3D software has become a go-to term for all things related to digital design. Since there isn’t a clear definition of it, we’ve selected a few different types of software that are relevant to 3D technology.
In this article, we’ll talk about some of these tools and provide some background as to what they are, how they’re used, and how they compare to each other. So let’s get started!
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
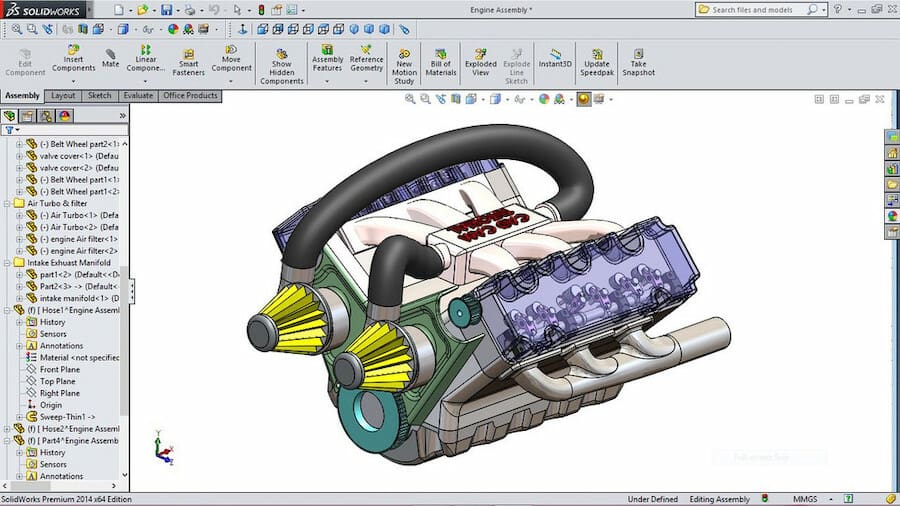
Perhaps the first 3D software to be widely adopted worldwide, 3D computer-aided design (CAD) was the natural evolution of the 2D drafting software first developed in the 1980s. It was designed as a platform to create 3D digital models of items that would eventually be built in the real world.
Previously, CAD was mainly employed for professional purposes, in particular by industries like civil construction and manufacturing. Today, however, CAD is accessible to virtually anyone with a computer and an internet connection, it covers most operating systems including MacOS and Linux, and some platforms are even suitable for children.
- Examples: AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Tinkercad
3D Modeling Software
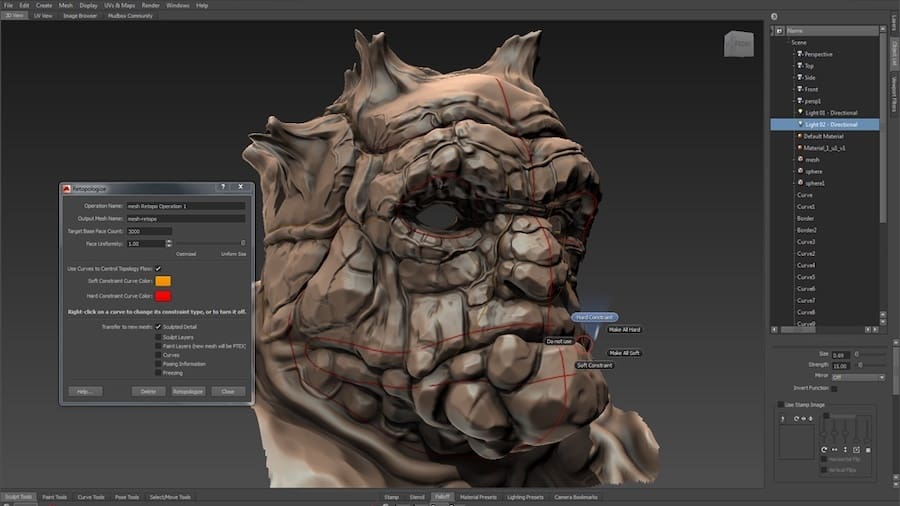
3D modeling software does essentially what CAD software does, but there’s an endless discussion of how they differ.
The term “3D modeling” is, by convention, more often than not associated with the entertainment industry, where the 3D models created won’t necessarily be recreated in the real world; think about gaming, animation, art, and visual effects. The way models are created in these programs also differs from CAD, being more like a digital sculpting process that involves organic shapes and forms. Texturing and painting also feature in these tools, adding another layer of detail.
- Examples: 3ds Max, Blender, ZBrushCoreMini
3D Animation
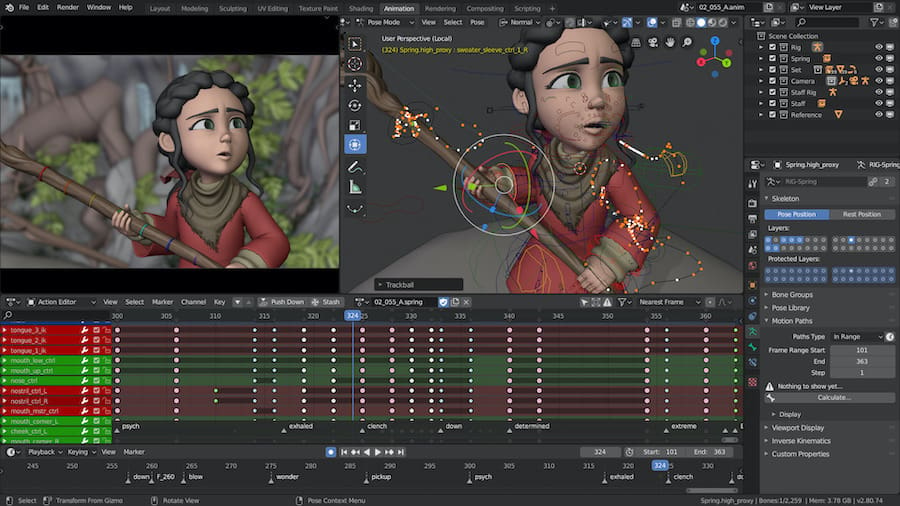
Instead of only creating three-dimensional objects, 3D animation software can add movement and can be used for storytelling.
3D animation dates back to stop-motion techniques from the 90s and it has somewhat recently graduated to the 100% digital creations we know today.
In addition to the requirements of 3D modeling, the process of animating 3D objects and scenes involves many steps like producing a layout, rigging models, correct lighting, and much more. It’s almost like directing a movie, but it’s all done from your computer. It goes without saying that powerful software is usually required, but there are also accessible web-based animation tools out there too.
3D Rendering
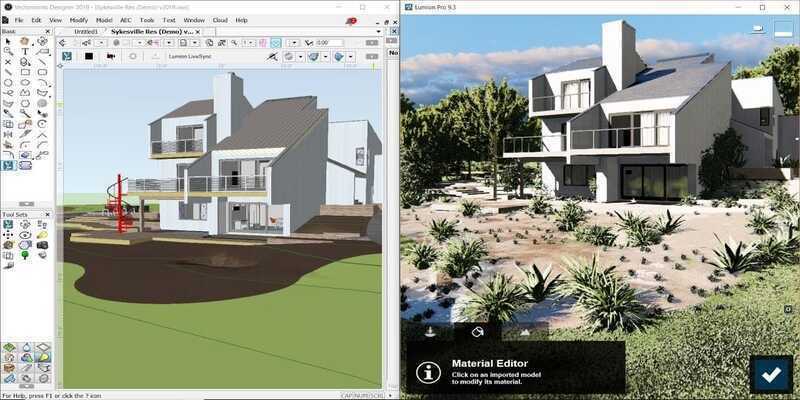
As odd as it may sound, 3D rendering is fundamentally the process of taking 2D images from 3D models or scenes. It’s much like taking a snapshot and applying effects to the photo, like shadows, lightning, and texture.
It’s mainly used as a communication tool, as it provides the means to show 3D models in context. For instance, architectural renderings communicate the architect’s vision for a proposed house or environment to clients, usually through photorealistic effects.
In terms of rendering software, it varies widely and depends on the final application. It often comes as plug-ins for CAD, 3D modeling, and 3D animation tools, but it’s also found in powerful standalone versions, too.
3D Scanning
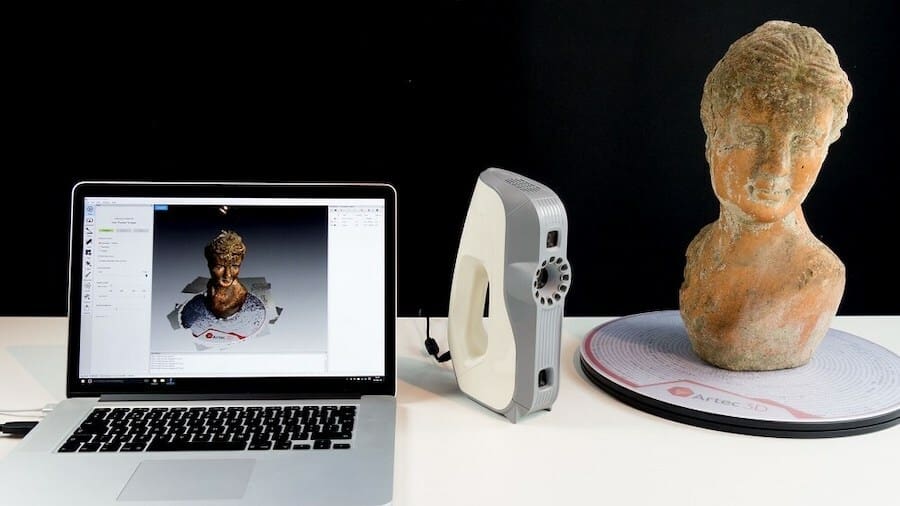

So far, the 3D software tools on this list have been focused on manipulating 3D digital objects to either make them real or to make them look real.
3D scanning works in the opposite direction. It translates real-life objects to digital environments, recreating actual forms and shapes in 3D models. It’s historically known as a reverse engineering tool, although it’s now closely associated with 3D printing.
3D scanning software relies on specific hardware to do this, ranging from handheld 3D scanners to some gaming devices, and even small smartphone cameras.
3D Mesh Editing & Repair
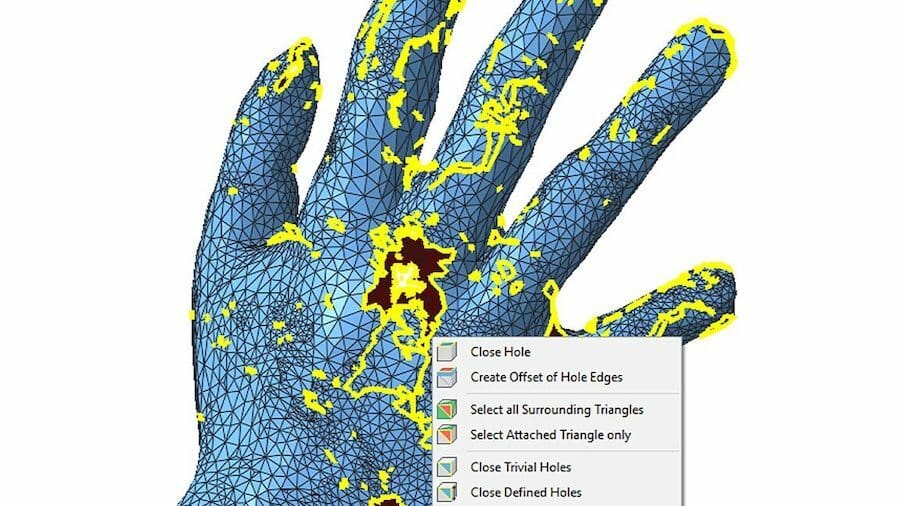
In a few words, a 3D mesh is a structural form of representing a 3D model through a set of polygons. These simple shapes are combined in great numbers to create surfaces that in turn will fully define a three-dimensional object.
Many 3D modeling programs work with this type of representation, but sometimes simpler and lighter software are required to either view, edit, convert, or quickly repair 3D meshes.
The STL format is one of the most known for 3D meshes due to its deep relation with 3D printing. This is why many mesh editing tools focus on this format, although they’re often compatible with other polygonal meshes.
3D Slicer
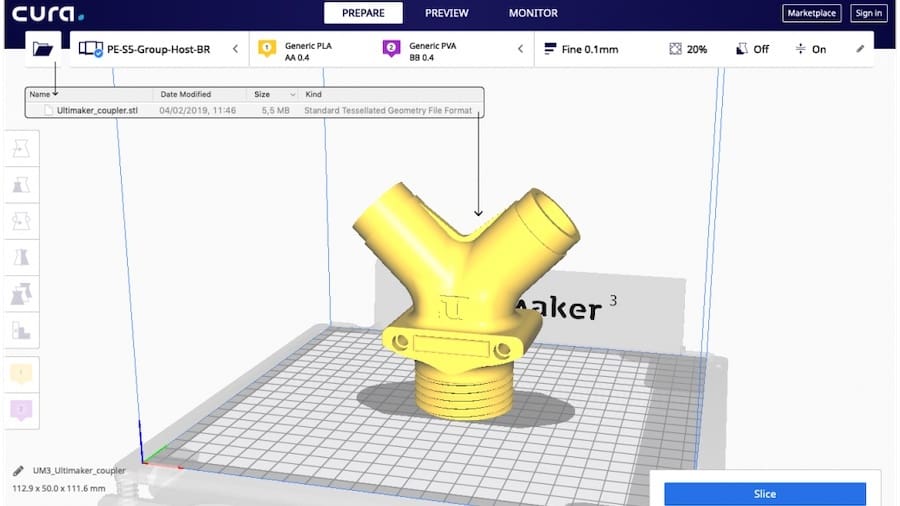
Finally, 3D slicers are perhaps the only 3D software category on this list that doesn’t work with 3D models’ appearance and geometry.
Slicing software is used to prepare the models for 3D printing. Each and every 3D printing job requires it at some point since it translates 3D geometry into instructions – G-code – for the machine to perform during printing.
3D slicers are usually specific to a given machine or to a 3D printing technology, like FDM or SLA. Due to the popularity of 3D printing, they are increasing in number, with more third-party options becoming available, including some for free.
- Examples: Simplify3D, Cura, Chitubox
License: The text of "What Is 3D Software? – Simply Explained" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.