IntelliCAD, a computer-aided design (CAD) engine developed by the IntelliCAD Technology Consortium (ITC), has carved a niche for itself in the CAD space. Rather than a program meant for end users, it’s a platform that’s meant to be further developed and adapted to a variety of needs and uses.
Instead of purchasing a license or signing up for leaner versions, which is the case of other programs like Autodesk Fusion or Onshape, IntelliCAD offers a different system. Users opt for a membership and can then use the platform to create their own CAD program, which can then be distributed under different licenses. Rather than starting from scratch, CAD developers can access the foundation – similar to AutoCAD’s – and then format and further develop the product according to their aim.
We will delve into the software’s pricing, system requirements, user interface, features, real-world applications, community support, and alternatives, offering a comprehensive discussion about IntelliCAD.
Let’s get right to it!
Prices & Licensing
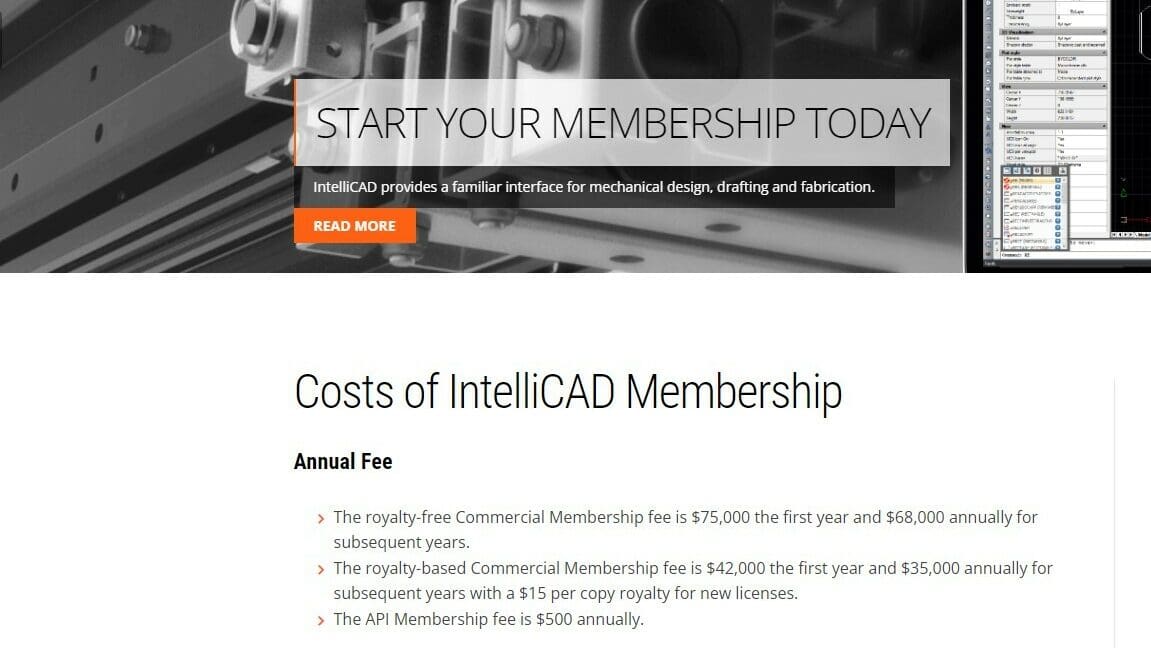
As mentioned, IntelliCAD operates on a membership model, with benefits varying for Commercial and API members. At time of writing, the licensing can be elaborated as follows:
- Commercial Members: These can choose between a royalty-free and a royalty-based membership. The former is $75,000 for the first year, followed by an annual membership of $68,000 in the subsequent years. The latter is $42,000 for the first year, and $35,000 per year after. The royalty-based membership also has a royalty of $15 per copy for new licenses.
- API Members: API members are meant to be developers; they are granted access to IntelliCAD’s application programming interface (API), enabling customization and integration. The API Membership fee is $500 annually.
There are also Special Interest Groups (SIG), which offer tailored funding while collaborating with the ITC team for the adoption of new technologies.
There is a 90-day free trial for CAD developers, and a variety of 15- or 30-day trials of IntelliCAD for end users are offered by ITC members.
System Requirements
According to the product installation guide, the following are the minimum requirements to run IntelliCAD:
- OS: Microsoft Windows 8 (64-bit computer)
- Processor: A minimum of 1 GHz
- RAM: A minimum of 4 GB
- ROM: 2.5 GB of hard disk space
- Graphic card: Open GL version 1.4
However, for the best user experience, the suggested specifications are:
- OS: Microsoft Windows 11
- Processor: A minimum of 2.5 GHz
- RAM: A minimum of 16 GB
- GPU: NVIDIA GTX or RXT PCs
If you have MacOS, you might need to do some research on how to enable virtualization (running your Windows app on a Mac), as IntelliCAD doesn’t directly support MacOS users.
UI & Layout
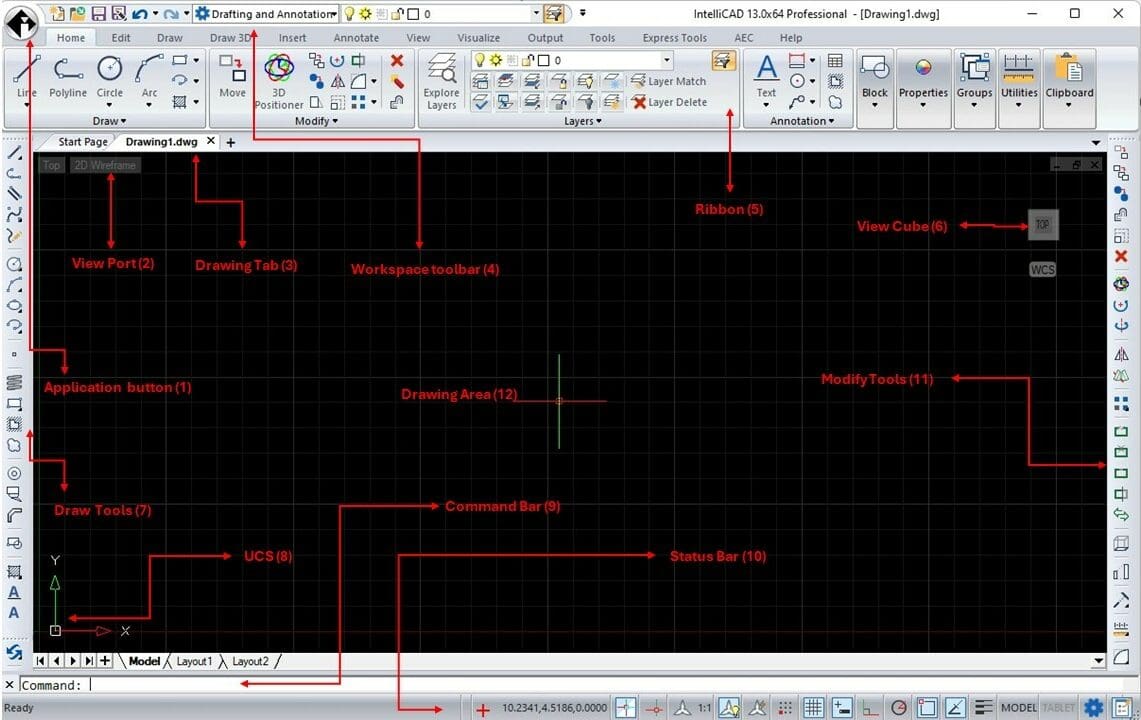
The IntelliCAD user interface (UI) is very similar to that of AutoCAD. Its tabs are arranged just like other CAD programs, while maintaining a very similar layout, and spread of the tool across the ribbon.
Just like in other tools, clicking on “new drawing” or typing “Ctrl + N”, launches the new drawing page, where you are asked to choose the template format you need. IntelliCAD has an “icad.dwt” template format for 2D drafting.
Let’s take a look at the UI:
- Application button: This lists all the file management options. You can import and export, access the sheet manager and drawing utilities, and publish files, to name a few.
- View Port: Here you can access the visual styles, such as wireframes, conceptual design, and more, for better designing and drawing implementation experiences.
- Drawing Tab: This allows the user to load, create, manipulate, and switch between multiple drawings.
- Workspace toolbar: This is where the user can switch from the drafting and annotation workspace to other tailored workspaces, like the “View and Markup” or the “DGN Markup.”.
- Ribbon: Similar to the majority of CAD programs, this area on the UI contains the tabs, panels, and the tools used to aid the drafting and annotation.
- View Cube: In addition to aiding the rotation and placement of drawings, it can be used to obtain information about the current orientation of the drawing area and how the object being drawn aligns (or not) with it.
- Draw Tools: This acts like a “quick access” toolbar, and it contains just the tools for drawing.
- USC: The User Coordinate System (UCS), besides specifying the orientation of the 2D or 3D objects, makes it possible to manipulate the direction of an object to be drawn with respect to the world coordinate system (WCS).
- Command Bar: As anticipated by its name, commands can be typed in and the program generates objects, modifies them, and follows the instructions.
- Status Bar: This holds the set of tools and configurations required to assist the drawing process; you can read what is transpiring with your object creation (i.e. the status of your drawing).
- Modify Tool: This acts as another “quick access” toolbar, like the Draw Tools menu, but this time it holds just what’s required to modify the drawn object.
- Drawing Area: Also called the drawing window, it’s where the drawn or imported objects, external references, blocks, and more, will be displayed. By default, you are in the “Model” tab. By clicking on the “Layout” tabs (e.g., Layout 1), you’ll switch to the “paper” area, where you get to annotate.
Because IntelliCAD is meant to work as the foundation for other CAD programs, if you have a license for software based on the platform, depending on your particular selection, there could be different layouts, color schemes, and features and tools available.
Features & Functions
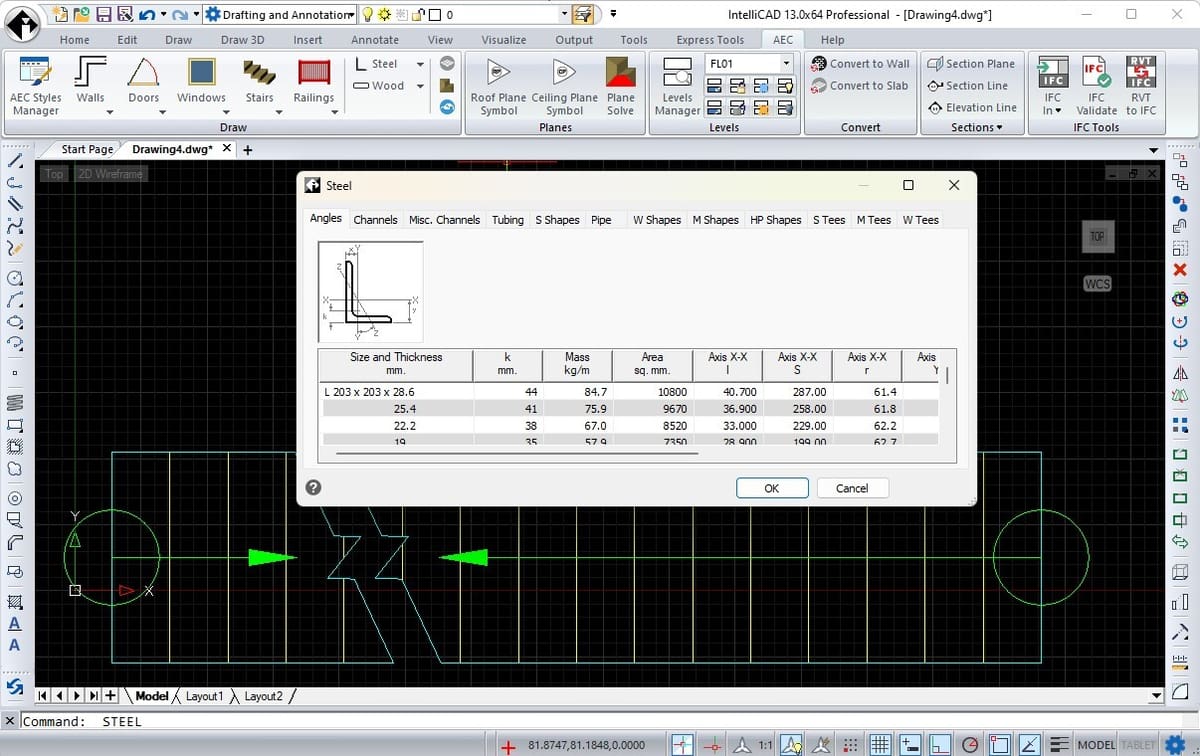
IntelliCAD is designed to offer a standard 2D drafting, annotation, and 3D design experience. It is well suited for a wide range of design projects, from architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries, to product design and manufacturing (PDM) fields.
Next, we’ll take a look at the main features and functions that are offered by the platform, and which can be further developed by members who seek to do so.
2D Drafting
Either by using the command line or by directly engaging the tool palettes, toolbars, and ribbons, IntelliCAD allows a professional 2D drafting experience. Users can easily set up drawing layers, drawing styles, and workspace limits, alongside drawing precision enablers (called entities). These entities (similar to “Object Snap” in some CAD tools) constitute the geometric, parallel, tangential, and intersection snap, to mention a few. To draft, users can create simple entities using lines, circles, ellipses, and arcs, as well as complex entities by engaging the polygons, polylines, planes (similar to hatched polygons), and more.
Regarding complex entities, there is a dedicated architectural set of entities. These allow the designer to create and insert automated drawings according to standards, featuring walls, doors, stairs, roof slabs, and steel, to name a few.
Annotation
IntelliCAD simplifies the addition of text, dimensions, multileaders, schedules (tables), annotative objects, revision clouds, and so on. Users can incorporate manufacturing details like center marks, centerlines, and geometric tolerances, leading to the accurate communication of drawing intent.
Users can set styles that directly influence how the objects (lines, text, symbols, and hatches) are displayed or represented. These objects can be created in layouts and, for example, multiple scales can be set to drawings, to automate and control their scaling.
Workflows & Drawing Files
IntelliCAD supports the use and customization of blocks, attributes, external references, and underlays (PDF, point cloud, BIM, DGN, DWF). It can work with images, data links, and even geographic locations. The data links allow the sharing of data between CAD drawings and spreadsheets (.xls or .xlsx). The content on the source file can be updated and the changes will be reflected in the drawing. Geographic locations allow the user to include specific locations in the drawings on maps corresponding to survey, civil, and architectural data.
Printing & Plotting
Either by printing your design or by customizing it, IntelliCAD facilitates the creation of drawing layouts and viewports, with respect to your choice of printing style. Users can add dimensions, title blocks, keynotes, and more, within the paper space (similar to a physical sheet of paper). Designs can be printed in standard sheet sizes (e.g. “A0”- “A4”) and printed directly from PDF format or by batch plotting (for more complex printing requirements).
Programming
This starts from basic customization, like the ability to fully customize the toolbars, menu bars, entities, tool palettes, and keyboard aliases, to name a few. IntelliCAD allows programming capabilities through TX/IRX applications, VBA, .NET applications, LISP routines, and DIESEL settings. Users can automate tasks by creating custom scripts and programs to automate repetitive or time-consuming tasks. New tools or features can be develop to extend IntelliCAD’s functionality. The platform can also be integrated with other systems, like applications or databases.
User Experience
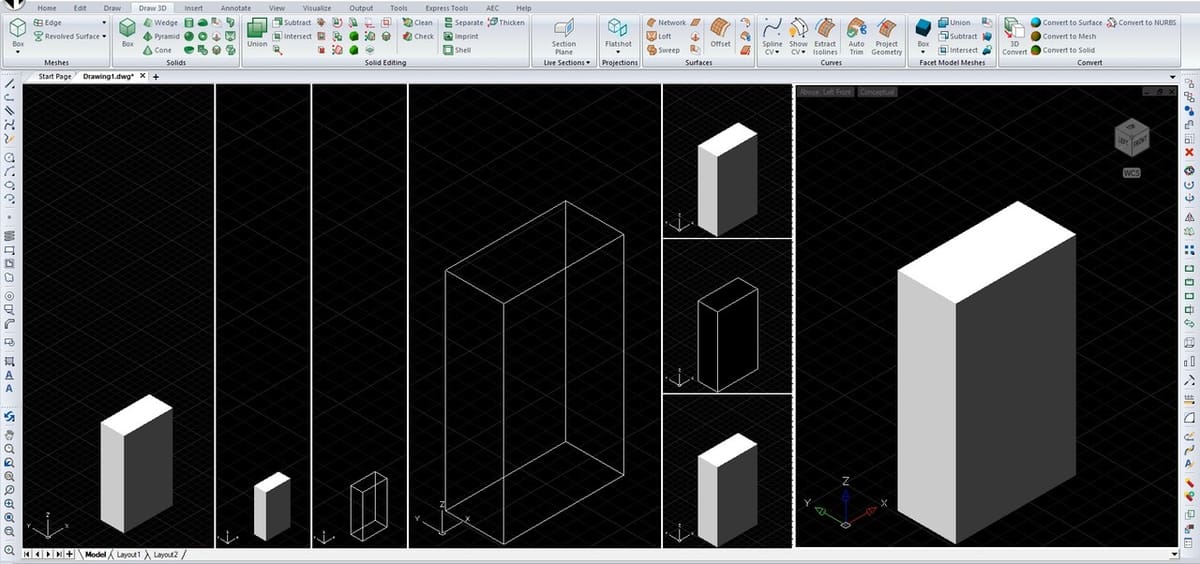
IntelliCAD allows multiple users from different disciplines to experience 2D drafting and annotation, as well as 3D design. Using the software feels like using AutoCAD, but with added features and function. These additions can range from the ability to create planes, splitting your viewport into a wide range of views (see image above), or having the “explode” tool displaying a fireworks icon, giving the user a hint of what to expect even without selecting the tool.
As mentioned before, because IntelliCAD is meant to be further developed by ITC members, and due to any differences in applications that may be presented for specific fields, the user experience is broad.
For example, for CMS IntelliCAD, users find drafting to be fast, while the overall comments point to a user-friendly and well-organized UI.
Use Cases & Applications:
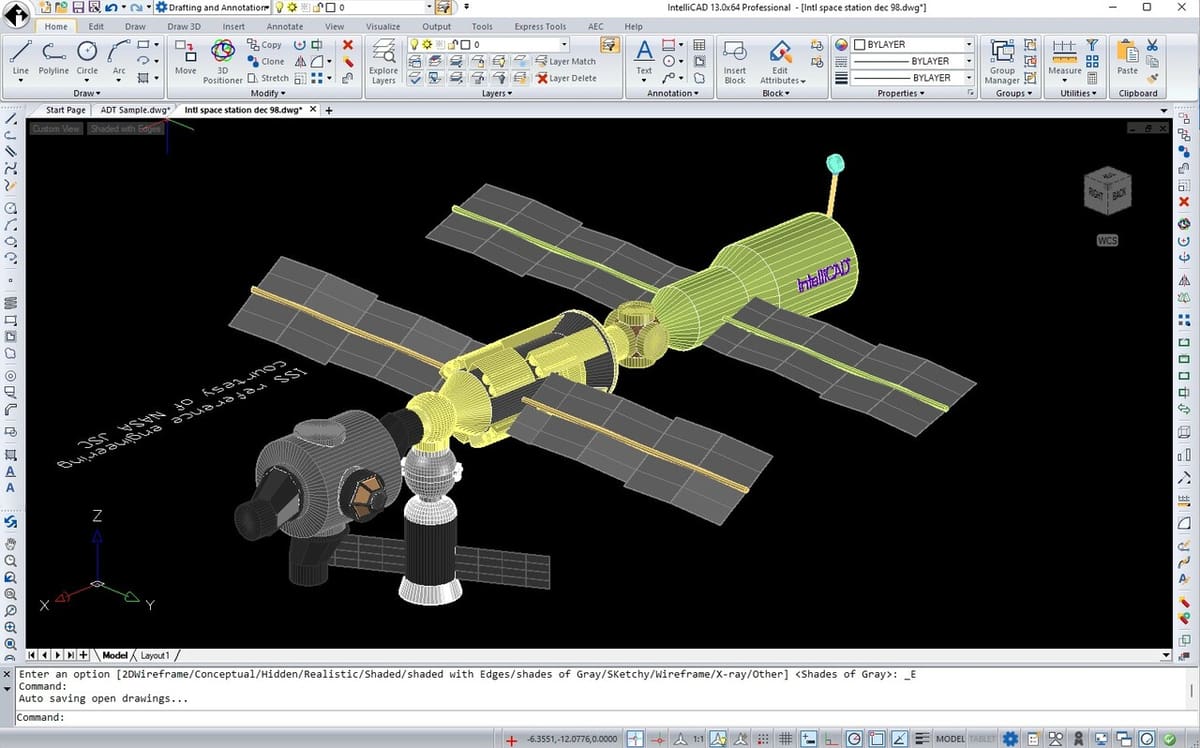
Because of its nature, IntelliCAD finds applications in various fields, not just as the base program, but also as a developed one by commercial members. Let’s take a look at a few:
- BIM: Building Information Modeling (BIM) involves creating and managing digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of buildings. IntelliCAD supports BIM workflows by allowing architects, engineers, and construction professionals to collaborate on building projects. The likes of ArCADia and 4MCAD joined the ITC to build advanced solutions for application in this industry.
- Interior design: Interior designers use IntelliCAD to create layout designs, visualizations, and detailed plans for interior spaces. The platform helps in designing furniture, fixtures, and other interior elements with precision. CAD Projekt K&A is a company that specializes in the creation of specialized tools for interior kitchen design and the arrangement of ceramic titles.
- Civil survey: IntelliCAD is employed for mapping, land surveying, and creating topographical maps. It helps surveyors and civil engineers in planning infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and drainage systems. Speaking of construction, mining, civil engineering, and land surveying, Carlson has built technologies to aid seamless workflows within this industry.
- Mechanical design: IntelliCAD is used in mechanical engineering to create detailed technical drawings and schematics. It allows engineers to design machinery, mechanical parts, and assemblies with high precision. The likes of FRAMECAD and CMS, which have been around for decades, are built solutions to aid advancement in this industry.
The commercial members are listed on ITC’s site.
Company & Community Support
When it comes to support, there are both company-provided resources and a vibrant community that offer assistance for IntelliCAD users.
The official website is the primary source for product information, documentation, and support resources. You can also find a contact form for customer support, as well as one for general queries. There’s also a blog, where the ITC shares latest platform and company developments, and an official YouTube channel and Facebook page.
From the community side of things, while there’s no subreddit, users have shared their questions on Reddit.
ITC members who offer their own program(s) based on IntelliCAD also have individual websites and resources for their end users. For example, for CMS IntelliCAD users, there’s a forum to discuss topics, ask questions, and share tips and tricks related to the platform.
Alternatives
Because IntelliCAD can be the foundation for a program that focus on a specific market – e.g. architecture – looking for alternatives can be rather tricky. That said, we opted for the general approach to CAD features offered by the base platform.
AutoCAD
Known for its industry standards and extensive features, AutoCAD is one of the most recognized CAD software tools in the industry. AutoCAD offers a more extensive set of tools for 2D and 3D design, and documentation. It supports specialized tool sets for architecture, mechanical design, electrical schematics, and more. AutoCAD works with a variety of file formats, such as DWG and DXF, ensuring seamless collaboration with other professionals who may be using different CAD programs.
BricsCAD
This software has a similar interface and functionality to AutoCAD, but at a lower cost, which might explain why it’s a fast growing alternative to AutoCAD. Because of their similar environment, it’s easy to transition between the two. Like IntelliCAD, BricsCAD supports both 2D drafting and 3D modeling, and it also includes additional features for building information modeling (BIM), making it versatile for different industries.
DraftSight
DraftSight is CAD software owned by Dassault Systèmes meant for 2D drafting and annotation. The professional version of DraftSight includes additional features such G-code generation, API access, batch printing, and advanced drawing tools, making it suitable for complex projects. Additionally, DraftSight has a user-friendly interface that is easy to learn, especially for those familiar with AutoCAD. This makes it a good alternative for users who need a simple, cost-effective solution for 2D drafting and annotations.
License: The text of "IntelliCAD: All You Need to Know About this CAD Software" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
