Autodesk 123D and Autodesk Meshmixer, further enhancing its capabilities.
Autodesk uses subscription plans for its software licenses. The complete software, without limitations, is available for free to students with proof of enrollment. Do note, however, that students must be 13 years of age or older and that the software must be used exclusively for learning purposes.
Users can also get certified in Fusion, which is great to showcase on an application or resume. To get started with the software or to prepare for the certification exam, Autodesk has lots of resources and courses avalible for free.
- Platform: Windows, Mac
- Main Features: CAM, CAE, PCB, BOM, FEA, structural simulation, fluid dynamics simulation, collaborative product design, additive manufacturing, and more
- Price: Free for registered students
Solid Edge
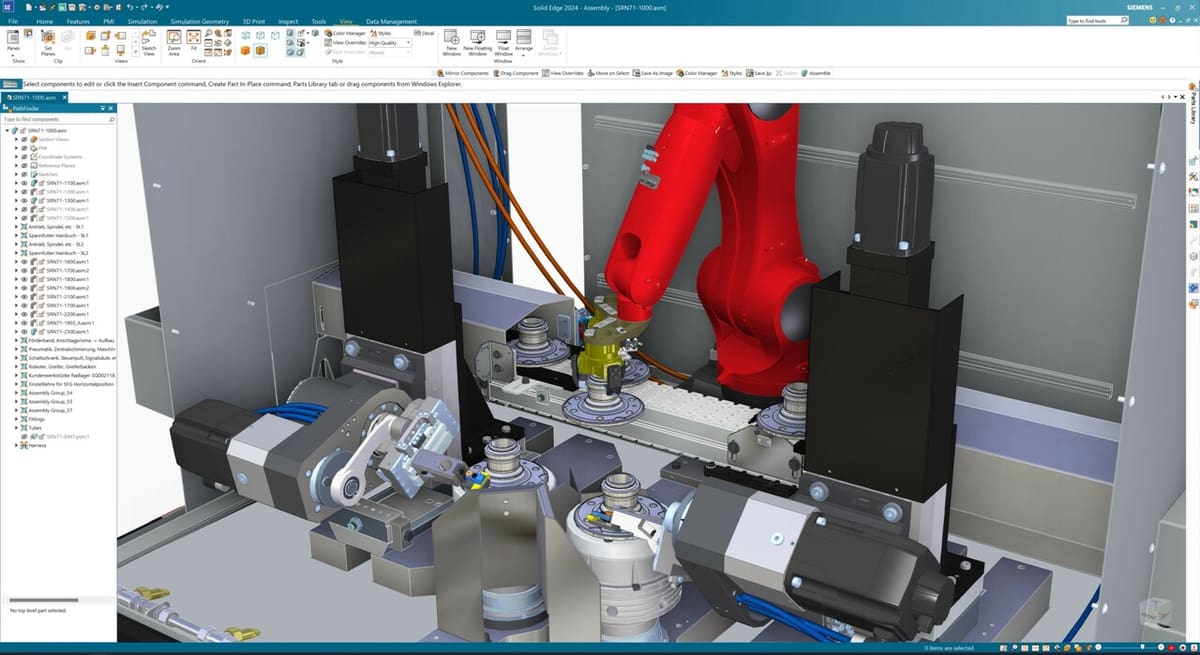
Solid Edge, owned by Siemens, is a significant player in the CAD market, dating back to its official release in 1995. Known for its user-friendly interface and widespread use in product design, Solid Edge also features tools for industrial manufacturing, simulation, and more. It can also be considered a little sister to Siemen’s other CAD offering, NX, which offers advanced capabilities, especially in specialized industries such as automotive and aerospace. These two programs have seamless interoperability, allowing the same project to be easily shared between them.
Although Solid Edge and NX differ in their complexity, they also share important similarities. One of them is Synchronous modeling, which combines the speed and simplicity of direct modeling with the flexibility and control of parametric design. This approach creates a workflow that allows changes to be made without time-consuming adjustments, in addition to maintaining a history of changes. They also both offer great PLM resources, which is invaluable when working on collaborative projects in school or on the job. The 2024 version of Solid Edge brings even more features for productivity, including incorporating AI to speed up repetitive tasks.
When it comes to students, there’s a student version of Solid Edge that is free to download with proof of enrollment and is nearly identical to the one used professionally. The only difference is that the files generated in the student version cannot be opened in the professional version and 2D drawings get watermarked. Siemens also makes Solid Edge CAM Pro Student Edition available free of charge, which has a heavier focus on numerical control (NC) programming and other manufacturing processes.
Siemens also hosts a specific community for academia, the Xcelerator Academy, where you will find free and paid learning materials that cover everything from basic techniques like sketching, to advanced topics like sheet metal, generative design, and STEM projects. It’s also worth noting the involvement of Siemens in STEM-based extracurriculars such as First Robotics, Greenpower, and Solar Car Challenge. To conclude and satisfy your curiosity, yes there is a free version of Siemens NX for students as well.
- Platform: Windows
- Main Features: CAM, CAE, PDM, FEA, BOM, CFD, PMI, IoT, thermal simulation, Synchronous modeling, sheet metal stress analysis, and more
- Price: Free for registered students
Honorable Mentions
Now that you’ve learned about the best CAD software options for students, keep in mind that there are many others out there that can help get you familiar with CAD software and develop skills that translate to real-world applications.
Next, we’ll take a quick look at options that stood out due to their industry relevance or simply for being a powerful free tool with solid resources that can help save you time and money while on your academic journey.
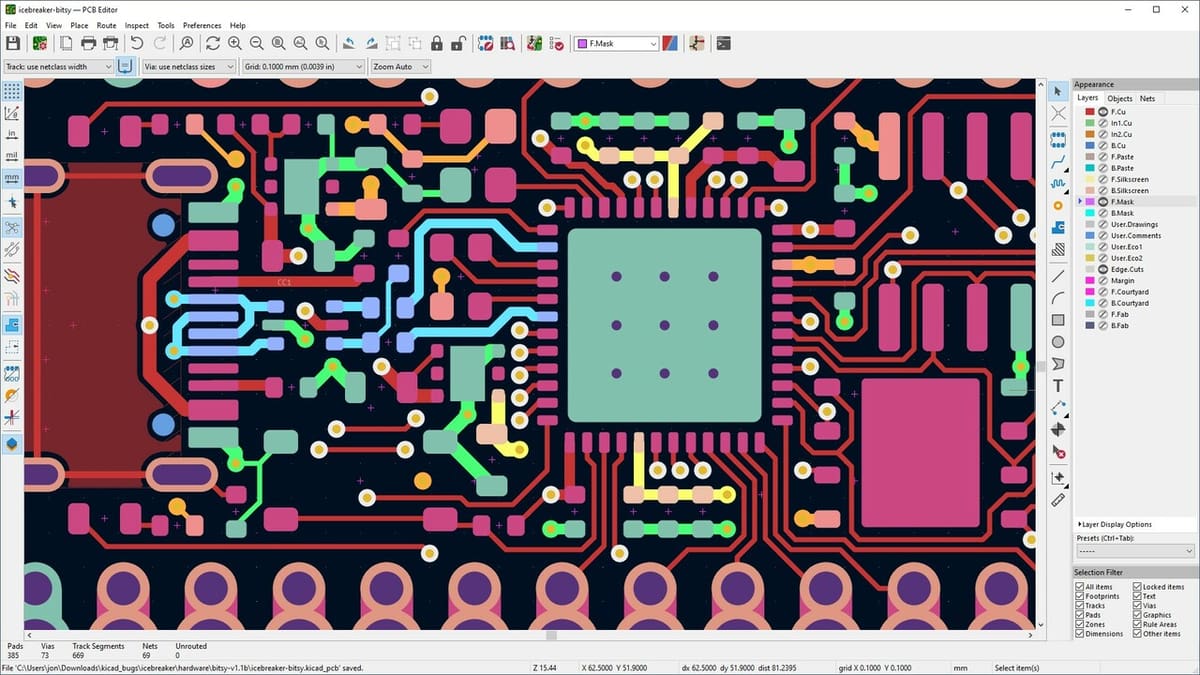
KiCad
KiCad is an open-source CAD software solution for electronic circuit design. Created in 1992 by Jean-Pierre Charras, KiCad has been a popular choice among students, hobbyists, and electronics professionals due to its versatile toolset and lack of a price barrier. In a world that’s becoming increasingly automated, this option is a game changer for electrical engineering students.
KiCad offers a wide range of features for designing printed circuit boards (PCBs), including schematics, PCB layout, track routing, impedance analysis, and more. For students, one of the most notable features is the integration with circuit simulation tools that allow for the testing of designs before purchasing components. KiCad’s active and collaborative community is not to be overlooked as they contribute to its continuous development and provides additional support and resources to users.
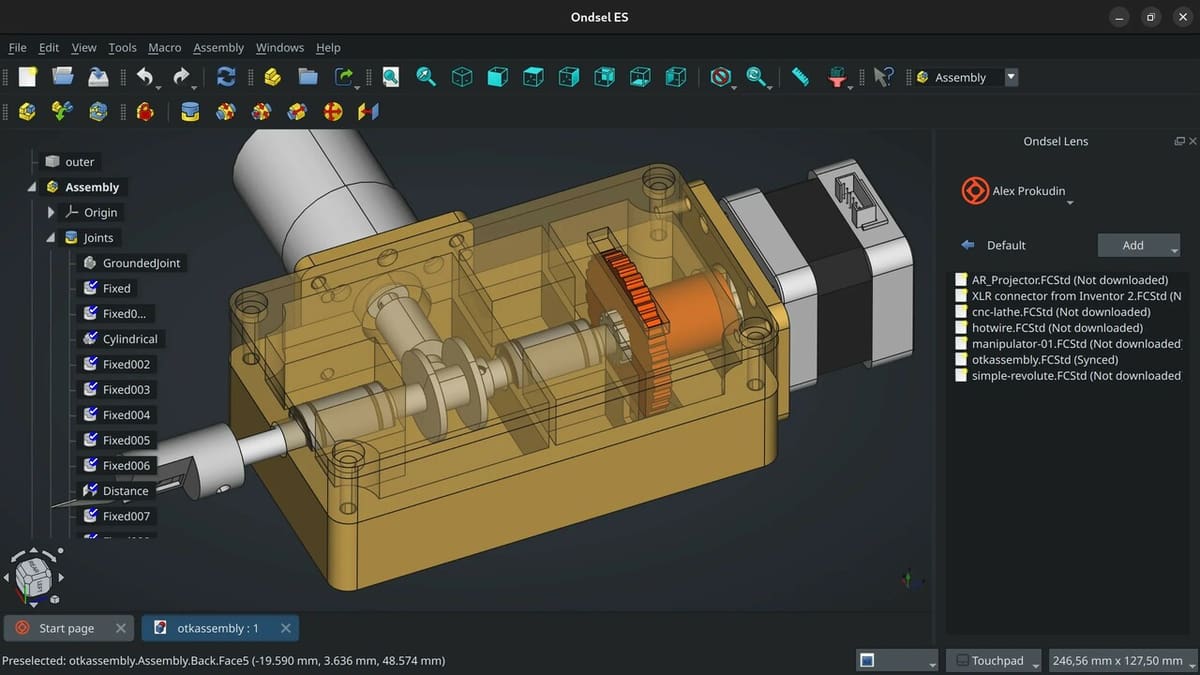
Ondsel & FreeCad
Ondsel recently arrived on the market, and despite sounding like something completely new, it’s actually an improved and commercialized version of software familiar to designers, FreeCAD. Its new look and organization of the interface have received praise from users who welcome the upgrade to this long-standing, powerful, open-source tool. Ondsel is not just a CAD program, but a suite for engineers and architects that offers several valuable features such as CAM, BIM, FEA, PDM, and assembly.
FreeCAD, which is the core of Ondsel, is an open-source parametric CAD program capable of tons of different workflows, including product design, mechanical engineering and FEA, 2D sketching, and even architecture. It’s great to learn the fundamentals of CAD in this free program with lots of support out there.
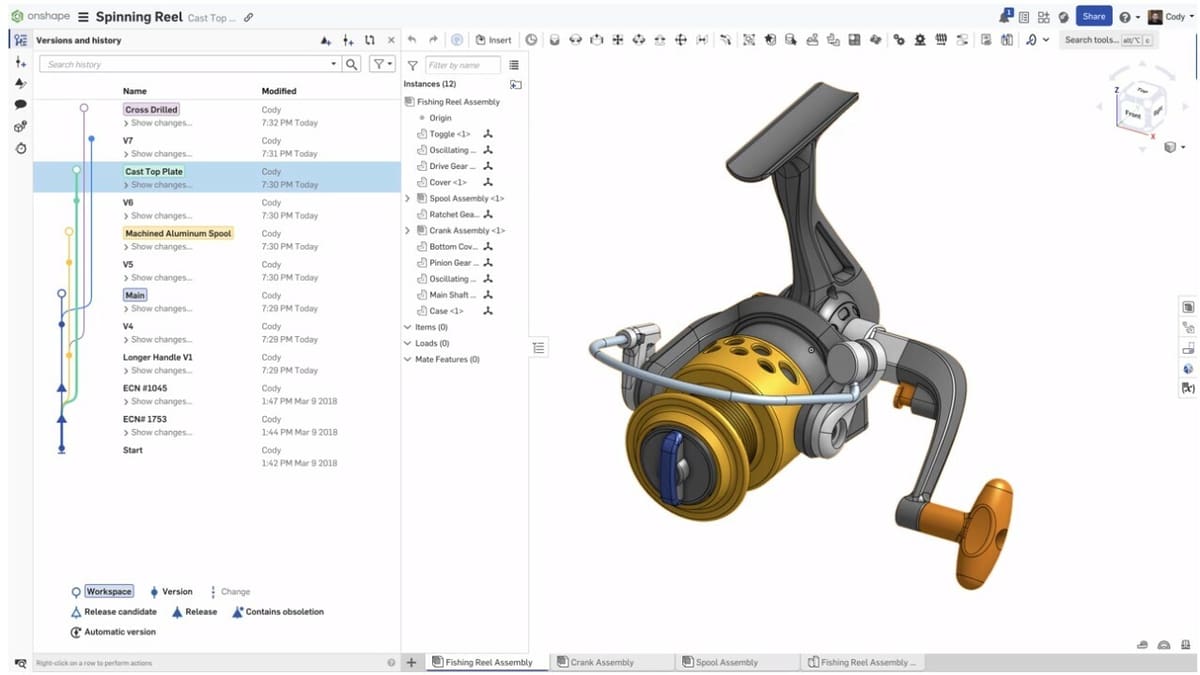
Onshape
PTC’s Onshape is a powerful and affordable tool for engineering students, offering a cloud-based platform, advanced parametric modeling, real-time collaboration, and free access with proof of enrollment. Despite some direct modeling limitations and other features that are only found in Creo, it does have much of the same functionality, including PDM.
Onshape’s strengths are in product development and mechanical engineering, with tools for assemblies, simulation, PCB design, versioning, and other collaboration tools. PTC has also been teasing an integrated CAM studio that should be coming to Onshape soon.
Final Thoughts
We hope that some of these options are the right fit for your goals, but if you still haven’t found exactly what you were looking for, don’t be discouraged, there are countless new CAD solutions for just about any specialty.
In case you need something more specific, be sure to check out our other articles on the best CAD programs for various interests:
- Free: The Best Free CAD Software
- Open source: The Best Open-Source CAD Software
- 3D printing: The Best Free CAD Software for 3D Printing
- Sketching and 2D: The Best 2D CAD Software
Whether you want to build a small educational project, a capstone project, or even participate in an engineering competition, CAD software will be the tool to bring your ideas to life and make the most of your potential, so get to work! The future can’t wait for what you will be able to design and accomplish!
License: The text of "CAD for Student: The Best Options" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.