The Context of This Innovation

Technology has played an important role in the evolution of dentistry by bettering work conditions both in dental offices and in dental laboratories. And one notable advancement is CAD/CAM dentistry. This simply refers to the digital design of dental fixtures, crowns, and more using CAD, and the fabrication of those products using CAM.
With the accuracy and reliability of modern fabrication processes, not to mention the accuracy and efficiency of 3D scanning, dental object fabrication became a lot more potent.
Dig into this detailed guide to dental CAD/CAM.
What Is It?
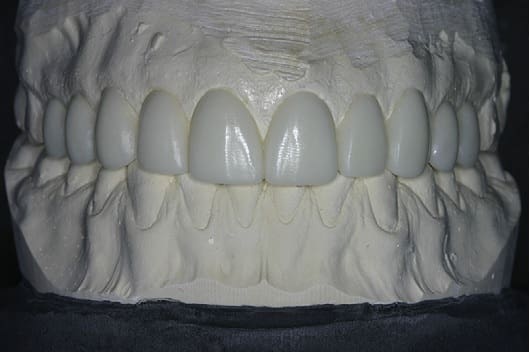
CAD/CAM dentistry, as its name implies, is a discipline of dentistry which use CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems to improve the design and fabrication of dental restorations.
It can be used in the design and construction of veneers, implant abutments, crowns, inlays, onlays, fixed partial dentures and full-mouth reconstruction. Also, we can use CAD/CAM in orthodontics. But in dentistry specifically, it was only used for the first time a decade after its creation. In the 1960s, this technology was used in the aircraft and automotive industries.
Pros and Cons

Advantages:
- The quality of CAD/CAM restorations is high and they have a natural appearance because the ceramic blocks emulate enamel.
- The measurements and fabrication are precise.
- If there’s a milling machine in a dental office, patients could receive their permanent restoration the same day, and there is no need for a second appointment. (These savings in time and labor have the potential to reduce costs, too.)
- Digital scans are faster and easier than conventional impressions because wax-ups, casting, firing, and investing are eliminated.
- Precision in the adaptation of the teeth with an exact marginal dental sealing which ensures its long-term performance.
- Dentists know exactly where they should place the implants.
Disadvantages:
- The initial cost of software and equipment is high.
- High barrier of entry in terms of technical proficiency required.
System Components
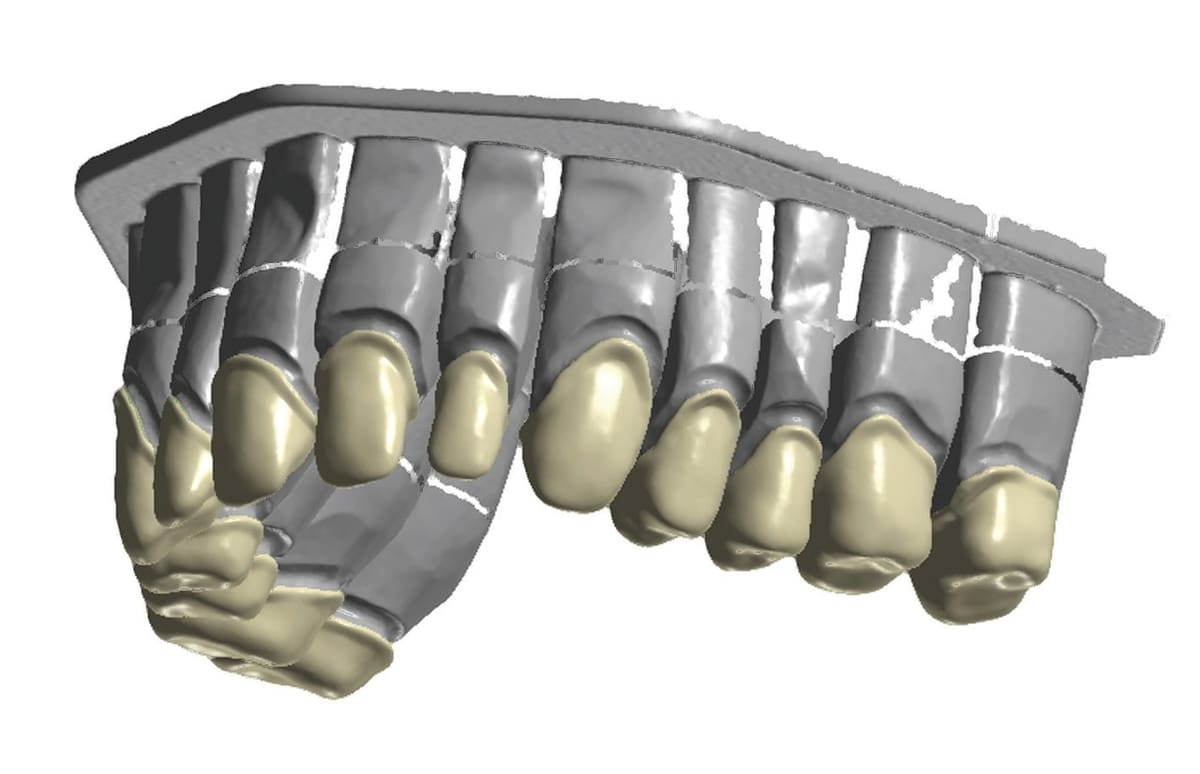
All CAD/CAM systems consist of three components:
1. Computerized Surface Digitization Using Scanners.
Geometry is transformed into digital data which can be processed by a computer. The data acquisition involves making an optical impression of the preparation. We can do so with the help of:
- 3D surface digitizing or scanning methods, which we can separate into:
- Direct (at the tooth)
- Indirect (via impression making and model fabrication)
- Various surface digitization techniques, such as:
- Laser scanning
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Computed tomography
- Contact profilometry
A scanner in dentistry refers to a data collection device which measures three dimensional jaw and tooth structures to transform them into digital data sets.
There are two types:
- Optical Scanners: They work collecting three-dimensional data using a process called “triangulation.”
- Mechanical Scanners: in this case, the master cast is read mechanically by means of a ruby ball and the three-dimensional data is acquired.
2. CAD
Data is obtained from the scanning process and, depending on the application, a data set is produced to fabricate the product. We can store the data of the construction in various data formats, but the standard is often STL files.
With CAD software, we can provide various dental restoration designs to the CAM unit.
3. CAM
A production technology which transforms the data set into the desired product through milling. We can differentiate the processing devices according to:
- Dry or Wet Milling
- Dry Processing: Can be applied to zirconium oxide blanks with a low degree of pre-sintering.
- Wet Processing: A spray of cool liquid protects the milling diamond or carbide cutter to avoid damage due to the heat. This process is necessary for metals and glass ceramic.
- Number of Milling Axes
- 3-axis: This milling device has degrees of movement in the three spatial directions.
- 4-axis: This device includes the tension bridge rotations as the fourth axis of movement.
- 5-axis: The fifth axis is rotating the milling spindle.
Types of Production
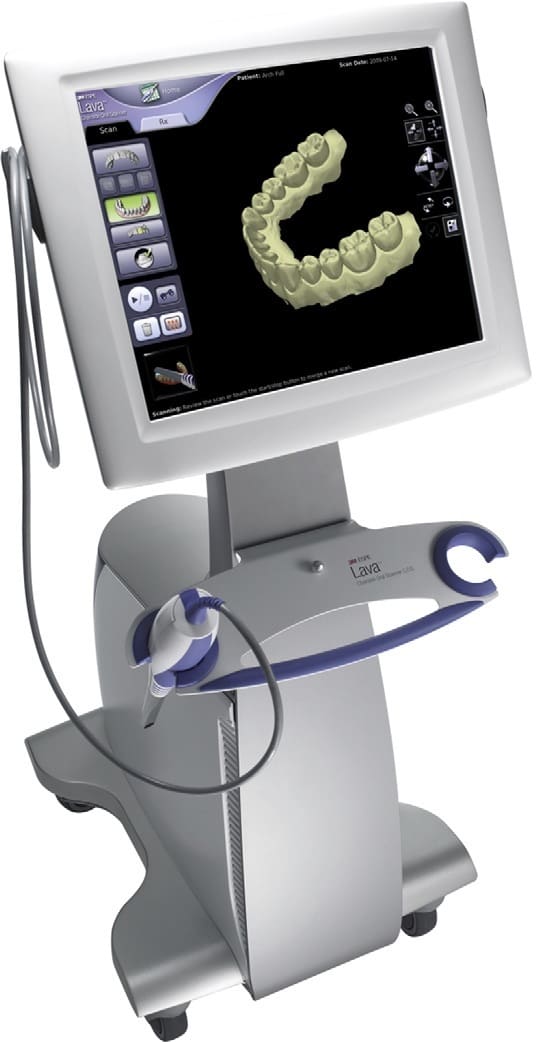
The production concepts depend on the location of the components of the CAD/CAM systems:
- Chairside Production: We can find the components in the dental surgery.
- Laboratory Production: The manufacturers carry out the CAD/CAM production steps.
- Centralized Fabrication: “Satellite scanners” in the dental laboratory can connect with a production center through the internet.
Materials
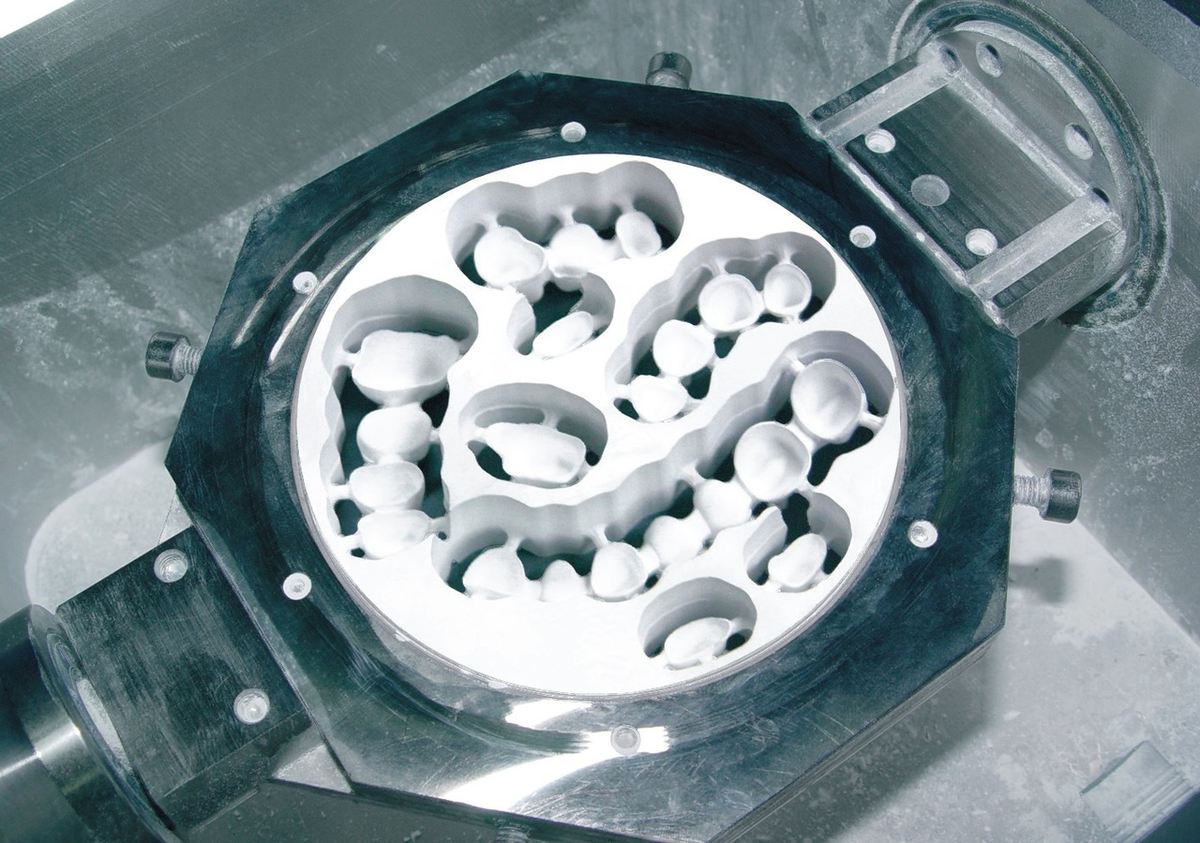

Now we can show you the materials which we can use on dental CAD/CAM devices:
- Metal: Such as titanium, titanium alloys, and chrome cobalt alloys.
- Resin Materials: Used for the milling of lost wax frames for casting technology and as crown and FPD (Fixed Partial Denture) frameworks for long-term provisional or for full anatomical long-term temporary prostheses.
- Silica-based Ceramics: For the production of veneers, onlays, inlays, partial crowns, and full crowns.
- Infiltration Ceramics: Three variations which we can use, that is Vita In-Ceram Alumina, Vita In-Ceram Zirconia, and Vita In-Ceram Spinell. They are adequate for producing crown copings and FPD frameworks.
- Oxide High-performance Ceramics: Blocks of aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide, used to produce crowns, FPD frameworks, and even implant abutments.
Case Study: Creating a Restoration

Firstly, the process depends on the system used. There are some systems which provide you same-day, in-office restorations, and we’re going to focus on this possibility due to its many advantages.
- The process of crowning a tooth starts with removing any decay that is present, then shaping the tooth with a dental drill, so that it will fit perfectly inside the crown.
- When you start using the system, the restoration site is prepared in the same way as in the traditional impression. Then, the scanner must be placed near the target tooth to provide the image.
- Looking at a computer monitor, it is possible to center the image of the target tooth. A foot pedal, which activates the image capture using software, is then released. The software prompts the dentist to adjust the scanner for the next image and gradually creates a 3-D image, as each picture is taken. To confirm the totality of the scan it is necessary to see it from any angle of the image.
- With an impression material, it is possible to create an occlusal registration which is placed atop the target tooth. The scanner captures the combination of registration material and uncovered teeth, using this information to design restorations of the correct heights.
- The finish lines and marks are automatically detected by the design system. Once the dentist approves these markings, the computer proposes a restoration model for the target tooth.
- When the restoration is approved, the in-house milling machine or a dental laboratory receives the data. Then, the office milling machine will manufacture the restoration from the chosen blocks of ceramic or composite.
Pricing

According to Davidowitz and Kotick: “Dentists who wish to begin providing same-day restorations can purchase a complete CAD/CAM system at a cost of approximately $90,000 to $112,000. A lower-cost option is to purchase a digital scanner only; prices for these range from about $24,000 to $41,000. Each scan costs between $16 and $35.
Using a complete system has the potential to reduce costs related to impression material, provisional crowns, time in the office, and laboratory bills. Dr. Parag Kachalia estimated that dentists who switch to office CAD/CAM systems can reduce their laboratory bill by 60% to 70%.”
Closing Thoughts

As you can see, dental CAD/CAM is a sector ripe with innovation. This provides dentists and patients a better experience in terms of quality, speed, ease of use, precision, and economy.
Finally, if you want learn more, we’ve got just the thing:
- Carbon Takes a Bigger Bite of the Dental Market with New Materials and Partnerships
- Dental 3D Printing – All You Need to Know in 2020
- Formlabs Announces 2 New Materials for Dentistry, Partnership with 3Shape
Sources:
- Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation.
- Computer Aided Designing/Computer Aided Manufacturing in Dentistry (CAD/CAM) – A Review.
- Digital dentistry: an overview of recent developments for CAD/CAM generated restorations.
- The application of CAD /CAM technology in Dentistry.
- The Use of CAD/CAM in Dentistry.
Feature image source: medgadget.com
License: The text of "Dental CAD/CAM – All You Need to Know" by All3DP Pro is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.