Fusion (until recently, Fusion 360) is a 3D computer-aided design (CAD) program by Autodesk. Its name comes from the software’s ability to allow users to go through much of the design pipeline without ever needing to switch programs. It was first launched in 2013 and became an almost instant hit. Fusion has only grown in popularity since.
Its popularity derives from the accessible price, flexible options, and versatile applications. The program can be used for 3D modeling, generative design, failure mode simulation, electrical circuits, and more.
With so many capabilities, Fusion can be a bit daunting and overwhelming to a beginner. So, we’ll give you the rundown of the software’s essentials in this article. Let’s dive in!
Prices & Licensing
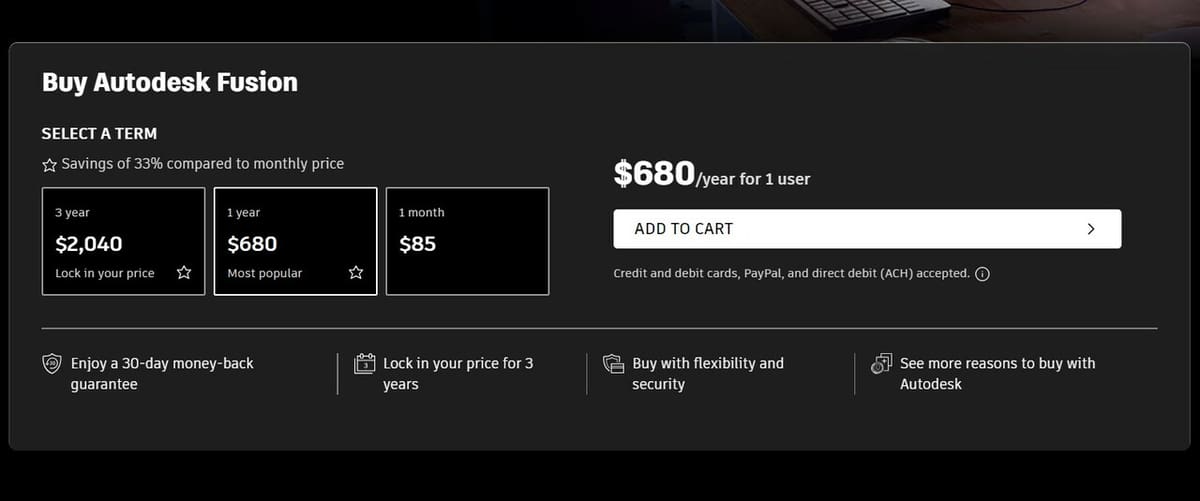
Fusion’s license is subscription based, and there are different plans you can choose from:
- Monthly: $85
- Annual: $680 (~$56/month)
- Triennial: $2,040 (~$56/month)
- Free trial: 30-day
- Student version: Students can access the full program, and it doesn’t matter if their academic institution has a version or not. Simply log in to Autodesk and provide proof of enrollment. Educational licenses are available for one year, after which you have to either renew the proof of enrollment or get a different license.
- Free version: Hobbyists and personal users can get a free, limited version that only has the CAD, CAM, and PCB workspaces.
- Start-up option: Qualifying startups can access Fusion for $150 per user for 3 years. Requirements include it being a registered company (e.g. LLC) with a professional email domain and a valid company website, and must have a venture, angel-backed, or bootstrapped status, among others. Service providers, resellers, contract manufacturers, consultants, maker spaces, non-profits, and design agencies aren’t eligible.
System Requirements
Fusion, like most Autodesk programs, is available for Windows and MacOS. Below are the recommended specifications to run Fusion:
- OS: Windows 10 (version 1809 or newer), 11; MacOS 12 Monterey, 13 Ventura (version 2.0.15289 or newer), Sonoma (known issues); MacOS 11 Big Sur is no longer supported as of March 2024
- CPU: 64-bit processor, 4 cores or more, 1.7 GHz or greater
- RAM: Minimum 4 GB
- Graphics card: Minimum 1 GB of VRAM for dedicated GPU, 6 GB of RAM for integrated graphics
- Disk space: 8.5 GB of storage
- Display resolution: 1366 x 768 (1920 x 1080 or greater at 100% scale recommended)
- Internet: 5 Mbps or faster download; 500 Kbps or faster upload
In addition to the requirements listed above, if you’re familiar with CAD and 3D modeling software, you know that a three-button mouse is more than recommended – it is practically mandatory. But if you want to step up and get an even better experience, we recommend using a pointing device like a Wacom tablet or a 3D mouse. Don’t worry, Fusion provides support for both.
UI & Layout
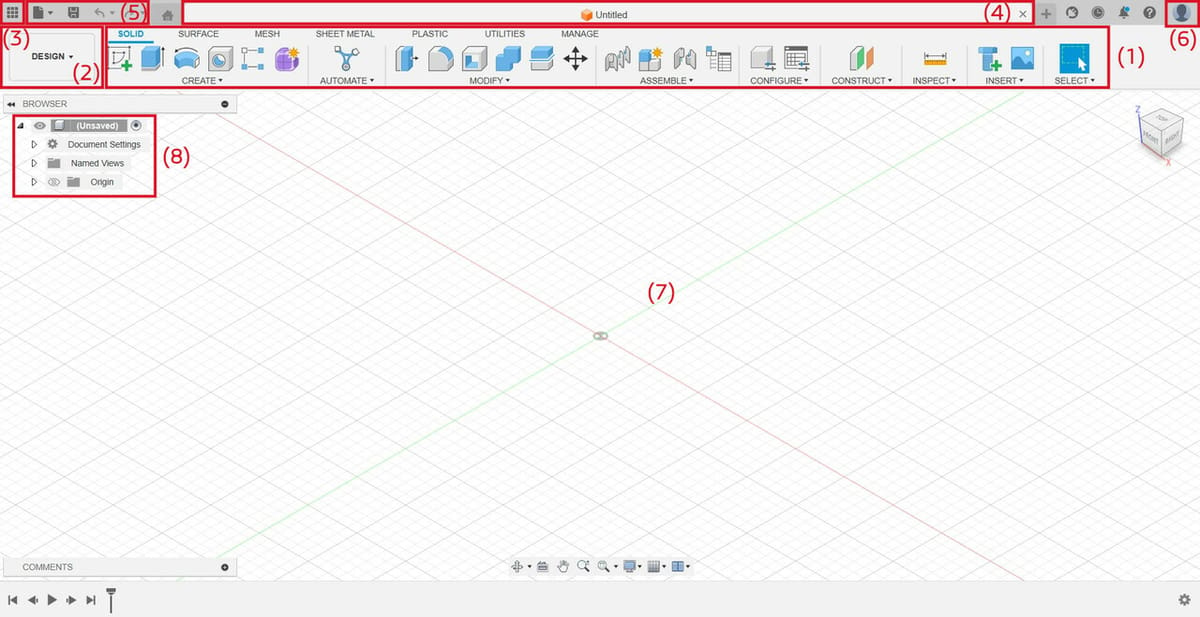
As mentioned previously, Fusion has many features, and to organize them, it uses workspaces. We can define a workspace as a specific environment in which Fusion displays the tools that are available according to the type of data you’re working with. The use of workspaces helps keep the UI clean and, hence, improve the workflow. The available workspaces in Fusion are Design, Generative Design, Render, Animation, Simulation, Manufacture, and Drawing.
Main Toolbar
The Main Toolbar (1) is where you find the essential tools. You can see the current workspace (2) on the left. When you switch workspaces, the available tools will change as well, and they’re organized in tabs to help better locate everything.
In this example, we’re in the Design workspace, and you can see the various tools in the Main Toolbar organized in tabs, including Solid, Surface, and Sheet Metal, among others.
Application Bar
Above the Main Toolbar are the Application Bar (3) and the tabs for any open files (4). From the Application Bar, you can open the application menu or use the Quick Menu (5) for things such as Save, New Project, Undo, and Redo.
To the right of the Main Toolbar, you can see your Profile (6), where you can manage your license and projects saved in the cloud.
Canvas
The main working area where you see the model is called the Canvas (7). To the left of the Canvas, you find a floating menu called the Browser (8) that lists every available feature on the Canvas, including solids, meshes, and even measurement systems.
The Marking Menu is a floating right-click menu with commonly used tools. When you use a feature – for example, a milling operation in the Manufacturing workspace – a setup window opens up where you finish setting it up. While this isn’t something you can immediately see when opening the application, some additional tools may be located in that window.
Features & Functions
To provide a better insight into the capabilities of Fusion, let’s describe each one of its workspaces. It’s worth mentioning that, despite each workspace having its own purpose, some tools are available in multiple spaces, like the ones belonging to the Sketch tab.
Design
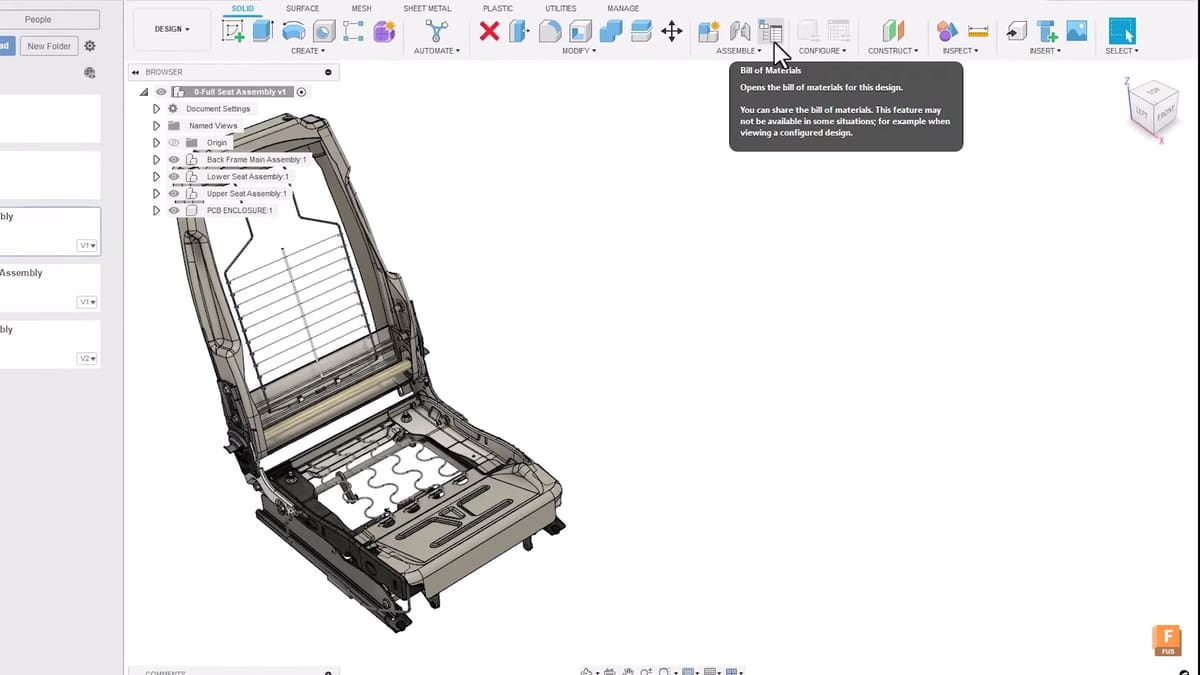
In this workspace, you can model parts from scratch or imported files. You can draw sketches and use operations such as Extrude and Revolve to make them into 3D volumes. Additionally, it has Surface, Mesh, and Sheet Metal modeling tools, as well as Plastic, which is for injection mold design. The Utility tab includes options to check interference or measurements.
A recently included feature is the “Bill of Materials”, which is a complete list of all the items in the design. It acts as a structure for the product in terms of its components based on their design. From a production perspective, this feature can improve the workflow by reducing complexity and saving time.
As a special note, there is a tool under the Utility tab called “Make” that links Fusion to a previously selected slicer, to directly export the 3D model and continue with the slicing process. This way, you won’t have to first save the 3D model as an STL file and then open it in the slicer of your choice; Fusion does it for you.
Generative Design
Generative Design is one of Fusion’s most unique capabilities. It takes a structure in an existing model and optimizes it, reducing material spent while attempting to improve shear and normal resistance. It provides an analysis of these factors as well.
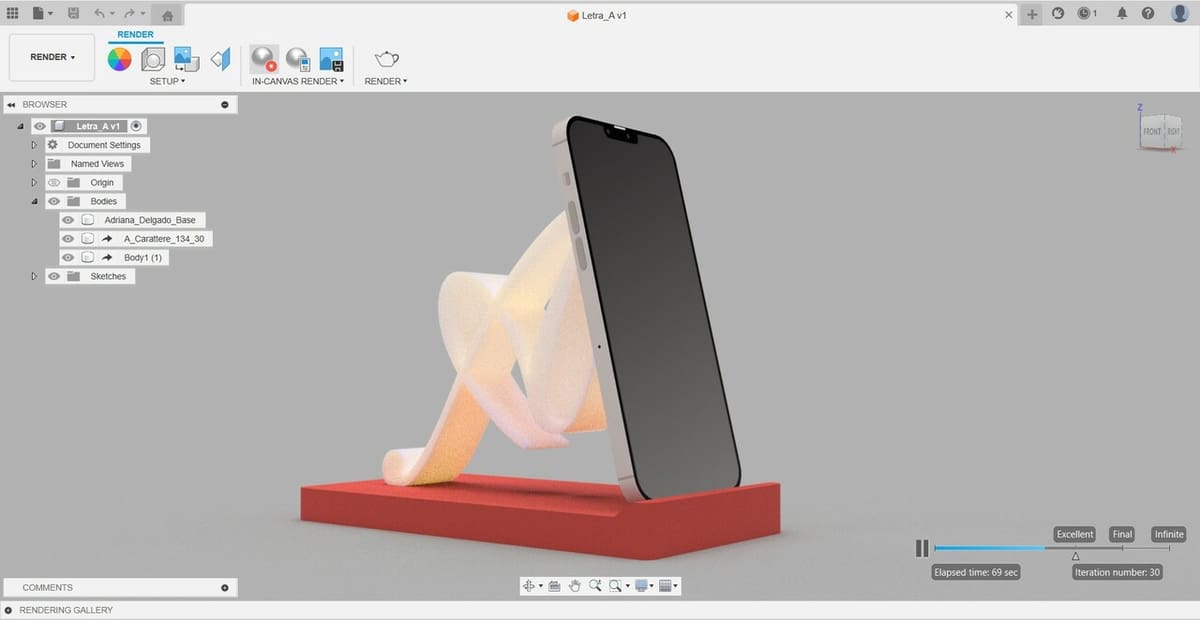
Render
Fusion has very good and surprisingly fast rendering capabilities, especially compared to software like SolidWorks, which is quite slow in rendering. You can create realistic renders with different materials and backgrounds. Rendering is a useful tool when presenting a design proposal, as it allows you to see a representation of your design in the real world.
Animation
The animation suite is made to create motion animations of a system. The principle is very simple: You choose a fixed part (a part that acts like an anchor to the system) and an input part (a part that enforces rotation or translational motion), then check out how the complete assembly moves. It’s also possible to record and export videos of the animation.
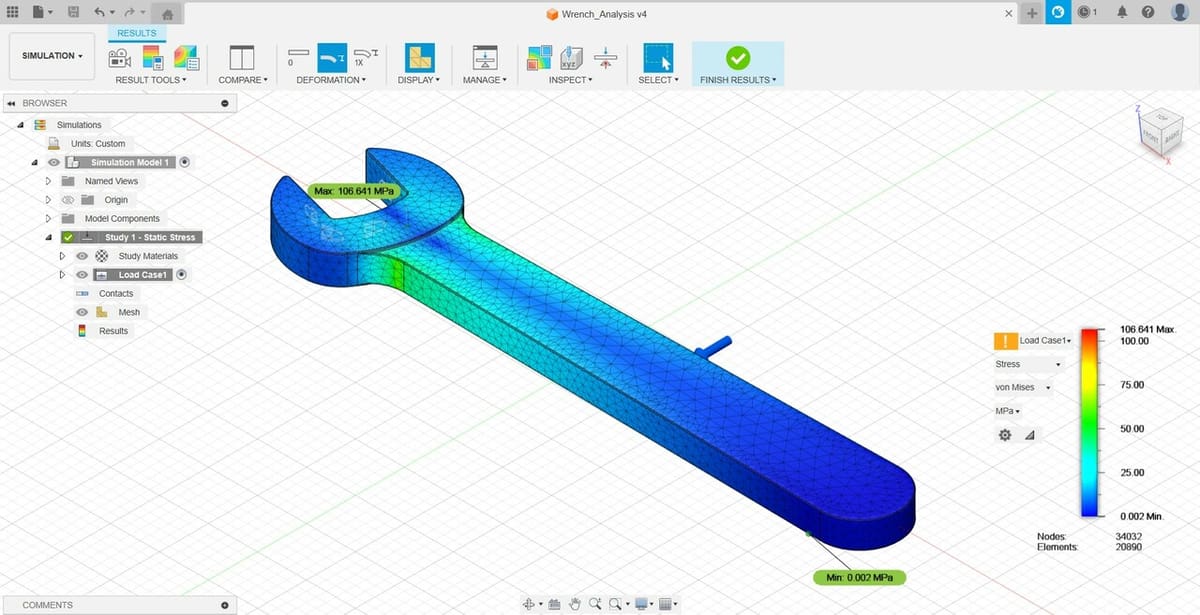
Simulation
Fusion uses finite element analysis to evaluate the mechanical properties of your model. It does so graphically, meaning you don’t need to concern yourself with the theory and programming behind it. It’s enough for some industries but not for academia and specialized industries requiring greater precision, like aerospace.
The newest update (v.2.0.18477) provides a new option to visualize the results in the Injection Molding Simulation type of study. This allows you to compare the Fill Animation results for different cases at once, by synchronizing their animations. The capability of directly and simultaneously comparing results can help in the decision-making process.
Manufacture
This workspace is one of Fusion’s most powerful and popular parts. It has tools for milling, turning, and 3D printing, located under the Additive tab. It can do operations like contouring, face milling, and engraving for 2D and 2.5D CNC. You can simulate the path of the operations and have multiple operations inside one G-code file.
The new Arrange feature under the Additive tab allows you to organize the parts within the 3D printer’s build area or volume based on your decision to give priority to volume production or component production. In order to use this feature, you must have previously defined an “Additive setup” and had an additive machine selected.
Drawing
A critical step during the design process is to accurately communicate not only the geometric aspect of a model, but also the design intent. To do so, relevant information can be shared via 2D representations of the 3D model. This is done in the Drawing workspace. You can create 2D drawings starting from the 3D model and assign dimensions and tolerances to it. You can pick a previously created template for your drawing following the ASME or ISO standard, or you can create your own from scratch.
To properly represent your 3D model, you can choose from the many available views, including the recently added “Perspective Views”, which use narrow or wide focal lengths to provide a sense of depth. To make your drawing look more professional, you can include standardized symbols for Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T).
Extensions
If these versions of workspaces aren’t enough for you, Fusion offers extended capabilities in the form of extensions. As the name implies, they provide you with an extended version of features in the majority of workspaces. As an example, inside the Design workspace, you can find additional features like “Volumetric Lattice”, “Geometric Patterning”, and “Feature-based Automation”, among others. Extensions can be added to Fusion by means of a monthly, yearly, or a three-year subscription (additional to Fusion’s license).
User Experience
Fusion is very stable software once running, but launching it and loading an existing file can take several minutes.
If you’ve never done any 3D modeling, this program offers advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, it’s extremely accessible. You can start learning it on your own to prepare for future endeavors, create your own start-up, or just begin designing your ideas. This is in contrast to software like SolidWorks, which is extremely expensive. Individuals usually have to get a license through their company or educational institution.
On the other hand, even though the software uses a lot of symbols to indicate the purpose of tools, the actual design process in Fusion isn’t as intuitive as it could be. You have to know your way around and understand that many setups require right-clicking to open menus.
Fusion has worked on “Performance Updates”, whose main goal is to provide a smoother and faster operation environment, delivering a more fluid workflow. Autodesk reports certain commands’ response times up to 10x faster compared to earlier versions. Another considerable improvement is related to exporting objects as STL and OBJ files. However, despite arguably reducing times, they still recognize the existence of “Not responding” situations.
Community & Company Support
Fusion has a dedicated site filled with resources, self-paced learning, and webinars. They also have the Community Forum for posting questions and troubleshooting. A good unofficial resource is the Fusion360 subreddit, which is relatively responsive to questions. Finally, YouTube is filled with tutorials and resources for all things Fusion. You can try keywords such as “simulation”, “CAM”, or “beginner” to help you find more specific information.
If you want some resources to get started, Product Design Online’s Learn Fusion 360 in 30 days is one of the most recommended Fusion courses. This course is completely free on YouTube, including the necessary demo files, but you can support the creator on other platforms.
As part of the latest update, Autodesk included the solution to “Customer Reported Fixes”, providing a list of solved issues (around 90), properly divided into categories. This is a clear statement of Autodesk’s recognition of problems in Fusion and their commitment to the community.
Use Cases & Applications
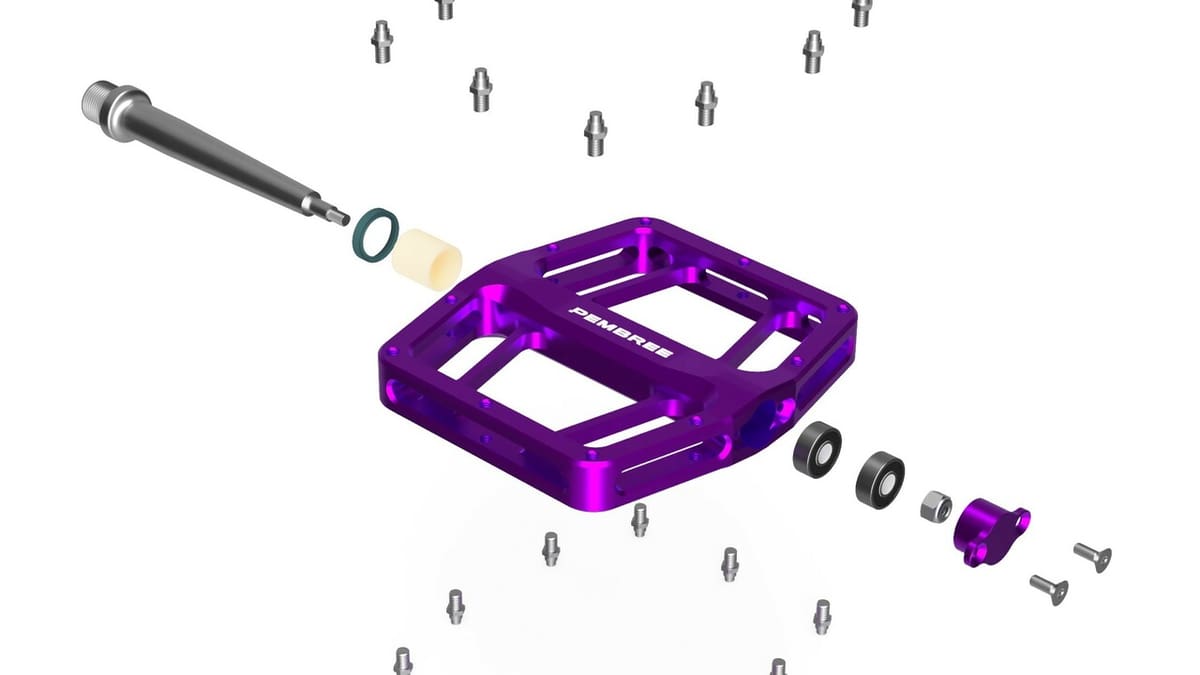
Fusion is used for design by independent users, hobbyists, and start-ups thanks to its accessibility. On top of that, it’s one of the most popular programs for CAM because it’s complete and has a user-friendly UI and high-quality simulation. It allows for a lot of customization of operations needed on a project – all at a very affordable price. Fusion also prioritizes cloud storage over hard disk storage, which makes it better suited for collaborative work.
One example of a company that uses Fusion is Pembree. They use the software to design bicycle components such as pedals. Thanks to Fusion’s 5D CAM operations, they also use it to plan their manufacturing. Another example is Iterate, which uses Fusion for feasibility studies that aim to determine the functionality, manufacturability, and marketability of a product.
Alternatives
Now that you know all the basics about Fusion, perhaps you’ve decided that it’s not for you after all, or maybe you want to see what else is out there before making a decision. In that case, you can also check these alternatives and see if something else is a better fit.
The following are Fusion’s direct competitors. They share many aspects, but in the end, the devil’s in the details.
Inventor
Inventor is like a more optimized and powerful version of Fusion, allowing for more complex designing. It’s a more industrial and bigger-scale option, which is why its target audience differs a bit from Fusion’s. This is reflected in its price, which is set at about $2,500 annually (vs. Fusion’s $680 annual subscription).
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is arguably Fusion’s and Inventor’s most direct competitor. It’s by a completely different company, Dassault Systèmes. Since it’s an industry staple, learning it can open many doors. However, it’s also very expensive. Purchasing it yourself can be complicated because you can’t buy it online; you have to contact an authorized reseller (called “VAR”) and get a personalized quotation.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is a free and open-source 3D CAD program. Since it also has many workbenches, you wouldn’t be sacrificing functionality too much. The main disadvantage, however, is that it’s way less stable than Fusion. Also, the design workflow in FreeCAD isn’t the most optimized, as it’s still a work in progress and open source.
License: The text of "What Is Fusion 360? – Simply Explained" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
CERTAIN CONTENT THAT APPEARS ON THIS SITE COMES FROM AMAZON. THIS CONTENT IS PROVIDED ‘AS IS’ AND IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE OR REMOVAL AT ANY TIME.