PLA has long been the go-to filament for hobbyists due to its ease of printing, even on low-cost, entry-level machines such as the ever-popular Creality Ender 3. However, it comes with one major caveat: heat resistance. Under heavy loads, PLA tends to deform and sag at just ~40 °C, making it unsuitable for outdoor applications.
Engineering plastics like ABS have a significantly higher heat deflection temperature (HDT) than PLA. Unfortunately, it’s often difficult to print such materials on unenclosed, hobbyist machines. This is where heat-resistant PLA can save the day. Heat-resistant PLA is regular PLA with additives that improve the HDT. It offers the same ease of printing as regular PLA, just with the added benefit of improved heat resistance.
In this article, we’ll take you through some printing tips for heat-resistant PLA before exploring the best brands out there. Let’s get started!
Considerations

To determine our list of the top heat-resistant PLA filaments, we considered the following criteria:
- Heat Resistance: As the name implies, heat-resistant PLA must have a high HDT. As a benchmark, PETG’s HDT is ~70 °C which is still quite easy to print on hobbyist, unenclosed machines.
- Printability: The purpose of heat-resistant PLA is its ability to fabricate parts tolerant to heat while maintaining ease of printing comparable to regular PLA. Hence, the filaments on this list do not require an all-metal hot end or an enclosure, and printing will not be difficult compared to standard PLA.
- Mechanical properties: Good heat-resistant PLA should not have major losses in mechanical properties compared to regular PLA. After all, we don’t want a heat-resistant part that is still unusable due to losses in other mechanical properties, do we?
- Availability: The heat-resistant PLA must be available for purchase and still be actively produced by the manufacturer.
Printing Tips
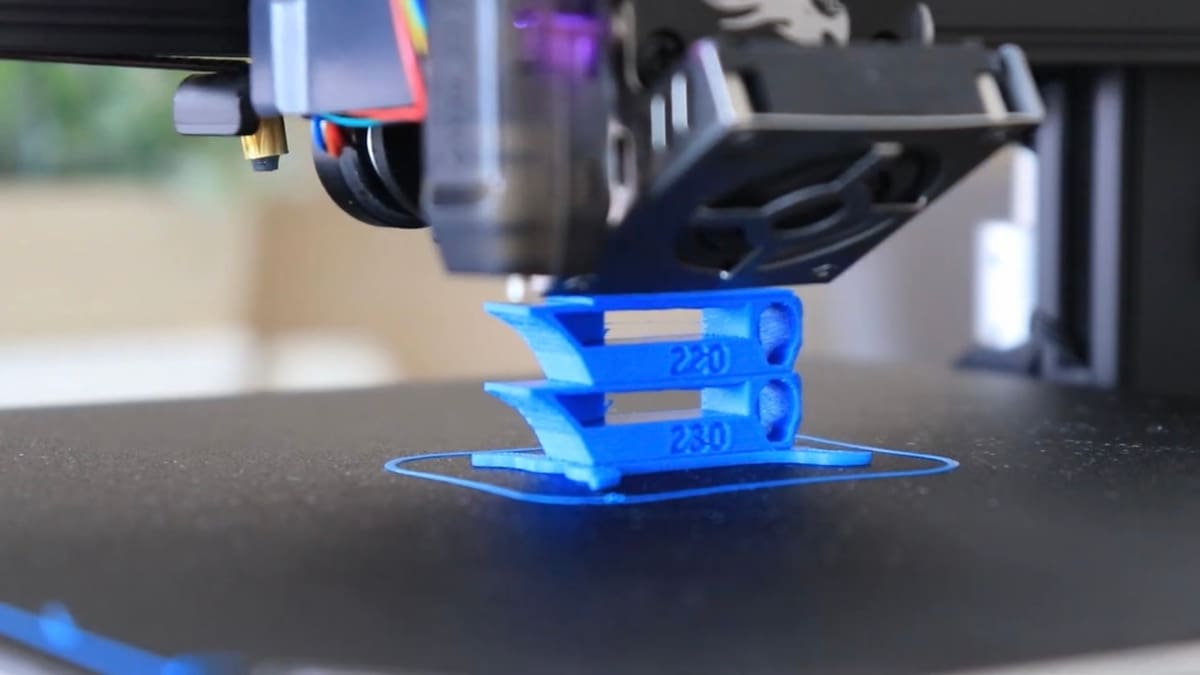

Although heat-resistant PLA typically prints similarly to regular PLA, there are a couple of printing tips to consider:
- Higher nozzle temperature: Similar to other filaments, it’s good to start at the higher end of the filament’s recommended nozzle temperature for better layer adhesion. Also, some heat-resistant PLA should be printed at a slightly higher temperature than regular PLA (at around 230 °C).
- Thicker walls and denser infill: Although heat-resistant PLA is formulated to reduce dimensional deformation during annealing, thicker walls and denser infill will help to further reduce shrinkage.
Another important thing to keep in mind when printing heat-resistant PLA is that HDT does not fully represent the temperature resistance of the material under load. HDT is usually tested using the ISO75 standard, which defines the max deformation to be 0.34 mm (under a 0.45 or 1.8 MPa load). However, parts will typically deform slightly below the HDT, and with larger loads, deformation will be larger. Creeping (slow deformation under load) occurs very quickly near the HDT. To be safe, users typically use the material at 20 °C under the rated HDT, to avoid creeping or deformation.
Annealing Process
There are two main types of heat-resistant PLA, one of which is PLA which doesn’t require annealing. These parts have a high HDT right off the print bed and do not require any post-processing to achieve the desired heat resistance.
However, the other type does require annealing, which means parts achieve a high HDT only after undergoing a process that heats the material to a temperature high enough so that it recrystallizes but low enough to avoid melting. If annealed, regular PLA often suffers sizeable dimensional deformations. Heat-resistant PLA is formulated to largely avoid or even eliminate this dimensional deformation.
PLA is a semicrystalline material, meaning it contains both amorphous and crystalline regions, similar to PETG. Annealing rearranges its polymer chains to grow the crystalline regions, improving its mechanical properties, including heat resistance.
Here’s a simple overview of the process:
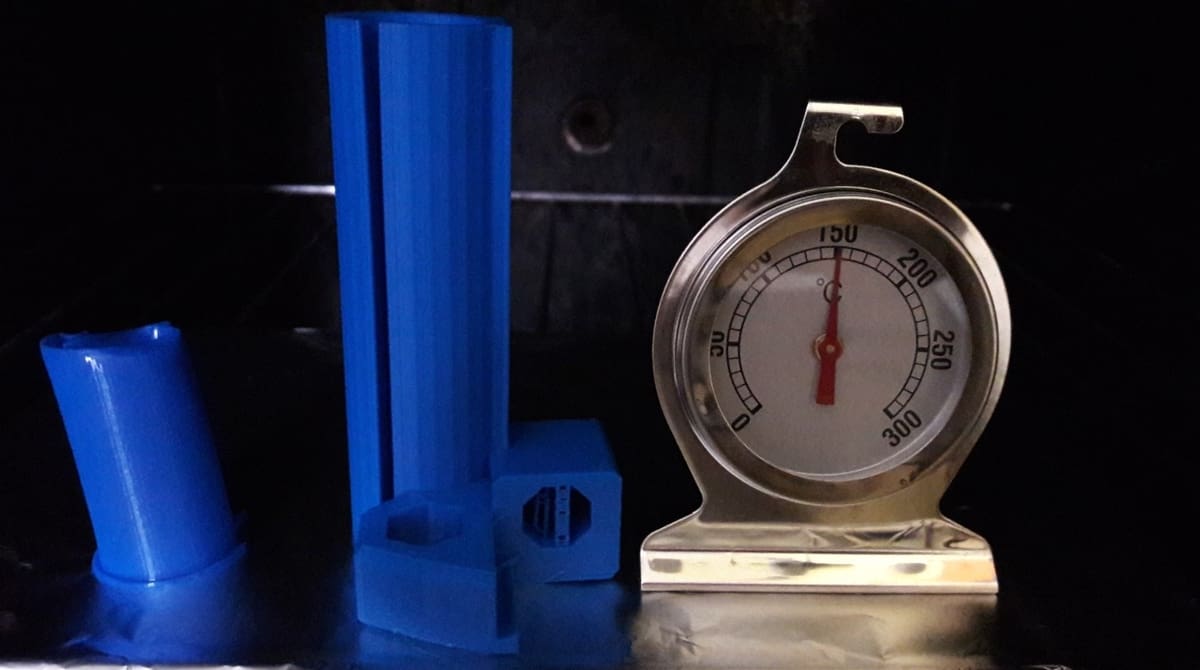
- Heat your oven to the desired annealing temperature and wait for the temperature to stabilize.
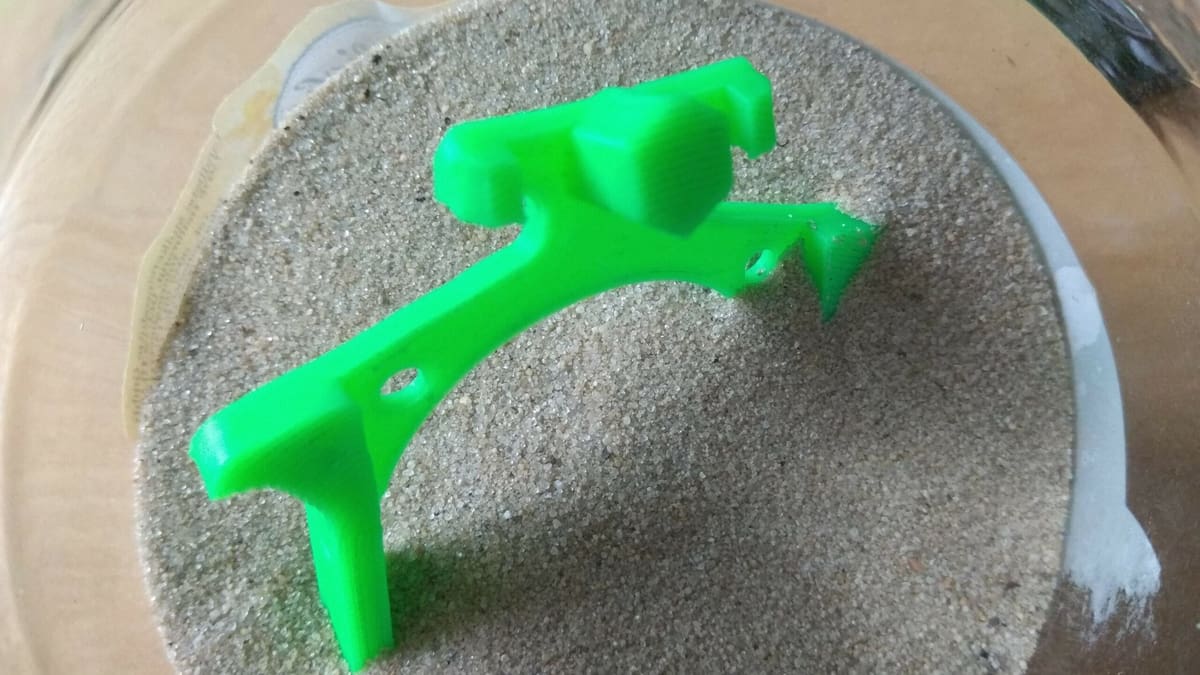
- Submerge the part in a container of sand, burying the parts entirely. Then, place the container in the oven.
- Wait for 10-60 minutes (depending on the size of the parts), and then remove the container from the oven.
- Wait for the parts to cool at room temperature.
For a more detailed overview of the process, check out our guide on annealing PLA. Often, detailed annealing instructions for a specific filament are available on the manufacturer’s website.
Now that you know the basics, let’s get to our filaments!
Formfutura Volcano PLA
Apart from heat resistance, Formfutura’s Volcano PLA boasts a high melt flow index of 6 g/10 min (at 210 °C), making it suitable for high-speed printing. A higher printing temperature is recommended for even higher flow rates and layer adhesion.
Also, the manufacturer claims a shrinkage of under 0.3% during annealing, ensuring that parts remain dimensionally accurate. Detailed annealing instructions can be found on their product page.
This filament also has a beautiful matte finish and improved impact resistance compared to regular PLA. However, it’s rather pricey at ~$44 for 750 g.
- Heat Resistance: 95 °C (after annealing)
- Hot End Temperature: 230-265 °C
- Diameter: 1.75 mm, 2.85 mm
- Colors: Black, white, light gray, dark gray, dark blue, gold, red, silver
- Price: ~$44 for 750 g (~$58/kg)
ColorFabb PLA-HP
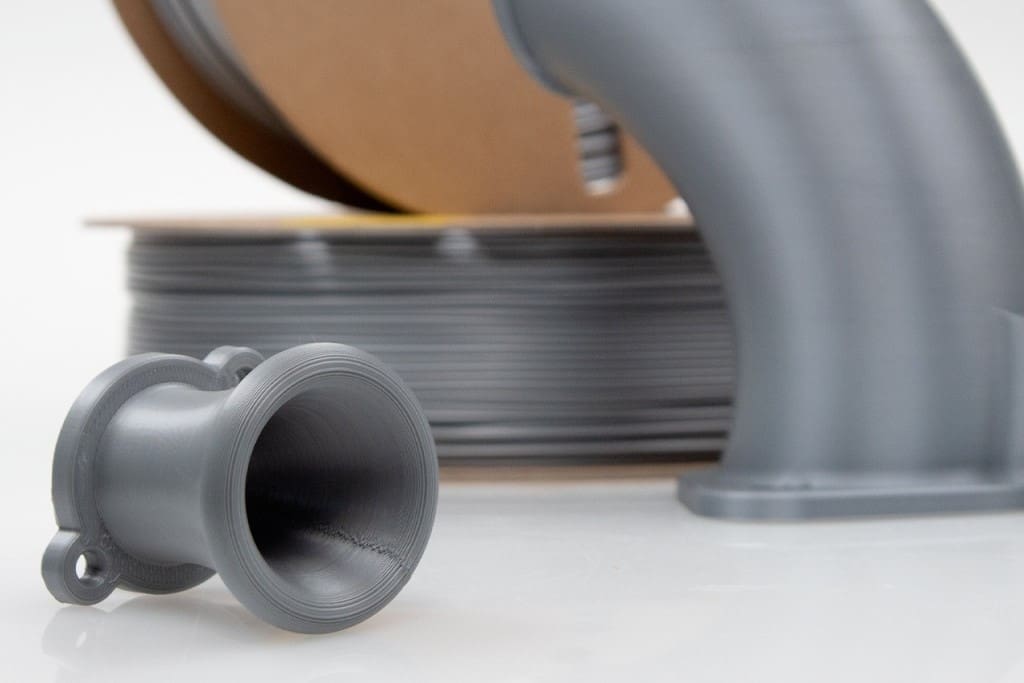

Let’s cut to the chase: If you are looking for more bang for your buck, this is the heat-resistant PLA to go for. ColorFabb’s PLA-HP achieves a very high HDT of 130 °C right off the build plate. That’s right, no need for annealing!
Furthermore, this filament is also 100% biobased, meaning it’s fully derived from non-petroleum biological resources (in this case, plants). Price-wise, this option is significantly cheaper than the others on this list, giving you great value for money.
- Heat Resistance: 130 °C (without annealing)
- Hot End Temperature: 200-220 °C
- Diameter: 1.75 mm, 2.85 mm
- Colors: Black, silver, white
- Price: ~$23 for 750 g (~$31/kg)
ProtoPasta HT PLA
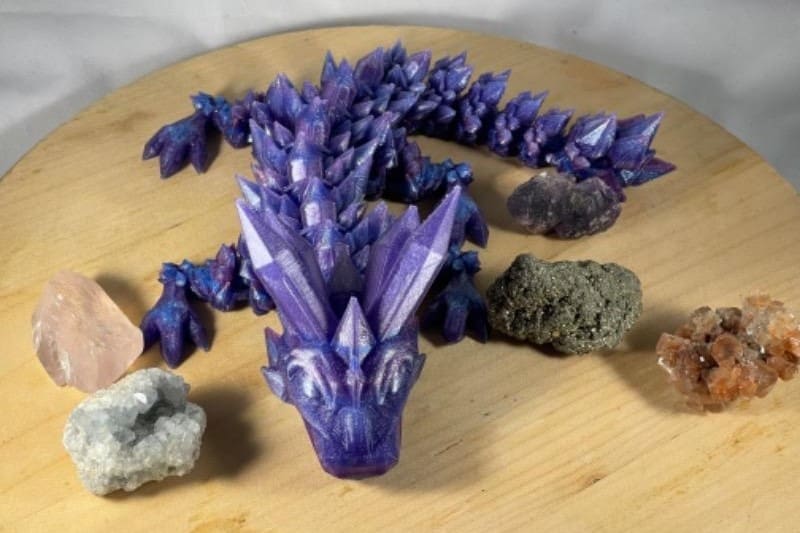

ProtoPasta’s HT PLA offers a wide variety of colors and options, including translucent, opaque, metallic, galaxy, multicolor, matte fiber-filled, and even metal-filled options! In case you can’t decide which one to get, it’s available in 50 g samples for $5-12 for you to try out.
ProtoPasta’s HT PLA requires annealing, to attain its high HDT of 115 °C. For optimal dimensional accuracy, ProtoPasta recommends an XY-axis scaling of 102% and a Z-axis scaling of 99%, with an annealing temperature of 95-110 °C for 10+ minutes. More information can be found on their website and technical datasheets.
- Heat Resistance: 115 °C
- Hot End Temperature: 190-230 °C
- Diameter: 1.75 mm, 2.85 mm (depending on the variant)
- Colors: Many colors for each option, including standard, metal-filled, matte fiber-filled
- Price: ~$50 for 1 kg (standard), ~$50 for 500 g (metal-filled), ~$40 for 500 g (matte fiber-filled)
Filaticum Engineering PLA
Filaticum Engineering PLA has an incredible HDT of 140 °C, without any need for annealing. This almost puts it at the same level as pure polycarbonate (PC), a high-performance plastic often used in demanding applications, such as the canopy of the F-22 Raptor.
According to mechanical tests by My Tech Fun, this PLA has a much higher impact resistance than regular PLA. Although HDT is confirmed to reach 140 °C, the tests also show that this material creeps noticeably at temperatures above 50 °C under heavy loads.
The ultra-high HDT comes with an ultra-high price tag, making it the most expensive option on this list.
- Heat Resistance: 140 °C (without annealing)
- Hot End Temperature: 195-245 °C
- Diameter: 1.75 mm, 2.85 mm
- Colors: Black, blue, white
- Price: ~$63 for 750 g (~$84/kg)
Push Plastic High Heat PLA

After annealing, Push Plastic’s High Heat PLA will offer a high HDT with minimal warping. Push Plastic claims this PLA’s mechanical properties exceed ABS in terms of impact strength.
While the filament boasts a reasonable price tag, some users noted that parts of the spool may be brittle. The manufacturer recommends annealing the filament while it’s still on the spool to fix the issue.
- Heat Resistance: 80-90 °C
- Hot End Temperature: 210-220 °C
- Diameter: 1.75 mm, 2.85 mm
- Colors: Black, white, natural, ultra blue, maroon
- Price: ~$39 for 1 kg
License: The text of "The Best Heat-Resistant PLA Filaments" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
CERTAIN CONTENT THAT APPEARS ON THIS SITE COMES FROM AMAZON. THIS CONTENT IS PROVIDED ‘AS IS’ AND IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE OR REMOVAL AT ANY TIME.





