Arduino has released a power management library offering a suite of tools that help users reduce power consumption of devices like IoT and wearables.
The library is currently supported by the Arduino Portenta H7, Portenta C33, and Nicla Vision. It lets users track and monitor battery health and performance, and adjust charging settings and power rail voltages.
There are also sleep and standby modes, the former of which particularly stands out, if only for Arduino’s claim that it allows a device “months or even years of continuous runtime on a single charge”, boasting consumption of less than 100 microamperes (uA).
Combined, these features should result in better device performance and an increased lifespan. By tracking exactly what stage of charging your device is in, for example, you can better take steps to avoid overvoltage or overheating.
Going further, by connecting the aforementioned sleep mode to a clock or motion sensor, you can set a time for a device to wake up – significantly improving battery life in the long run.
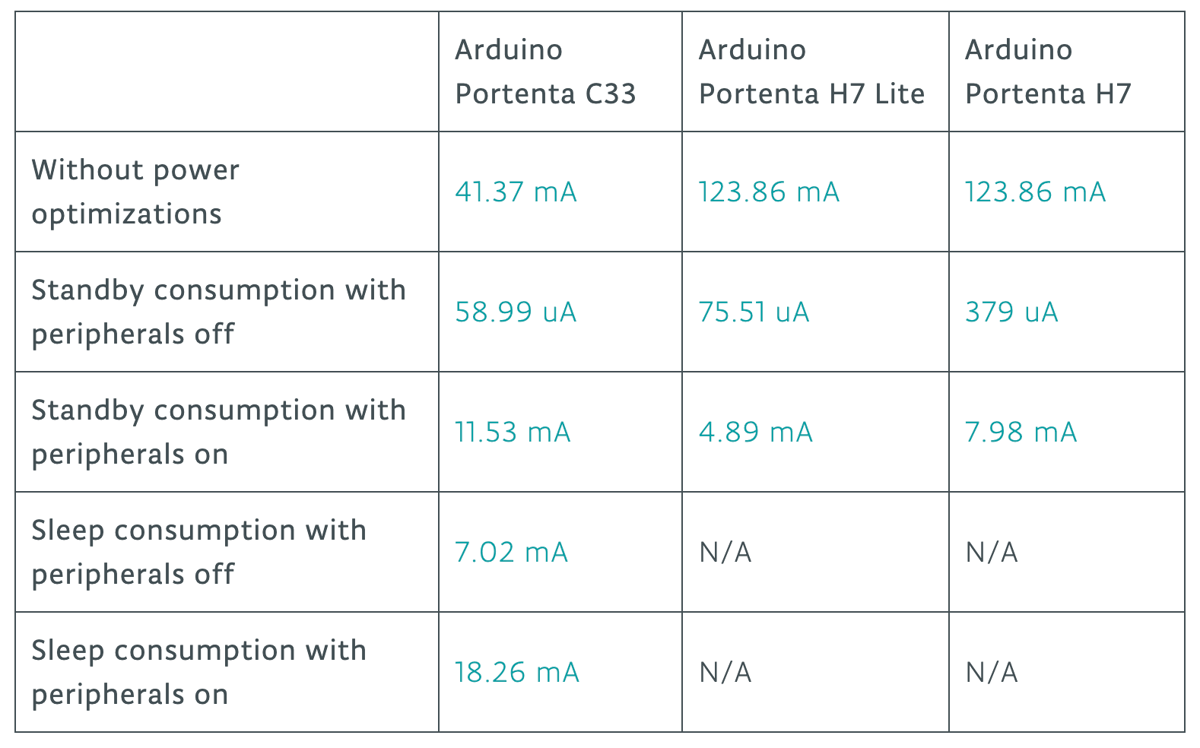
There’s quite a bit more to explore about Arduino’s power management library, which is now available on the compatible boards list above, so be sure to check out Arduino’s blog post before getting started saving juice.
Read more recent news:
License: The text of "Arduino Introduces New Power Management Library for Low Power Consumption" by All3DP is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 Stay Informed, Save Big, Make More
Stay Informed, Save Big, Make More