The Lightweights

Back in 1976, one of the world’s first single-board computers (SBCs), the “Dyna-micro“, was released. Since then, SBCs have been integral in the development of computing. They were prominent in the early history of home computers, as seen in the BBC Micro.
As personal computers (PCs) became more popular, fewer SBCs were being used in home computers. In the last decade, however, there has been a resurgence in popularity. As its name implies, an SBC is an entire computer built onto a single circuit board! Even though SBCs can’t do some things that PCs do, they are used in a range of educational, commercial, and industrial applications.
Where microcontrollers are limited to running one program, SBCs offer more flexibility. Because they have an operating system, they can run many programs. In addition, SBCs typically have more available processing power than microcontrollers, which enables you to do more computation-intensive work.
In this article, we take a look at two popular SBCs: the ubiquitous Raspberry Pi 4 and the Odroid XU4. We’ll go over each board’s specifications, including price, processor, memory, important ports, and other bells and whistles. We’ll even highlight some popular operating system options.
Let’s get started!
Meet the Contenders
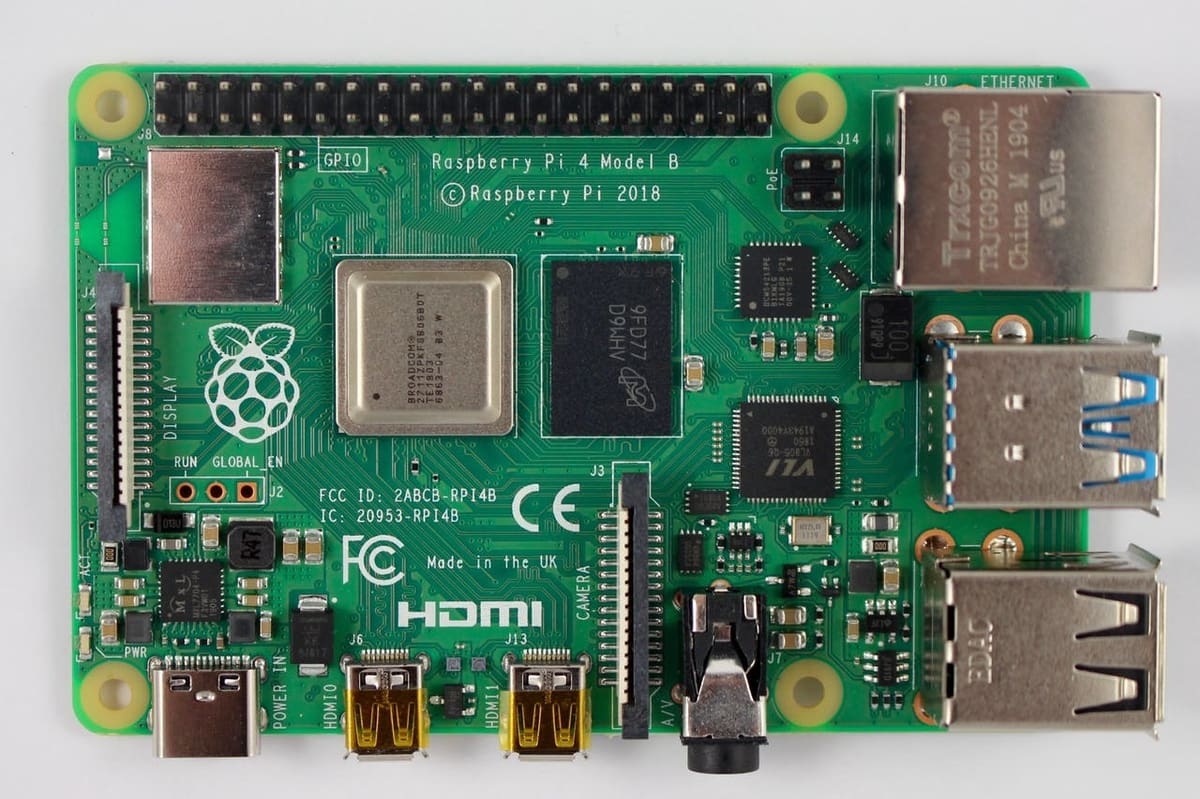
Raspberry Pi 4
The Raspberry Pi 4 is the latest in the ultra-small and affordable computers from the Raspberry Pi Foundation. It has been heralded as a great tool for STEM education and has also gained popularity in the maker community.
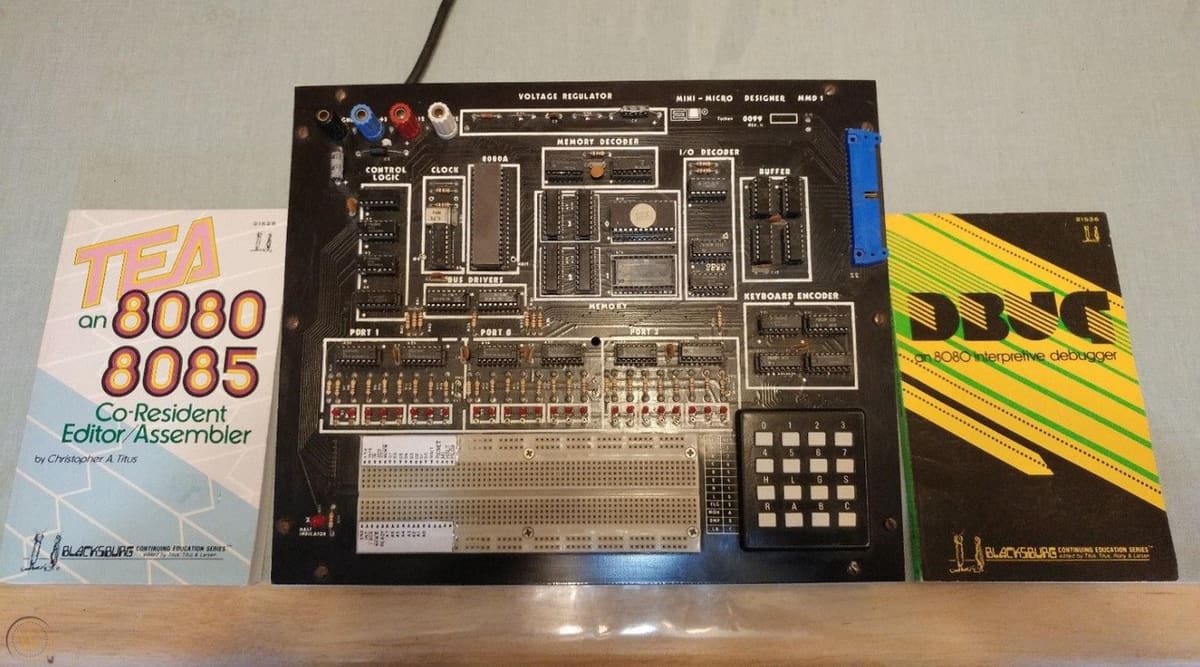
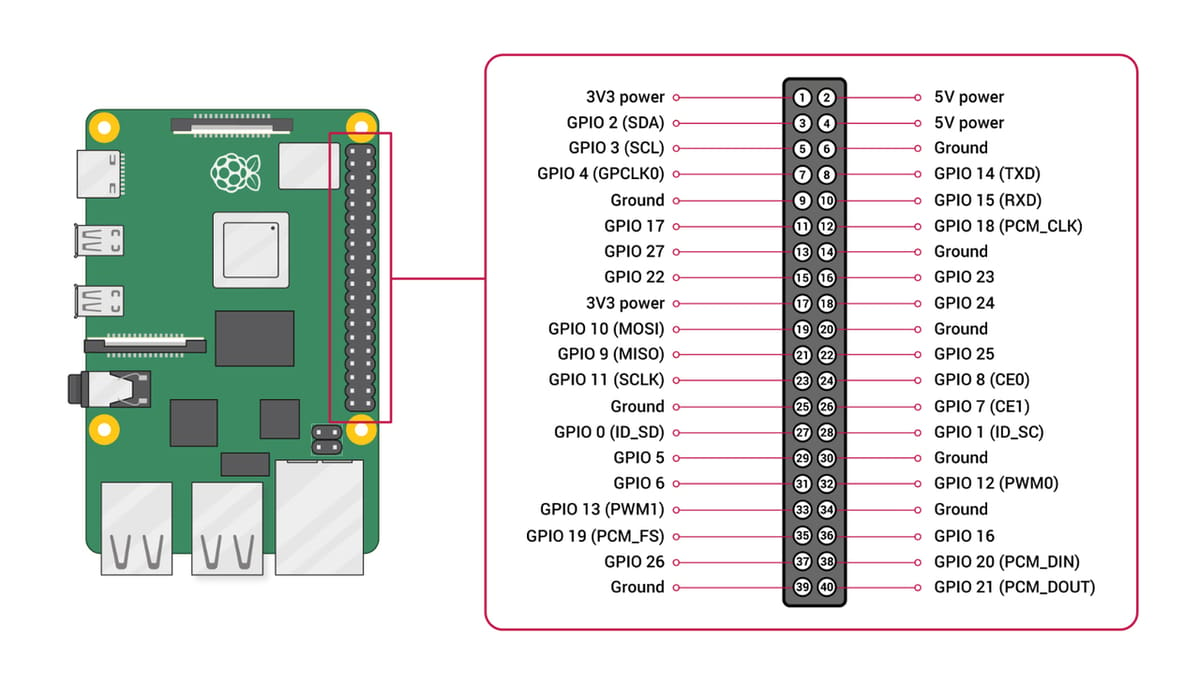
This handy little board comes with 40 general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins, opening the doors to physical computing. This is further accelerated thanks to the wide range of 3.3 V sensors and actuators, as well as a global user base. In addition, there are plug-and-play HATs, which stands for “hardware attached on top”. This is a hardware specification for add-on modules exclusively designed for the Raspberry Pi.
Odroid XU4
The Odroid is a series of single-board computers created by the South Korean company Hardkernel. At first, it was designed to act as a development platform for developers. Now, it’s popular with the hobbyist market. With Hardkernel’s SBCs, many multi-purpose projects have been created including a home theater PC for Kodi.
The Odroid XU4 was released in 2015 but remains a contender. Even though the SBC comes with GPIO pins, the XU4 functions at 1.8 V, a marked difference from the Pi’s 3.3 V. As a result, the XU4 is incompatible with many accessories on the market that operate at 3.3 V or 5 V.
That said, this problem can be solved with the addition of a Shifter Shield, which enables the Odroid to be used with higher voltage accessories. This accessory gives some leverage, but hardware-based pulse-width modulation (PWM), software PWM, and serial peripheral interface (SPI) are not supported.
Head to Head

Price
- A Raspberry Pi 4 (1 GB) starts at approximately $35. Currently, the 2 GB variant also costs around the same price! For a few dollars more, there’s also the 4 GB version. If you want even more, the 8 GB version costs ~$75.
- The Odroid XU4 is priced at ~$50.
Processor
- The Raspberry Pi 4 offers a big leap in specifications from previous generations. It packs a new Broadcom BCM2711 system-on-chip (SoC), which has a quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A72 CPU capable of running up to 1.5 GHz.
- The Odroid XU4 is built around a Samsung Exynos5422 SoC that features four Cortex-A15 cores at 2.0 GHz and four Cortex-A7 cores at 1.4 GHz.
Memory
- The Raspberry Pi 4 offers four options for RAM: 1-GB, 2-GB, 4-GB, and 8-GB LPDDR4-2400 SDRAM.
- The Odroid XU4 comes in a single 2-GB LPDDR3 version.
Display
- The Raspberry Pi 4 has dual-screen functionality as its dual Micro-HDMI ports allow users to connect two display monitors to it. The Pi also includes 4K 60 fps decoding features.
- The Odroid XU4 enables a single HDMI 1.4a connection at 1080p output.
Ports
- The Raspberry Pi 4 has two USB 3.0 ports as well as two USB 2.0 ports. Therefore, a transmission speed of 5 gigabits per second can be expected.
- The Odroid XU4 has two USB 3.0 ports available but only one USB 2.0 port.
Ethernet
- The Raspberry Pi 4 supports Gigabit Ethernet. It also has built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth functionality.
- The Odroid XU4 is also capable of Gigabit Ethernet. However, it does not have Wi-Fi functionality, so a USB adaptor is needed to achieve this.
Boot Partition
- For the Raspberry Pi 4, the boot partition is stored on a Micro SD Card.
- For the Odroid XU4, it can be stored on either a micro SD Card or the much faster embedded Multi-Media Card (eMMC) module.
Operating Systems
- The Raspberry Pi 4 supports Raspberry Pi OS (formerly known as Raspbian), Ubuntu MATE, LibreELEC, and many other operating systems (OS).
- Likewise, there are many OS options for the Odroid XU4. It supports Linux, Android, and a range of third-party images, including Recalbox and RetroPie. Android, as well as different third-party images, are available.
The Verdict
On paper, the Odroid XU4 is comparable in performance to the Raspberry Pi 4. Faster boot-up, web browsing, and even gaming are possible thanks to blazingly fast data transfer speeds through the eMMC module, USB 3.0, and Gigabit Ethernet interface. The XU4, however, is still missing Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity without an adapter.
On the other hand, the Raspberry Pi 4, though comparable performance-wise with the XU4, comes with a range of RAM sizes. The 2-GB version is powerful enough to run as a desktop computer for tasks such as programming and web browsing. Having the 4-GB Pi offers you more breathing room for multitasking and a smoother experience. Want to run virtual machines or a database server? The 8-GB version will be your best bet.
Raspberry Pi also has a huge global community that is unmatched. This means there’s ample information and supports for new users as well as continued development and maintenance of software and hardware options. Though the Odroid community is growing, it’s likely that you’ll need to spend more time to figure out and resolve issues. If you want fast community support and many cool projects to get ideas from, the Raspberry Pi may be more ideal.
That being said, choosing between the two is dependent on your project’s requirements and needs. Think about your end use, and based on that, decide which SBC best meets your needs.
Lead image source: Beomagi
License: The text of "Odroid XU4 vs Raspberry Pi 4: The Differences" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
CERTAIN CONTENT THAT APPEARS ON THIS SITE COMES FROM AMAZON. THIS CONTENT IS PROVIDED ‘AS IS’ AND IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE OR REMOVAL AT ANY TIME.