There are many different 3D modeling programs, each somewhat different in the way that it allows users to create three-dimensional models. While 3D computer-aided design (CAD) programs are meant to create a three-dimensional final product, they often have many tools inspired by 2D design and drawing. These allow for intuitive design processes that accommodate particular types of design.
In this way, “3D drawing” has become a design term that usually refers to the drawing-like functions in a 3D CAD program, such as sketching and blueprinting. However, “3D drawing” can also generally refer to 3D modeling methods, as “drawing” and “designing” are often used interchangeably.
In this article, we’ll go over 3D drawing functions – namely sketching and blueprinting – as well as the main types of 3D modeling, including surface modeling, wireframe modeling, solid modeling, and sculpting.
We’ll discuss how each of these work, their main techniques, software examples, and more!
Sketching
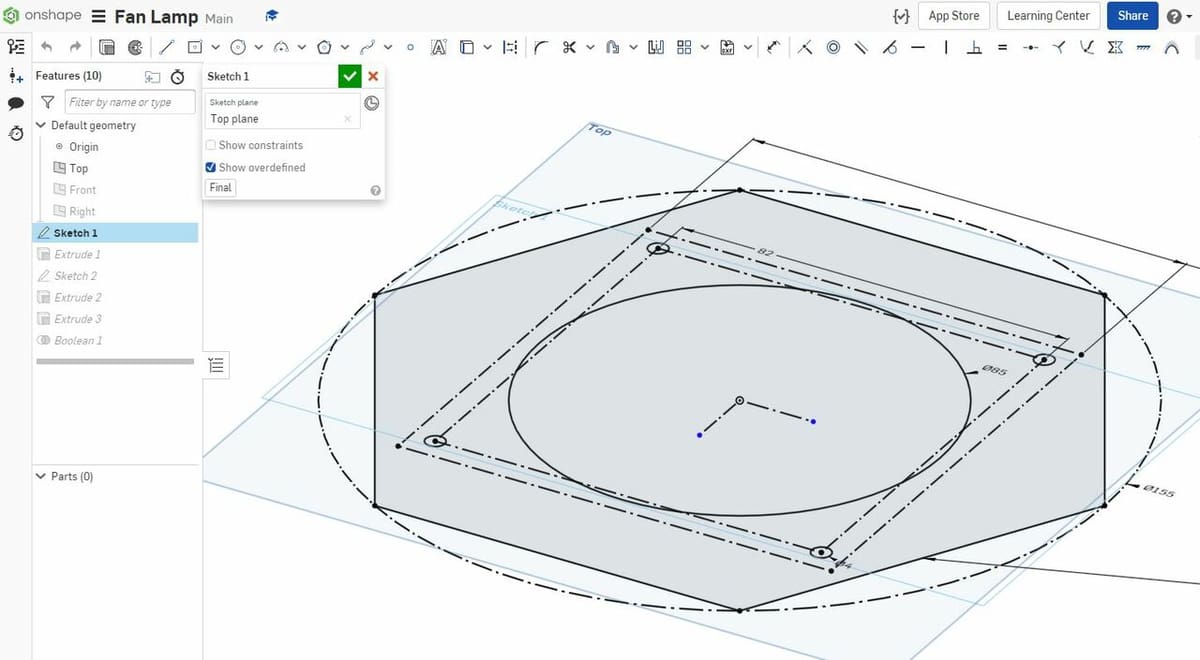
First, we have sketching, which is probably what most people think of when they hear or say “3D drawing”. Sketches, like drawings, are made up of two-dimensional features, such as lines and arcs. Yet, in CAD, sketches can obtain a 3D component, whether they act as the basis of a 3D model or are drawn to collectively exist in a three-dimensional space.
The most common technique for sketching involves using 2D features that you could draw, like lines, boxes, or circles, to create a “closed” shape within a single plane. Then, a designer can use specific functions, like extrude, revolve, or loft, to give the 2D feature height (or depth).
Most modern designing applications have features for sketching, as sketching makes adjusting the dimensions and features of a 3D model very easy. Some popular options with sketching features include Autodesk Fusion 360, Onshape, and Autodesk Inventor.
Blueprinting
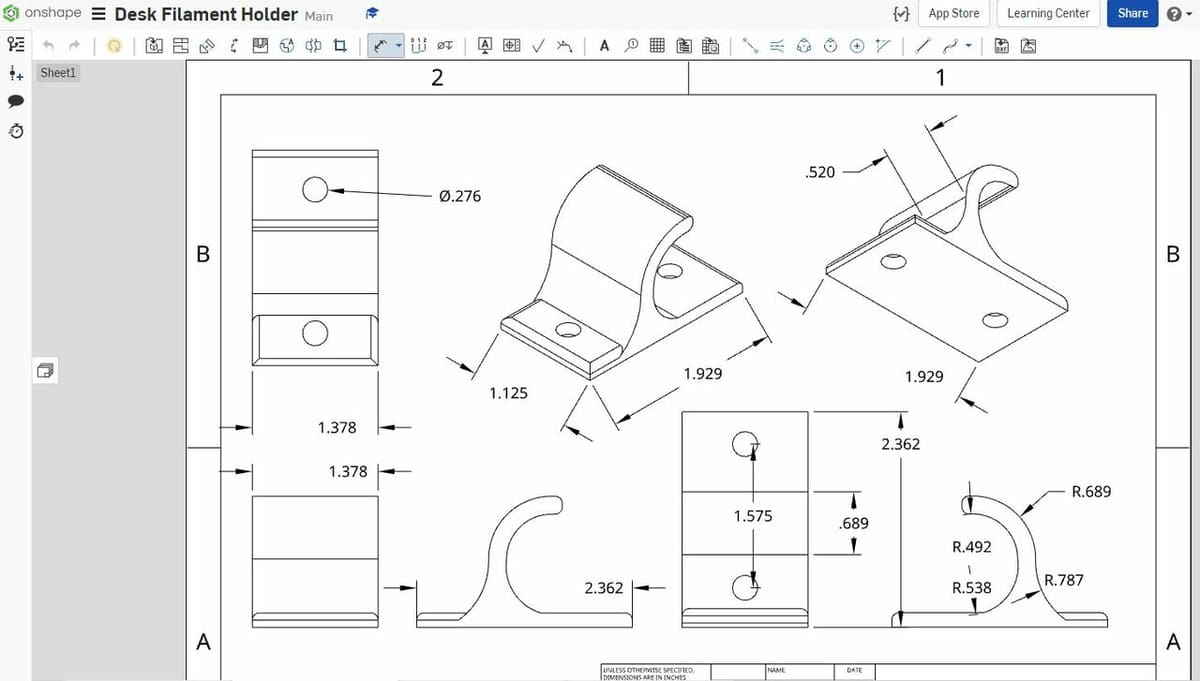
Blueprinting is the creation of a digital schematic (blueprint) of a 3D model or 3D assembly. Blueprints are an important part of the design process for structures, like houses or skyscrapers, but they can also be used for basic objects, like a 3D printable phone stand. In this context, “3D drawing” might be used to refer to the final result.
Whatever the specific method of generation, 2D outlines of a 3D design, represented from different viewpoints, are arranged on a blueprint sheet. Blueprints also usually include dimensions and other information about the design (e.g. name, scale, version date).
Most CAD programs contain similar blueprinting or drawing features, but they may vary in the specific elements of the blueprint sheet. For example, some programs offer non-standard viewpoints or take more dimensions for your 3D model.
Blueprinting isn’t as frequently used as sketching, but there are many software options that have this 3D drawing tool. Onshape and SolidWorks are two programs that have great blueprinting (or “drawing”) features.
Solid Modeling
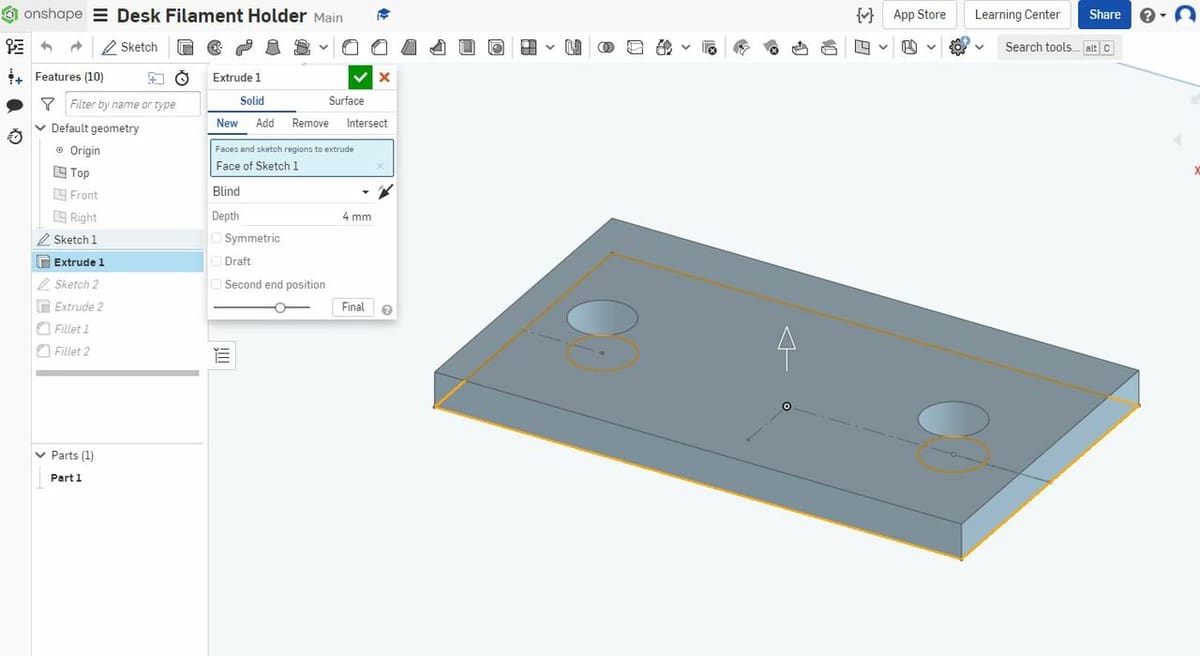
Solid modeling is the most popular form of 3D drawing for manufacturing and is what most people probably think about when they hear “3D design”. That’s because solid modeling is the basic designing method for creating 3D objects, used for making 3D printable models (that can be imported into a 3D slicer), digital copies (twins), and other designs.
As the name suggests, solid modeling is for creating solid 3D designs, and all created models have to meet certain criteria. Moreover, all created models have to be closed figures, full (solid) bodies, and require a length, width, and height.
There are a few different techniques for solid modeling, and the most common ones are parametric and direct modeling. Parametric modeling entails using constraints (e.g. dimensions) and component relationships to design a model, while direct modeling is more of a push-and-pull method used to adjust shapes.
CAD programs contain different sets of solid modeling tools, but a few common solid modeling operations include union (boolean) and shell tools. There are hundreds of different software options for solid modeling, including Inventor, Fusion 360, Onshape, Solidworks, Tinkercad, CATIA, FreeCAD, and AutoCAD.
Surface Modeling
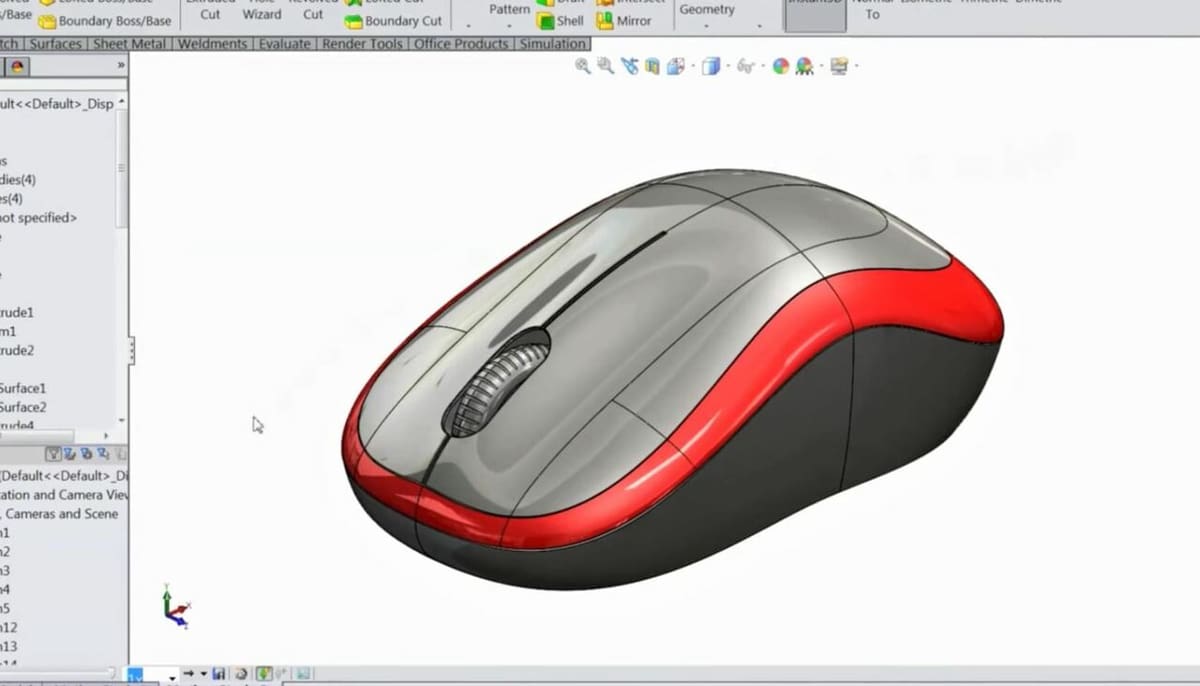
Surface modeling is a 3D modeling and 3D drawing technique very similar to solid modeling but with a twist. Unlike solid modeling, where 3D objects have filled volumes, surface modeling makes use of straight and curved “sheets”, known as surfaces, in a three-dimensional environment.
To understand surface modeling, consider a cube. Obviously, it exists in all three dimensions and occupies a particular set of X, Y, and Z coordinates. Yet, instead of thinking of the cube as a solid, like a die, think about it as a collection of 2D surfaces, like a box. This is kind of what surface modeling is: creating representations of solid objects using surfaces.
In surface modeling, the surfaces are created with 2D figures and always require an area. If you want to make a surface from an open-ended 2D feature, like a line or arc segment, you have to extrude it. Then, with simple surfaces, like squares and circles, you can create more nuanced surfaces by bending or molding them into particular shapes.
The resulting surfaces are like custom-shaped sheets of material, but importantly, they have no width. That’s because they bend in on themselves or connect with other surfaces in order to represent the exterior of a 3D model.
Surface modeling can be performed in a few ways, but the two most popular techniques are basic surface modeling and freeform surface modeling. The former method involves extruding a 2D feature without area into a surface, while the latter allows you to create a blanket-like surfaces and adjust their shapes by moving different points. You can use surface modeling in most advanced CAD programs, like Fusion 360, Inventor, Onshape, and SolidWorks.
Wireframe Modeling
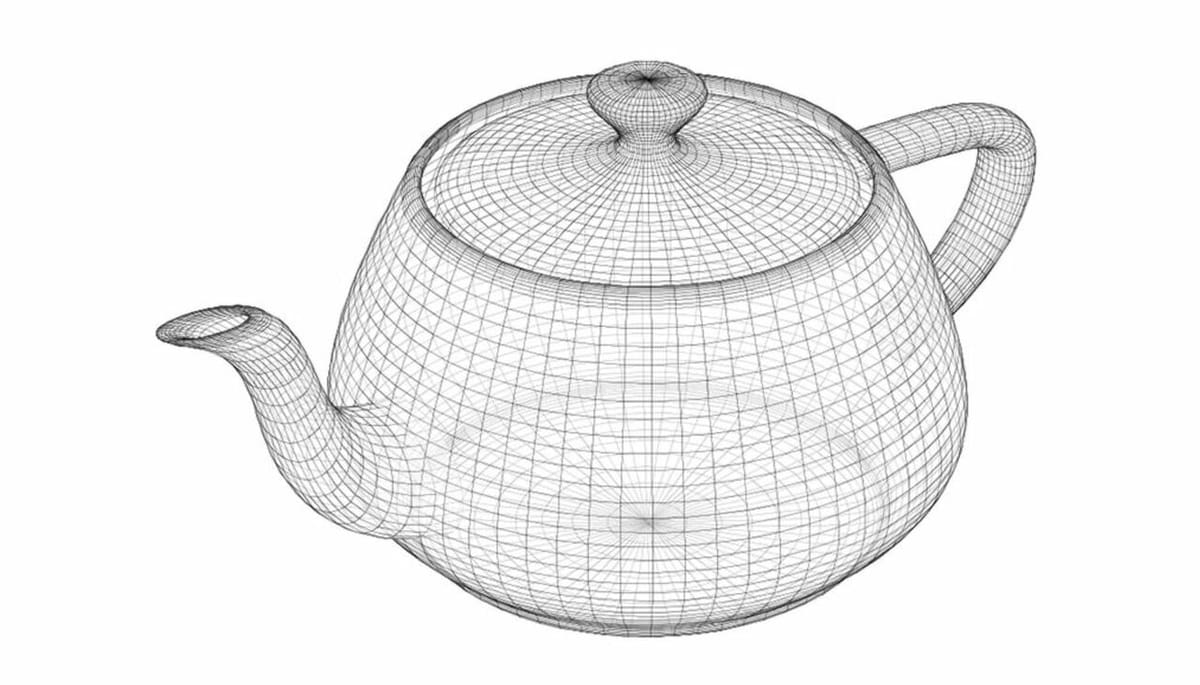

Next, wireframe modeling is another form of 3D modeling (or drawing) that uses vertices and edges to create connected surfaces. In this sense, wireframe modeling is like surface modeling in that the end result is meant to represent the exterior of a 3D model. The main difference is that the surfaces are here composed of many finite polygons.
The result of this designing method is what you would expect if you bent a wire or taught string to form a closed figure. This method of 3D drawing can be advantageous because it allows you to create a structure using another design for reference (e.g. making a shell around an object). Wireframe modeling also makes it easy to manipulate the shape of the design as you can push or pull a point of the wireframe mesh to adjust its shape.
There isn’t much variation in the techniques for wireframe modeling, and most programs allow you to plot different points and connect them to form the wireframe mesh. Many programs also allow you to turn a wireframe model into a solid or surface model. You can find this 3D drawing method on a few different CAD programs like Blender and Fusion 360.
Sculpting
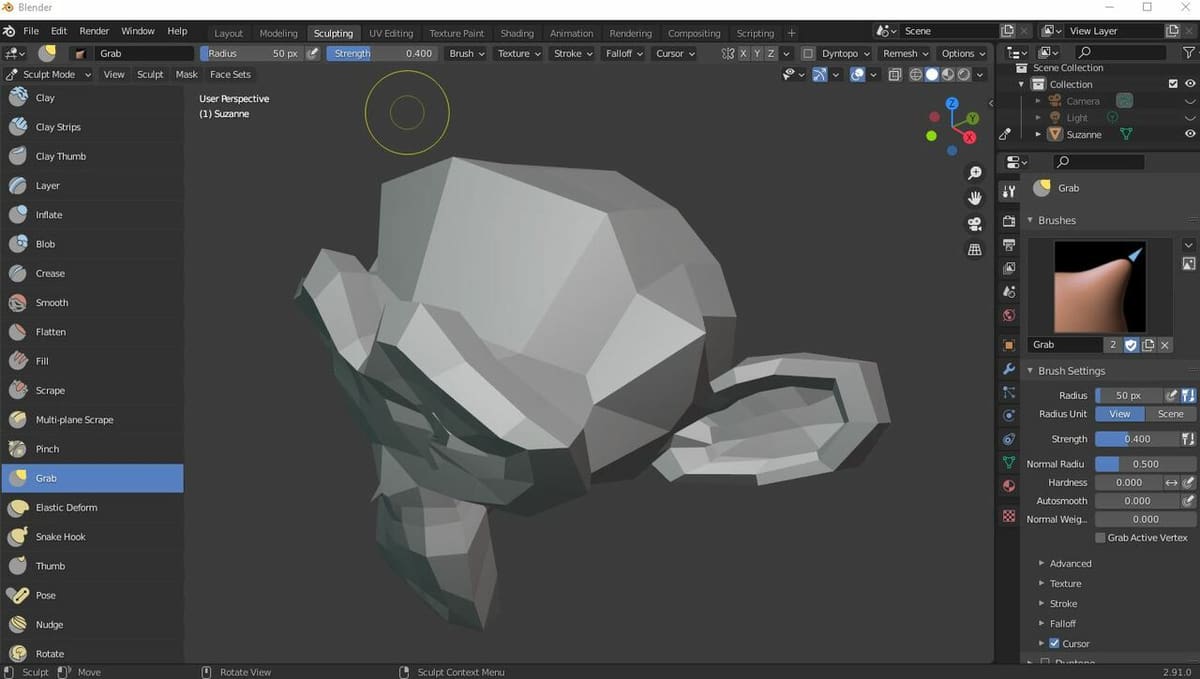
Lastly, digital sculpting is a type of 3D drawing similar to real sculpting (e.g. clay sculpting) in that it involves different brushes and manipulation tools for modifying the structure of a base object. Each brush and manipulation tool has a specific function and affects the model differently.
Sculpting programs typically offer brushes that can achieve effects on the base model that would otherwise be extremely difficult to match with traditional real sculpting and other forms of 3D drawing. A few popular brushes include the crease brush, smooth brush, flatten brush, thumb brush, and grab brush.
Different sculpting programs (usually a sub-part of a CAD application) contain different modification tools, but there’s not much variation in the actual techniques. The main technique is to start with a base model, which can be a drag-and-drop design (e.g. cube, sphere) or an imported model (e.g. custom design), and then use the brushes. Sculpting is available in modeling programs such as Blender, ZBrush, Meshmixer, and Mudbox.
License: The text of "What Is 3D Drawing Software? – Simply Explained" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


